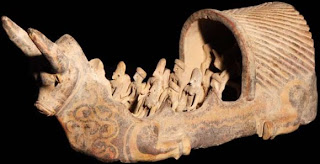
h097 Text 4251 h097 Pict-95: Seven robed figures (with stylized twigs on their head and pig-tails) standing in a row.
Annex A
[Pleiades, scarfed, framework, scarfed person, worshipper, markhor, ficus religiosa] Brief memoranda:
The bottom register has hieroglyphs of: worshipper, ram, ficus, buffal-horned person: bhaTa 'worshipper' Rebus: bhaTa 'furnace' meDha 'ram' Rebus: meD 'iron', loa 'ficus' Rebus: loh 'copper, metal' taTThAr 'buffalo horn'
Rebus: ṭhaṭherā 'brass worker' (Punjabi) Thus, the message of this portion of the epigraph is: brass worker furnaces of loh 'copper' and meD 'iron'
The top register has scarfed, pleiades: Hieroglyph: dhatu 'scarf' Rebus: dhatu 'mineral ore' bahulA 'Pleiades' Rebus 1:bagalo 'Arab merchant vessel, boat' Rebus 2: bāhula 'armour for the arms'
Hieroglyph: worshipper: bhaṭā G. bhuvɔ m. ʻ worshipper in a temple ʼ rather < bhr̥ta --(CDIAL 9554) Yājñ.com., Rebus: bhaṭā ‘kiln, furnace’
Hieroglyph: ram, markhor: Dm. mraṅ m. ‘markhor’ Wkh. merg f. ‘ibex’ (CDIAL 9885) Tor. miṇḍ ‘ram’, miṇḍā́l ‘markhor’ (CDIAL 10310) Rebus: meḍ(Ho.); mẽṛhet ‘iron’ (Munda.Ho.)
Hieroglyph: standing person with buffalo horn: taTThAr 'buffalo horn' Rebus: taTTAr 'brass worker' Ta. taṭṭāṉ gold or silver smith; fem. taṭṭātti. Ma. taṭṭu a blow, knock; taṭṭuka to tap, dash, hit, strike against, knock; taṭṭān goldsmith; fem. taṭṭātti; taṭṭāranwasherma(DEDR 3039) *ṭhaṭṭhakāra- brassworker;(CDIAL 5490) *ṭhaṭṭh ʻ strike ʼ. [Onom.?]
N. ṭhaṭāunu ʻ to strike, beat ʼ, ṭhaṭāi ʻ striking ʼ, ṭhaṭāk -- ṭhuṭuk ʻ noise of beating ʼ; H. ṭhaṭhānā ʻ to beat ʼ, ṭhaṭhāī f. ʻ noise of beating ʼ. ṭhaṭṭhakāra ʻ brass worker ʼ. 2. *ṭhaṭṭhakara -- . [*ṭhaṭṭha -- 1, kāra -- 1] 1. Pk. ṭhaṭṭhāra -- m., K. ṭhö̃ṭhur m., S. ṭhã̄ṭhāro m., P. ṭhaṭhiār, °rā m.
2. P. ludh. ṭhaṭherā m., Ku. ṭhaṭhero m., N. ṭhaṭero, Bi. ṭhaṭherā, Mth. ṭhaṭheri, H. ṭhaṭherā m.(CDIAL 5490, 5493).
Hieroglyph: loa ‘ficus’ Rebus: lo ‘copper’ Hieroglyph: loa 'ficus religiosa' Rebus: lo, loh 'copper, metal' (Samskritam)Rebus: lo 'copper' lōhá ʻ red, copper -- coloured ʼ ŚrS., ʻ made of copper ʼ ŚBr., m.n. ʻ copper ʼ VS., ʻ iron ʼ MBh. [*rudh -- ] Pa. lōha -- m. ʻ metal, esp. copper or bronze ʼ; Pk. lōha -- m. ʻ iron ʼ, Gy. pal. li°, lihi, obl. elhás, as. loa JGLS new ser. ii 258; Wg. (Lumsden) "loa"ʻ steel ʼ; Kho. loh ʻ copper ʼ; S. lohu m. ʻ iron ʼ, L. lohā m., awāṇ. lōˋā, P. lohā m. (→ K.rām. ḍoḍ. lohā), WPah.bhad. lɔ̃un., bhal. lòtilde; n., pāḍ. jaun. lōh, paṅ. luhā, cur. cam. lohā, Ku. luwā, N. lohu, °hā, A. lo, B. lo, no, Or. lohā, luhā, Mth. loh, Bhoj. lohā, Aw.lakh. lōh, H. loh, lohā m., G. M. loh n.; Si. loho, lō ʻ metal, ore, iron ʼ; Md. ratu -- lō ʻ copper ʼ. WPah.kṭg. (kc.) lóɔ ʻ iron ʼ, J. lohā m., Garh. loho; Md. lō ʻ metal ʼ.(CDIAL 11158)
Hieroglyph: Te. pilaka a tuft or knot of hair. Konḍa pilka, pilika pigtail, dangling ends of hair. Kuwi (F.) pilka lovelock (worn curled under the ear by males).(DEDR 4179) Rebus: pĩṛulo ʻ calf of leg, thigh ʼ; A. pirā ʻ severed leg of an animal with flesh still attached ʼ, pīri ʻ lump of earth taken with a plant for transplanting ʼ;pī˜ṛī ʻ platform of lingam ʼ; Mth. pĩṛ, pĩṛā ʻ lump ʼ(CDIAL 8168)
Brief memoranda:
baṭa = rimless pot (Kannada) Rebus: baṭa = a kind of iron (Gujarati)
muka ‘ladle’ (Tamil)(DEDR 4887) Rebus: mū̃h ‘ingot’ (Santali) PLUS dula 'pair' Rebus: dul 'cast metal'. (See two ladles). Thus, the offering on the stool denotes: a metal ingot.
Annex B
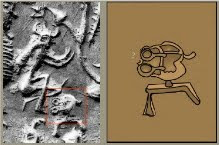
Seal m 1186 Mohenjo-daro
Decipherment: ![]()
![]()
![]() kole.l 'temple' Rebu: kole.l 'smithy' (Kota) baTa 'rimless pot' Rebus: bhaTa 'furnace, kiln'.
kole.l 'temple' Rebu: kole.l 'smithy' (Kota) baTa 'rimless pot' Rebus: bhaTa 'furnace, kiln'.
dhatu + bhaTa 'scarf + worshipper, bard' Rebus: dhatu bhaTa 'iron ore smelter'
Offering hieroglyph-multiplex: worshipper, scarfed + human face+ markhor: cast iron ingots
Hieroglyph: miṇḍāl markhor (Tor.wali) meḍho a ram, a sheep (G.) Rebus: meḍ (Ho.); mẽṛhet‘iron’ (Munda.Ho.)
Hieroglyph: mũhe ‘face’ (Santali) Rebus: mũh opening or hole (in a stove for stoking (Bi.); ingot (Santali) mũh metal ingot (Santali) mũhã̄ = the quantity of iron produced at one time in a native smelting furnace of the Kolhes; iron produced by the Kolhes and formed like a four-cornered piece a little pointed at each end; mūhā mẽṛhẽt = iron smelted by the Kolhes and formed into an equilateral lump a little pointed at each of four ends; kolhe tehen mẽṛhẽt ko mūhā akata = the Kolhes have to-day produced pig iron (Santali)
m1186 (DK6847) [Pleiades, scarfed, framework, ficus religiosa , scarfed person, worshipper, twigs (on head), horn, markhor, human face ligatured to markhor, stool, ladle, frame of a building] Brief memoranda:
![]() Ficus benghalensis
Ficus benghalensis
Hieroglyph: karã̄ n. pl. wristlets, bangles: kará1 ʻ doing, causing ʼ AV., m. ʻ hand ʼ RV. [√kr̥1]Pa. Pk. kara -- m. ʻ hand ʼ; S. karu m. ʻ arm ʼ; Mth. kar m. ʻ hand ʼ (prob. ← Sk.); Si. kara ʻ hand, shoulder ʼ, inscr. karā ʻ to ʼ < karāya. -- Deriv. S. karāī f. ʻ wrist ʼ; G. karã̄ n. pl. ʻ wristlets, bangles ʼ.(CDIAL 2779)
Hieroglyph: dhatu 'scarf' Rebus: dhatu 'mineral ore' Thus, dhatu + karã̄ Rebus: dhatu khār ' iron ore (mineral) worker'.
Hieroglyph: scarf: *dhaṭa2, dhaṭī -- f. ʻ old cloth, loincloth ʼ lex. [Drav., Kan. daṭṭi ʻ waistband ʼ etc., DED 2465]Ku. dhaṛo ʻ piece of cloth ʼ, N. dharo, B. dhaṛā; Or. dhaṛā ʻ rag, loincloth ʼ, dhaṛi ʻ rag ʼ; Mth. dhariā ʻ child's narrow loincloth ʼ.*dhaṭavastra -- .Addenda: *dhaṭa -- 2. 2. †*dhaṭṭa -- : WPah.kṭg. dhàṭṭu m. ʻ woman's headgear, kerchief ʼ, kc. dhaṭu m. (also dhaṭhu m. ʻ scarf ʼ, J. dhāṭ(h)u m. Him.I 105).(CDIAL 6707)
Rebus: dhā̆vaḍ iron smelter: dhāˊtu n. ʻ substance ʼ RV., m. ʻ element ʼ MBh., ʻ metal, mineral, ore (esp. of a red colour) ʼ Mn., ʻ ashes of the dead ʼ lex., ʻ *strand of rope ʼ (cf. tridhāˊtu -- ʻ threefold ʼ RV.,ayugdhātu -- ʻ having an uneven number of strands ʼ KātyŚr.). [√dhā]
Pa. dhātu -- m. ʻ element, ashes of the dead, relic ʼ; KharI. dhatu ʻ relic ʼ; Pk. dhāu -- m. ʻ metal, red chalk ʼ; N. dhāu ʻ ore (esp. of copper) ʼ; Or. ḍhāu ʻ red chalk, red ochre ʼ (whence ḍhāuā ʻ reddish ʼ; M. dhāū, dhāv m.f. ʻ a partic. soft red stone ʼ (whence dhā̆vaḍ m. ʻ a caste of iron -- smelters ʼ, dhāvḍī ʻ composed of or relating to iron ʼ); -- Si. dā ʻ relic ʼ; -- S. dhāī f. ʻ wisp of fibres added from time to time to a rope that is being twisted ʼ, L. dhāī˜ f.(CDIAL 6773)
khār 1 खार् । लोहकारः m. (sg. abl. khāra 1 खार; the pl. dat. of this word is khāran 1 खारन्, which is to be distinguished from khāran 2, q.v., s.v.), a blacksmith, an iron worker (cf. bandūka-khār, p. 111b, l. 46; K.Pr. 46; H. xi, 17); a farrier (El.). This word is often a part of a name, and in such case comes at the end (W. 118) as in Wahab khār, Wahab the smith (H. ii, 12; vi, 17).
khāra-basta खार-बस््त । चर्मप्रसेविका f. the skin bellows of a blacksmith. -büṭhü -ब&above;ठू&below; । लोहकारभित्तिः f. the wall of a blacksmith's furnace or hearth. -bāy -बाय् । लोहकारपत्नी f. a blacksmith's wife (Gr.Gr. 34). -dŏkuru -। लोहकारायोघनः m. a blacksmith's hammer, a sledge-hammer. -gȧji -ग&above;जि&below; or -güjü - । लोहकारचुल्लिः f. a blacksmith's furnace or hearth. -hāl -हाल् । लोहकारकन्दुः f. (sg. dat. -höjü -), a blacksmith's smelting furnace; cf. hāl 5. -kūrü - । लोहकारकन्या f. a blacksmith's daughter. -koṭu । लोहकारपुत्रः m. the son of a blacksmith, esp. a skilful son, who can work at the same profession. -küṭü -। लोहकारकन्या f. a blacksmith's daughter, esp. one who has the virtues and qualities properly belonging to her father's profession or caste. -më˘ʦü 1 -म्य&above;च&dotbelow;ू&below; । लोहकारमृत्तिका f. (for 2, see [khāra 3] ), 'blacksmith's earth,' i.e. iron-ore. -nĕcyuwu -न्यचिवु&below; । लोहकारात्मजः m. a blacksmith's son. -nay -नय् । लोहकारनालिका f. (for khāranay 2, see [khārun] ), the trough into which the blacksmith allows melted iron to flow after smelting. -ʦañĕ -च्&dotbelow;ञ । लोहकारशान्ताङ्गाराः f.pl. charcoal used by blacksmiths in their furnaces. -wān वान् । लोहकारापणः m. a blacksmith's shop, a forge, smithy (K.Pr. 3). -waṭh -वठ् । आघाताधारशिला m. (sg. dat. -waṭas -वटि), the large stone used by a blacksmith as an anvil.(Kashmiri)
Hieroglyph: vaṭa1 m. ʻ the banyan Ficus indica ʼ MBh.Pa. vaṭa -- m. ʻ banyan ʼ, Pk. vaḍa -- , °aga -- m., K. war in war -- kulu m., S. baṛu m. (← E); P. vaṛ, baṛ m., vohṛ, bohṛ f. ʻ banyan ʼ, vaṛoṭā, ba° m. ʻ young banyan ʼ (+?); N. A. bar ʻ banyan ʼ, B. baṛ, Bi. bar (→ Or. bara), H. baṛ m. (→ Bhoj. Mth. baṛ), G. vaṛ m., M. vaḍ m., Ko. vaḍu.*vaṭapadra -- , *vaṭapātikā -- .Addenda: vaṭa -- 1: Garh. baṛ ʻ fig tree ʼ.(CDIAL 11211) *vaṭapadra ʻ a place -- name ʼ. [vaṭa -- 1, padrá -- ?] Pk. vaḍavadda -- n. ʻ name of a town in Gujarat ʼ, G. vaṛod ʻ Baroda ʼ ODBL 497. (CDIAL 11214) *vaṭapātikā ʻ falling from banyan ʼ. [vaṭa -- 1, pāta -- ]G. vaṛvāī f. ʻ hanging root of banyan tree ʼ.(CDIAL 11215) Rebus: bhaṭṭhā 'kiln' bhaṭhī 'furnace'.
bhráṣṭra n. ʻ frying pan, gridiron ʼ MaitrS. [√bhrajj]Pk. bhaṭṭha -- m.n. ʻ gridiron ʼ; K. büṭhü f. ʻ level surface by kitchen fireplace on which vessels are put when taken off fire ʼ; S. baṭhu m. ʻ large pot in which grain is parched, large cooking fire ʼ, baṭhī f. ʻ distilling furnace ʼ; L. bhaṭṭh m. ʻ grain -- parcher's oven ʼ, bhaṭṭhī f. ʻ kiln, distillery ʼ, awāṇ. bhaṭh; P. bhaṭṭh m., °ṭhī f. ʻ furnace ʼ, bhaṭṭhā m. ʻ kiln ʼ; N. bhāṭi ʻ oven or vessel in which clothes are steamed for washing ʼ; A. bhaṭā ʻ brick -- or lime -- kiln ʼ; B. bhāṭi ʻ kiln ʼ; Or. bhāṭi ʻ brick -- kiln, distilling pot ʼ; Mth. bhaṭhī, bhaṭṭī ʻ brick -- kiln, furnace, still ʼ; Aw.lakh.bhāṭhā ʻ kiln ʼ; H. bhaṭṭhā m. ʻ kiln ʼ, bhaṭ f. ʻ kiln, oven, fireplace ʼ; M. bhaṭṭā m. ʻ pot of fire ʼ, bhaṭṭī f. ʻ forge ʼ. -- X bhástrā -- q.v.
bhrāṣṭra -- ; *bhraṣṭrapūra -- , *bhraṣṭrāgāra -- .Addenda: bhráṣṭra -- : S.kcch. bhaṭṭhī keṇī ʻ distil (spirits) ʼ.*bhraṣṭrapūra ʻ gridiron -- cake ʼ. [Cf. bhrāṣṭraja -- ʻ pro- duced on a gridiron ʼ lex. -- bhráṣṭra -- , pūra -- 2]P. bhaṭhūhar, °hrā, bhaṭhūrā, °ṭhorū m. ʻ cake of leavened bread ʼ; -- or < *bhr̥ṣṭapūra -- .*bhraṣṭrāgāra ʻ grain parching house ʼ. [bhráṣṭra -- , agāra -- ]
P. bhaṭhiār, °ālā m. ʻ grainparcher's shop ʼ.(CDIAL 9656-9658)
kuṭire bica duljad.ko talkena, they were feeding the furnace with ore. In this Santali sentence bica denotes the hematite ore. For example, samṛobica, 'stones containing gold' (Mundari) meṛed-bica 'iron stone-ore' ; bali-bica, iron sand ore (Munda). mẽṛhẽt, meḍ ‘iron’(Munda. Ho.)
Meluhha rebus representations are: bica ‘scorpion’ bica ‘stone ore’.
Hieroglyph: 'human face': mũhe ‘face’ (Santali)
Rebus: mũh opening or hole (in a stove for stoking (Bi.); ingot (Santali) mũh metal ingot (Santali) mũhã̄ = the quantity of iron produced at one time in a native smelting furnace of the Kolhes; iron produced by the Kolhes and formed like a four-cornered piece a little pointed at each end; mūhā mẽṛhẽt = iron smelted by the Kolhes and formed into an equilateral lump a little pointed at each of four ends; kolhe tehen mẽṛhẽt ko mūhā akata = the Kolhes have to-day produced pig iron (Santali)
ḍabu ‘an iron spoon’ (Santali) Rebus: ḍab, ḍhimba, ḍhompo ‘lump (ingot?)’, clot, make a lump or clot, coagulate, fuse, melt together (Santali) ḍabe, ḍabea wide horns (Santali) Rebus: ḍhābā workplace (P.)
The stool on which the bowl is placed is also a hieroglyph read rebus:
Hieroglyphs: legs of stool: kuṭhe = leg of bedstead or chair (Santali.lex.) Rebus: kuṭhi 'a furnace for smelting iron ore, to smelt iron'; koṭe 'forged (metal)(Santali).
Kur. kaṇḍō a stool. Malt. Kanḍo stool, seat. (DEDR 1179) Rebus: kaṇḍ 'stone (ore)' as in: ayaskāṇḍ 'excellent iron' (Panini)
dhaṭu m. (also dhaṭhu) m. ‘scarf’ (WPah.) (CDIAL 6707) Allograph: ḍato = claws of crab (Santali) Rebus: dhātu = mineral (Skt.), dhatu id. (Santali)
See the human face ligatured to a ram's body (an indication of the hieroglyphic nature of the orthographic composition):
mũh 'face' (Santali). Rebus: mũh metal ingot (Santali) mũhã̄ = the quantity of iron produced at one time in a native smelting furnace of the Kolhes; iron produced by the Kolhes and formed like a four-cornered piece a little pointed at each end; mūhā mẽṛhẽt = iron smelted by the Kolhes and formed into an equilateral lump a little pointed at each end; kolhe tehen mẽṛhẽtko mūhā akata = the Kolhes have to-day produced pig iron (Santali.lex.)
miṇḍāl 'markhor' (Tor.wali) meḍho 'a ram, a sheep' (G.)(CDIAL 10120)mēṇḍhaʻramʼ(CDIAL 9606).मेंढा [mēṇḍhā] m (मेष S through H) A male sheep, a ram or tup. मेंढका or क्या [ mēṇḍhakā or kyā ] a (मेंढा) A shepherd (Marathi) Rebus: meḍ 'iron' (Ho.) mēṇḍh 'gold' as in: मेंढसर [ mēṇḍhasara ] m A bracelet of gold thread. (Marathi)मेढ [mēḍha] f A forked stake. Used as a post. Hence a short post generally whether forked or not. Pr. हातीं लागली चेड आणि धर मांडवाची मेढ.
m1186 (DK6847) [Pleiades, scarfed, framework, ficus religiosa , scarfed person, worshipper, twigs (on head), horn, markhor, human face ligatured to markhor, stool, ladle, frame of a building]
Brief memoranda:
bhaṭā G. bhuvɔ m. ʻ worshipper in a temple ʼ rather < bhr̥ta --(CDIAL 9554) Yājñ.com., Rebus: bhaṭā ‘kiln, furnace’ bhaṭā G. bhuvɔ m. ʻ worshipper in a temple ʼ rather < bhr̥ta --(CDIAL 9554) Yājñ.com., Rebus: bhaṭā ‘kiln, furnace’ mū̃h ‘human face’ Rebus: mū̃h ‘ingot’ (See human face ligatured to a markhor: Seal m1186) PLUS Dm. mraṅ m. ‘markhor’ Wkh. merg f. ‘ibex’ (CDIAL 9885) Tor. miṇḍ ‘ram’, miṇḍā́l ‘markhor’ (CDIAL 10310) Rebus: meḍ(Ho.); mẽṛhet ‘iron’ (Munda.Ho.)
lo, no ‘nine’ phonetic reinforcement of: loa ‘ficus’ Rebus: lo ‘copper’
dhaṭu m. (also dhaṭhu) m. ‘scarf’ (Western Pahari) (CDIAL 6707) Rebus: dhatu ‘minerals’ (Santali)
maṇḍa m. ʻ ornament ʼ Rebus: meḍ (Ho.); mẽṛhet ‘iron’ (Munda.Ho.)
Hieroglyph: మండ [ maṇḍa ] manḍa. [Tel.] n. A twig with leaves on it. Rebus: mã̄ḍ m. ʻ array of instruments &c. (CDIAL 9736) maṇḍa 'iron dross, slag' Sa. <i>mE~R~hE~'d</i> `iron'. ! <i>mE~RhE~d</i>(M). Ma. <i>mErhE'd</i> `iron'.Mu. <i>mERE'd</i> `iron'. ~ <i>mE~R~E~'d</i> `iron'. ! <i>mENhEd</i>(M).Ho <i>meD</i> `iron'.Bj. <i>merhd</i>(Hunter) `iron'.KW <i>mENhEd</i> (Munda)
bahulā f. pl. ʻ the Pleiades ʼ VarBr̥S., °likā -- f. pl. lex. [bahulá -- ]Kal. bahul ʻ the Pleiades ʼ, Kho. ból, (Lor.) boul, bolh, Sh. (Lor.) b*lle.(CDIAL 9195) பாகுலம் pākulam , n. < bāhula. The month of Kārttikai = November-December; கார்த்திகை மாதம். (W.) పావడము [ pāvaḍamu ] pāvaḍamu. [Tel.] n. A present, gift. కానుక. बाहुल्य [ bāhulya ] n (S) Abundance, copiousness, plenty.
Rebus: Manifold: bāhula बाहुल a. Manifold. -लः Fire; शीतरुजं समये च परस्मिन् बाहुलतो रसिका शमयन्ती Rām. Ch.4.99. -2 The month Kārtika. -लम् 1 Manifoldness. -2 An armour for the arms, vantbrass. -ली The day of full moon in the month of Kārtika.
Rebus: பாகுடம் pākuṭam, n. < Pkt. pāuḍa < prābhṛta. [K. pāvuḍa.] 1. Gift, present; கையுறை. நரிப் படைக்கொரு பாகுடம்போலே (திவ். பெரியாழ். 4, 5, 8). 2. Royal revenue, impost, tribute; அரசிறை. (சூடா.)
Hieroglyph: bagala 'Pleiades' Rebus: బంగల [ baṅgala ] bangala. [Tel.] n. An oven. కుంపటి.(Telugu) பங்காரு paṅkāru
, n. < T. baṅgāru. [K. baṅgāra.] Gold; பொன். Loc.
Pa. Pk. bahala-- ʻ dense, thick ʼ(CDIAL 9182)
bhaṭā 'brick kiln' (Assamese) بټ baṯṯ, s.m. (2nd) A large iron pan or cauldron for roasting grain, a furnace, a kiln.(Pashto)
bhuvɔ m. ʻ worshipper in a temple ʼ (Gujarati) rather < bhr̥ta --(CDIAL 9554) Yājñ.com., Rebus: bhaṭā‘kiln, furnace’ Pk. bhuaga -- m. ʻ worshipper in a temple ʼPk. bhayaga -- m. ʻ servant ʼ, bhaḍa -- m. ʻ soldier ʼ(CDIAL 9558)
*bhr̥tagātu ʻ hero song ʼ. [bhr̥ta -- , gātú -- 2] Ku. bhaṛau ʻ song about the prowess of ancient heroes ʼ.(CDIAL 9590)

















 (E. Douglas van Buren.
(E. Douglas van Buren. 


 kole.l
kole.l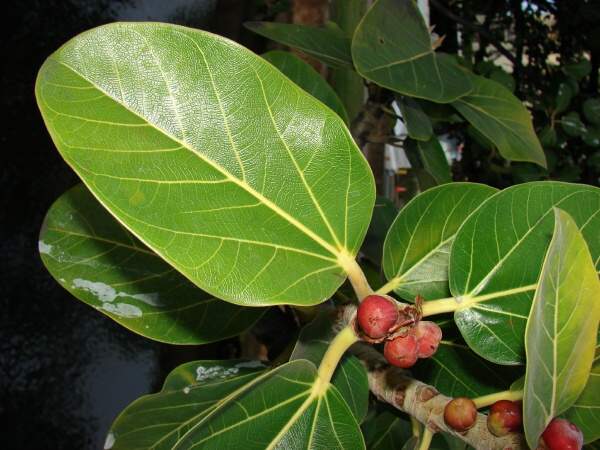 Ficus benghalensis
Ficus benghalensis
























