Mirror: http://tinyurl.com/h4s6h2b
Antelope is a hieroglyph pictorial motif. The pictorial depiction also highlights the short tail with three short strokes. Orthographic styles used in the corpora seem to indicate that a distinction is made between an antelope and a kid (young antelope or goat). It is suggested that the two are distinct signifiers of two distinct rebus readings to signify specific advances in archaeo-metallurgy, related to the hardening of copper mineral by adding other minerals (such as tin) to produce metal alloys.
Hieroglyph: Kur. xolā tail. Malt. qoli id. (DEDR 2135) Rebus: kol 'working in iron' kolhe 'smelters' kolle 'blacksmith'
This pictorial representation also is recognized as a 'sign' on some concordance lists of the Indus Script Corpora.
Antelope hieroglyph occurs in the context of smithy-forge implement cluster from out of 240 copper tablets:
Smithy-forge Implements cluster associated with typical hieroglyphs (both pictorial motifs and signs):
A11
Hieroglyph:
krammara 'look back' (Telugu) rebus: kamar 'blacksmith' mlekh 'goat' rebus: milakkhu, mlecchAs'a 'copper'
kaṇḍa ‘fire-altar’. Alternative: kanka 'rim of jar' rebus: kanga 'brazier'.
Hieroglyph: Ta. meṭṭu mound, heap of earth; mēṭu height, eminence, hillock; muṭṭu rising ground, high ground, heap. Ma. mēṭu rising ground, hillock; māṭu hillock, raised ground; miṭṭāl rising ground, an alluvial bank; (Tiyya) maṭṭa hill. Ka. mēḍu height, rising ground, hillock; miṭṭu rising or high ground, hill; miṭṭe state of being high, rising ground, hill, mass, a large number; (Hav.) muṭṭe heap (as of straw). Tu. miṭṭè prominent, protruding; muṭṭe heap. Te. meṭṭa raised or high ground, hill; (K.) meṭṭu mound; miṭṭa high ground, hillock, mound; high, elevated, raised, projecting; (VPK) mēṭu, mēṭa, mēṭi stack of hay; (Inscr.) meṇṭa-cēnu dry field (cf. meṭṭu-nēla, meṭṭu-vari). Kol. (SR.) meṭṭā hill; (Kin.) meṭṭ, (Hislop) met mountain. Nk. meṭṭ hill, mountain. Ga. (S.3 , LSB 20.3) meṭṭa high land. Go. (Tr. W. Ph.) maṭṭā, (Mu.) maṭṭa mountain; (M. L.) meṭā id., hill; (A. D. Ko.) meṭṭa, (Y. Ma. M.) meṭa hill; (SR.) meṭṭā hillock (Voc. 2949). Konḍa meṭa id. Kuwi (S.)metta hill; (Isr.) meṭa sand hill. (DEDR 5058) Rebus: mē̃d, mēd 'iron'
Link to B5: Hieroglyph: kANDA ‘rhinoceros’ rebus: khANDA ‘implements PLUS pattar 'trough' rebus: pattar 'guild'
 kaṇḍa kanka ‘rim of jar’ Rebus: karṇīka ‘account (scribe)’karṇī‘supercargo’.
kaṇḍa kanka ‘rim of jar’ Rebus: karṇīka ‘account (scribe)’karṇī‘supercargo’.kaṇḍa ‘fire-altar’. Alternative: kanka 'rim of jar' rebus: kanga 'brazier'.
Hieroglyph: Ta. meṭṭu mound, heap of earth; mēṭu height, eminence, hillock; muṭṭu rising ground, high ground, heap. Ma. mēṭu rising ground, hillock; māṭu hillock, raised ground; miṭṭāl rising ground, an alluvial bank; (Tiyya) maṭṭa hill. Ka. mēḍu height, rising ground, hillock; miṭṭu rising or high ground, hill; miṭṭe state of being high, rising ground, hill, mass, a large number; (Hav.) muṭṭe heap (as of straw). Tu. miṭṭè prominent, protruding; muṭṭe heap. Te. meṭṭa raised or high ground, hill; (K.) meṭṭu mound; miṭṭa high ground, hillock, mound; high, elevated, raised, projecting; (VPK) mēṭu, mēṭa, mēṭi stack of hay; (Inscr.) meṇṭa-cēnu dry field (cf. meṭṭu-nēla, meṭṭu-vari). Kol. (SR.) meṭṭā hill; (Kin.) meṭṭ, (Hislop) met mountain. Nk. meṭṭ hill, mountain. Ga. (S.3 , LSB 20.3) meṭṭa high land. Go. (Tr. W. Ph.) maṭṭā, (Mu.) maṭṭa mountain; (M. L.) meṭā id., hill; (A. D. Ko.) meṭṭa, (Y. Ma. M.) meṭa hill; (SR.) meṭṭā hillock (Voc. 2949). Konḍa meṭa id. Kuwi (S.)metta hill; (Isr.) meṭa sand hill. (DEDR 5058) Rebus: mē̃d, mēd 'iron' .

Signs 182, 183, 184 Mahadevan Concordance
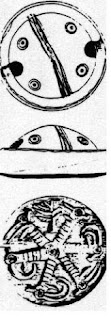
 m516B Copper tablet
m516B Copper tablet 117 antelope; sun motif. Dholavira seal impression. arka 'sun' Rebus: araka, eraka 'copper, moltencast' PLUS करडूं karaḍū 'kid' Rebus: karaḍā 'hard alloy'. Thus, together, the rebus message: hard alloy of copper.
117 antelope; sun motif. Dholavira seal impression. arka 'sun' Rebus: araka, eraka 'copper, moltencast' PLUS करडूं karaḍū 'kid' Rebus: karaḍā 'hard alloy'. Thus, together, the rebus message: hard alloy of copper.On arka in compound expressions: அருக்கம்¹ arukkam, n. < arka. (நாநார்த்த.) 1. Copper; செம்பு (Tamil) అగసాలి (p. 0023) [ agasāli ] or అగసాలెవాడు agasāli. [Tel.] n. A goldsmith. కంసాలివాడు.(Telugu) Kannada (Kittel lexicon):
 Bet Dwaraka turbinella pyrum seal. करडूं karaḍū 'kid' Rebus: karaḍā 'hard alloy'. barad 'ox' Rebus: bharata 'alloy of copper, pewter, tin' khond 'young bull' koD 'horn' Rebus: khond 'turner' koD 'workshop'. Thus workshop of hard alloys of copper, pewter, tin.
Bet Dwaraka turbinella pyrum seal. करडूं karaḍū 'kid' Rebus: karaḍā 'hard alloy'. barad 'ox' Rebus: bharata 'alloy of copper, pewter, tin' khond 'young bull' koD 'horn' Rebus: khond 'turner' koD 'workshop'. Thus workshop of hard alloys of copper, pewter, tin. karaṁḍa -- m.n. ʻ bone shaped like a bamboo ʼ, karaṁḍuya -- n. ʻ backbone ʼ (Prakrit) Rebus: करडा [karaḍā] Hard from alloy--iron, silver &c. (Marathi)
karaṁḍa -- m.n. ʻ bone shaped like a bamboo ʼ, karaṁḍuya -- n. ʻ backbone ʼ (Prakrit) Rebus: करडा [karaḍā] Hard from alloy--iron, silver &c. (Marathi) 40 Three-headed animal, plant; sun motifDholavira. Seal. Readings as above. PLUS kolmo 'rice plant' Rebus: kolami 'smithy, forge'. Thus, the message of the hieroglyph-multiplex is: smithy/forge for moltencast coper and hard alloys of copper, pewter, tin.
40 Three-headed animal, plant; sun motifDholavira. Seal. Readings as above. PLUS kolmo 'rice plant' Rebus: kolami 'smithy, forge'. Thus, the message of the hieroglyph-multiplex is: smithy/forge for moltencast coper and hard alloys of copper, pewter, tin.Hieroglyph: करडूं or करडें (p. 137) [ karaḍū or karaḍēṃ ] n A kid. कराडूं (p. 137) [ karāḍūṃ ] n (Commonly करडूं ) A kid. (Marathi) Rebus: करडा (p. 137) [ karaḍā ] Hard from alloy--iron, silver &c. (Marathi. Molesworth).
 Glyph: svastika; rebus: jasta ‘zinc’ (Kashmiri). Svastika: sathiyā (H.), sāthiyo (G.); satthia, sotthia (Pkt.) Rebus: svastika pewter (Kannada)
Glyph: svastika; rebus: jasta ‘zinc’ (Kashmiri). Svastika: sathiyā (H.), sāthiyo (G.); satthia, sotthia (Pkt.) Rebus: svastika pewter (Kannada) Circular seal, of steatite, from Bahrein, found at Lothal.
Circular seal, of steatite, from Bahrein, found at Lothal.ranku 'antelope' Rebus: ranku 'tin'
m417 Glyph: ‘ladder’: H. sainī, senī f. ʻ ladder ʼ Rebus: Pa. sēṇi -- f. ʻ guild, division of army ʼ; Pk. sēṇi -- f. ʻ row, collection ʼ; śrḗṇi (metr. often śrayaṇi -- ) f. ʻ line, row, troop ʼ RV. The lexeme in Tamil means: Limit, boundary; எல்லை. நளியிரு முந்நீரேணி யாக (புறநா. 35, 1). Country, territory.
The glyphics are:
Semantics: ‘group of animals/quadrupeds’: paśu ‘animal’ (RV), pasaramu, pasalamu = an animal, a beast, a brute, quadruped (Te.) Rebus: pasra ‘smithy’ (Santali)
Glyph: ‘six’: bhaṭa ‘six’. Rebus: bhaṭa ‘furnace’.
Glyph (the only inscription on the Mohenjo-daro seal m417): ‘warrior’: bhaṭa. Rebus: bhaṭa ‘furnace’. Thus, this glyph is a semantic determinant of the message: ‘furnace’. It appears that the six heads of ‘animal’ glyphs are related to ‘furnace’ work.
The glyphics are:
Semantics: ‘group of animals/quadrupeds’: paśu ‘animal’ (RV), pasaramu, pasalamu = an animal, a beast, a brute, quadruped (Te.) Rebus: pasra ‘smithy’ (Santali)
Glyph: ‘six’: bhaṭa ‘six’. Rebus: bhaṭa ‘furnace’.
Glyph (the only inscription on the Mohenjo-daro seal m417): ‘warrior’: bhaṭa. Rebus: bhaṭa ‘furnace’. Thus, this glyph is a semantic determinant of the message: ‘furnace’. It appears that the six heads of ‘animal’ glyphs are related to ‘furnace’ work.
This guild, community of smiths and masons evolves into Harosheth Hagoyim, ‘a smithy of nations’.
It appears that the Meluhhans were in contact with many interaction areas, Dilmun and Susa (elam) in particular. There is evidence for Meluhhan settlements outside of Meluhha. It is a reasonable inference that the Meluhhans with bronze-age expertise of creating arsenical and bronze alloys and working with other metals constituted the ‘smithy of nations’, Harosheth Hagoyim.
Dilmun seal from Barbar; six heads of antelope radiating from a circle; similar to animal protomes in Failaka, Anatolia and Indus. Obverse of the seal shows four dotted circles. [Poul Kjaerum, The Dilmun Seals as evidence of long distance relations in the early second millennium BC, pp. 269-277.] A tree is shown on this Dilmun seal.
Glyph: ‘tree’: kuṭi ‘tree’. Rebus: kuṭhi ‘smelter furnace’ (Santali).
It appears that the Meluhhans were in contact with many interaction areas, Dilmun and Susa (elam) in particular. There is evidence for Meluhhan settlements outside of Meluhha. It is a reasonable inference that the Meluhhans with bronze-age expertise of creating arsenical and bronze alloys and working with other metals constituted the ‘smithy of nations’, Harosheth Hagoyim.
Dilmun seal from Barbar; six heads of antelope radiating from a circle; similar to animal protomes in Failaka, Anatolia and Indus. Obverse of the seal shows four dotted circles. [Poul Kjaerum, The Dilmun Seals as evidence of long distance relations in the early second millennium BC, pp. 269-277.] A tree is shown on this Dilmun seal.
Glyph: ‘tree’: kuṭi ‘tree’. Rebus: kuṭhi ‘smelter furnace’ (Santali).
baTa 'six' Rebus: bhaTa 'furnace' ranku 'antelope' Rebus: ranku 'tin'
Izzat Allah Nigahban, 1991, Excavations at Haft Tepe, Iran, The University Museum, UPenn, p. 97. furnace’ Fig.96a.
There is a possibility that this seal impression from Haft Tepe had some connections with Indian hieroglyphs. This requires further investigation. “From Haft Tepe (Middle Elamite period, ca. 13th century) in Ḵūzestān an unusual pyrotechnological installation was associated with a craft workroom containing such materials as mosaics of colored stones framed in bronze, a dismembered elephant skeleton used in manufacture of bone tools, and several hundred bronze arrowpoints and small tools. “Situated in a courtyard directly in front of this workroom is a most unusual kiln. This kiln is very large, about 8 m long and 2 and one half m wide, and contains two long compartments with chimneys at each end, separated by a fuel chamber in the middle. Although the roof of the kiln had collapsed, it is evident from the slight inturning of the walls which remain in situ that it was barrel vaulted like the roofs of the tombs. Each of the two long heating chambers is divided into eight sections by partition walls. The southern heating chamber contained metallic slag, and was apparently used for making bronze objects. The northern heating chamber contained pieces of broken pottery and other material, and thus was apparently used for baking clay objects including tablets . . .” (loc.cit. Bronze in pre-Islamic Iran, Encyclopaedia Iranica, http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/bronze-i Negahban, 1977; and forthcoming).
Many of the bronze-age manufactured or industrial goods were surplus to the needs of the producing community and had to be traded, together with a record of types of goods and types of processes such as native metal or minerals, smelting of minerals, alloying of metals using two or more minerals, casting ingots, forging and turning metal into shapes such as plates or vessels, using anvils, cire perdue technique for creating bronze statues – in addition to the production of artifacts such as bangles and ornaments made of śankha or shell (turbinella pyrum), semi-precious stones, gold or silver beads. Thus writing was invented to maintain production-cum-trade accounts, to cope with the economic imperative of bronze age technological advances to take the artisans of guilds into the stage of an industrial production-cum-trading community.
Tablets and seals inscribed with hieroglyphs, together with the process of creating seal impressions took inventory lists to the next stage of trading property items using bills of lading of trade loads of industrial goods. Such bills of lading describing trade loads were created using tablets and seals with the invention of writing based on phonetics and semantics of language – the hallmark of Indian hieroglyphs.
S. Kalyanaraman
Sarasvati Research Center
January 28, 2016
Izzat Allah Nigahban, 1991, Excavations at Haft Tepe, Iran, The University Museum, UPenn, p. 97. furnace’ Fig.96a.
There is a possibility that this seal impression from Haft Tepe had some connections with Indian hieroglyphs. This requires further investigation. “From Haft Tepe (Middle Elamite period, ca. 13th century) in Ḵūzestān an unusual pyrotechnological installation was associated with a craft workroom containing such materials as mosaics of colored stones framed in bronze, a dismembered elephant skeleton used in manufacture of bone tools, and several hundred bronze arrowpoints and small tools. “Situated in a courtyard directly in front of this workroom is a most unusual kiln. This kiln is very large, about 8 m long and 2 and one half m wide, and contains two long compartments with chimneys at each end, separated by a fuel chamber in the middle. Although the roof of the kiln had collapsed, it is evident from the slight inturning of the walls which remain in situ that it was barrel vaulted like the roofs of the tombs. Each of the two long heating chambers is divided into eight sections by partition walls. The southern heating chamber contained metallic slag, and was apparently used for making bronze objects. The northern heating chamber contained pieces of broken pottery and other material, and thus was apparently used for baking clay objects including tablets . . .” (loc.cit. Bronze in pre-Islamic Iran, Encyclopaedia Iranica, http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/bronze-i Negahban, 1977; and forthcoming).
Many of the bronze-age manufactured or industrial goods were surplus to the needs of the producing community and had to be traded, together with a record of types of goods and types of processes such as native metal or minerals, smelting of minerals, alloying of metals using two or more minerals, casting ingots, forging and turning metal into shapes such as plates or vessels, using anvils, cire perdue technique for creating bronze statues – in addition to the production of artifacts such as bangles and ornaments made of śankha or shell (turbinella pyrum), semi-precious stones, gold or silver beads. Thus writing was invented to maintain production-cum-trade accounts, to cope with the economic imperative of bronze age technological advances to take the artisans of guilds into the stage of an industrial production-cum-trading community.
Tablets and seals inscribed with hieroglyphs, together with the process of creating seal impressions took inventory lists to the next stage of trading property items using bills of lading of trade loads of industrial goods. Such bills of lading describing trade loads were created using tablets and seals with the invention of writing based on phonetics and semantics of language – the hallmark of Indian hieroglyphs.
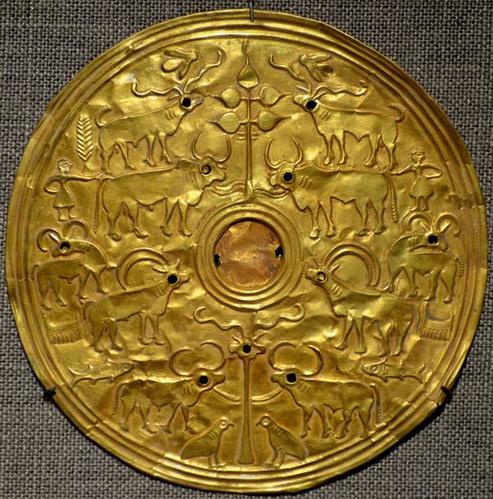
Thanks to Benoy Behl for disseminating the photograph of an exquisite gold disc now in al-Sabah collection of Kuwait National Museum. This gold disc is a veritable metalwork catalogue, consistent with the entire Indus Script Corpora as catalogus catalogorum of metalwork. The uniqueness of the collection of hieroglyph-multiplexs on this gold disc is that a large number of metalwork catalogue items (more than 12) have been presented on a circular space with 9.6 cm diameter validating the Maritime Tin Route which linked Hanoi to Haifa through the Persian Gulf.
"Gold disc. al-Sabah Collection, Kuwait National Museum. 9.6 cm diameter, which was obviously from the Indus Valley period in India. Typical of that period, it depicts zebu, bulls, human attendants, ibex, fish, partridges, bees, pipal free an animal-headed standard." Benoy K. Behl https://www.facebook.com/BenoyKBehlArtCulture
Source: http://tinyurl.com/nom5kkv
In the context of the bronze-age, the hieroglyphs are read rebus in Meluhha (mleccha) speech as metalware catalogs.
http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2013/05/indus-writing-as-metalware-catalogs-and_21.html
http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2013/05/tokens-and-bullae-evolve-into-indus.html
See examples of Dilmun seal readings at http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2013/05/see-httpbharatkalyan97.html
See examples of Sumer Samarra bowls: http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2013/04/bronze-age-writing-in-ancient-near-east.html
"Gold disc. al-Sabah Collection, Kuwait National Museum. 9.6 cm diameter, which was obviously from the Indus Valley period in India. Typical of that period, it depicts zebu, bulls, human attendants, ibex, fish, partridges, bees, pipal free an animal-headed standard." Benoy K. Behl https://www.facebook.com/BenoyKBehlArtCulture
Source: http://tinyurl.com/nom5kkv
In the context of the bronze-age, the hieroglyphs are read rebus in Meluhha (mleccha) speech as metalware catalogs.
http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2013/05/indus-writing-as-metalware-catalogs-and_21.html
http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2013/05/tokens-and-bullae-evolve-into-indus.html
See examples of Dilmun seal readings at http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2013/05/see-httpbharatkalyan97.html
See examples of Sumer Samarra bowls: http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2013/04/bronze-age-writing-in-ancient-near-east.html
In this perspective, the hieroglyphs on the Kuwait Museum gold disc can be read rebus:
1. A pair of tabernae montana flowers tagara 'tabernae montana' flower; rebus: tagara 'tin'
2. A pair of rams tagara 'ram'; rebus: damgar 'merchant' (Akkadian) Next to one ram: kuTi 'tree' Rebus: kuThi 'smelter' Alternative: kolmo 'rice plant' Rebus: kolimi 'smithy, forge'.
3. Ficus religiosa leaves on a tree branch (5) loa 'ficus leaf'; rebus: loh 'metal'. kol in Tamil means pancaloha'alloy of five metals'. PLUS flanking pair of lotus flowers: tAmarasa 'lotus' Rebus: tAmra 'copper' dula 'pair' Rebus: dul 'cast metal' thus, denoting copper castings.
4. A pair of bulls tethered to the tree branch: barad, barat 'ox' Rebus: bharata 'alloy of copper, pewter, tin' (Marathi) PLUS kola 'man' Rebus: kolhe 'smelter' kur.i 'woman' Rebus: kol 'working in iron' Alternative: ḍhangar 'bull'; rebus ḍhangar 'blacksmith' poLa 'zebu' Rebus: poLa 'magnetite'.
Two persons touch the two bulls: meḍ ‘body’ (Mu.) Rebus: meḍ ‘iron’ (Ho.) Thus, the hieroglyph composition denotes ironsmiths.
Two persons touch the two bulls: meḍ ‘body’ (Mu.) Rebus: meḍ ‘iron’ (Ho.) Thus, the hieroglyph composition denotes ironsmiths.
5. A pair of antelopes looking back: krammara 'look back'; rebus: kamar 'smith' (Santali); tagara 'antelope'; rebus: damgar 'merchant' (Akkadian) Alternative: melh, mr..eka 'goat' (Brahui. Telugu) Rebus: milakkhu 'copper' (Pali), mleccha-mukha 'copper' (Samskritam)
6. A pair of antelopes mē̃ḍh 'antelope, ram'; rebus: mē̃ḍ 'iron' (Mu.)
7. A pair of combs kāṅga 'comb' Rebus: kanga 'brazier, fireplace'
Phal. kāṅga ʻ combing ʼ in ṣiṣ k° dūm ʻI comb my hairʼ khyḗṅgia, kēṅgī f.;
kaṅghā m. ʻ large comb (Punjabi) káṅkata m. ʻ comb ʼ AV., n. lex., °tī -- , °tikã -- f. lex. 2. *kaṅkaṭa -- 2 . 3. *kaṅkaśa -- . [Of doubtful IE. origin WP i 335, EWA i 137: aberrant -- uta -- as well as -- aśa -- replacing -- ata -- in MIA. and NIA.]1. Pk. kaṁkaya -- m. ʻ comb ʼ, kaṁkaya -- , °kaï -- m. ʻ name of a tree ʼ; Gy. eur. kangli f.; Wg. kuṇi -- přũ ʻ man's comb ʼ (for kuṇi -- cf. kuṇälík beside kuṅälíks.v. kr̥muka -- ; -- přũ see prapavaṇa -- ); Bshk. kēṅg ʻ comb ʼ, Gaw. khēṅgīˊ, Sv. khḗṅgiā, Tor. kyäṅg ʻ comb ʼ (Dard. forms, esp. Gaw., Sv., Phal. but not Sh., prob. ← L. P. type < *kaṅgahiā -- , see 3 below); Sh. kōṅyi̯ f. (→ Ḍ. k*l ṅi f.), gil. (Lor.) kōĩ f. ʻ man's comb ʼ, kōũ m. ʻ woman's comb ʼ, pales. kōgō m. ʻ comb ʼ; K. kanguwu m. ʻ man's comb ʼ, kangañ f. ʻ woman's ʼ; WPah. bhad. kãˊke i ʻ a comb -- like fern ʼ, bhal. kãke i f. ʻ comb, plant with comb -- like leaves ʼ; N. kāṅiyo, kāĩyo ʻ comb ʼ, A. kã̄kai, B. kã̄kui; Or. kaṅkāi, kaṅkuā ʻ comb ʼ, kakuā ʻ ladder -- like bier for carrying corpse to the burning -- ghat ʼ; Bi. kakwā ʻ comb ʼ, kaka hā, °hī, Mth. kakwā, Aw. lakh. kakawā, Bhoj. kakahī f.; H. kakaiyā ʻ shaped like a comb (of a brick) ʼ; G. (non -- Aryan tribes of Dharampur)kākhāī f. ʻ comb ʼ; M. kaṅkvā m. ʻ comb ʼ, kã̄kaī f. ʻ a partic. shell fish and its shell ʼ; -- S. kaṅgu m. ʻ a partic. kind of small fish ʼ < *kaṅkuta -- ? -- Ext. with --l -- in Ku. kã̄gilo, kāĩlo ʻ comb ʼ.2. G. (Soraṭh) kã̄gaṛ m. ʻ a weaver's instrument ʼ?3. L. kaṅghī f. ʻ comb, a fish of the perch family ʼ, awāṇ. kaghī ʻ comb ʼ; P. kaṅghā m. ʻ large comb ʼ, °ghī f. ʻ small comb for men, large one for women ʼ (→ H. kaṅghā m. ʻ man's comb ʼ, °gahī, °ghī f. ʻ woman's ʼ, kaṅghuā m. ʻ rake or harrow ʼ; Bi. kãga hī ʻ comb ʼ, Or. kaṅgei, M. kaṅgvā); -- G. kã̄gsī f. ʻ comb ʼ, with metath. kã̄sko m., °kī f.; WPah. khaś. kāgśī, śeu. kāśkī ʻ a comblike fern ʼ or < *kaṅkataśikha -- .WPah.kṭg. kaṅgi f. ʻ comb ʼ; J. kāṅgṛu m. ʻ small comb ʼ.(CDIAL 2598)
Rebus: large furnace, fireplace: kang कंग् । आवसथ्यो &1;ग्निः m. the fire-receptacle or fire-place, kept burning in former times in the courtyard of a Kāshmīrī house for the benefit of guests, etc., and distinct from the three religious domestic fires of a Hindū; (at the present day) a fire-place or brazier lit in the open air on mountain sides, etc., for the sake of warmth or for keeping off wild beasts. nāra-kang, a fire-receptacle; hence, met. a shower of sparks (falling on a person) (Rām. 182). kan:gar `portable furnace' (Kashmiri)Cf. kã̄gürü, which is the fem. of this word in a dim. sense (Gr.Gr. 33, 7). kã̄gürü काँग्् or
kã̄gürü काँग or kã̄gar काँग््र्् । हसब्तिका f. (sg. dat. kã̄grĕ काँग्र्य or kã̄garĕ काँगर्य , abl. kã̄gri काँग्रि ), the portable brazier, or kāngrī, much used in Kashmīr (K.Pr. kángár, 129, 131, 178; káṅgrí, 5, 128, 129). For particulars see El. s.v. kángri; L. 7, 25, kangar;and K.Pr. 129. The word is a fem. dim. of kang, q.v. (Gr.Gr. 37). kã̄gri-khŏphürü kã̄gri-khŏphürü काँग्रि-ख्वफ््&above;रू&below; । भग्ना काष्ठाङ्गारिका f. a worn-out brazier. -khôru -खोरु&below; । काष्ठाङ्गारिका<-> र्धभागः m. the outer half (made of woven twigs) of a brazier, remaining after the inner earthenware bowl has been broken or removed; see khôru. -kŏnḍolu -क्वंड । हसन्तिकापात्रम् m. the circular earthenware bowl of a brazier, which contains the burning fuel. -köñü -का&above;ञू&below; । हसन्तिकालता f. the covering of woven twigs outside the earthenware bowl of a brazier.
It is an archaeometallurgical challenge to trace the Maritime Tin Route from the tin belt of the world on Mekong River delta in the Far East and trace the contributions made by seafaring merchants of Meluhha in reaching the tin mineral resource to sustain the Tin-Bronze Age which was a revolution unleashed ca. 5th millennium BCE. See: http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2015/08/indus-script-corpora-as-catalogus.html
Phal. kāṅga ʻ combing ʼ in ṣiṣ k° dūm ʻI comb my hairʼ khyḗṅgia, kēṅgī f.;
kaṅghā m. ʻ large comb (Punjabi) káṅkata m. ʻ comb ʼ AV., n. lex., °tī -- , °tikã -- f. lex. 2. *kaṅkaṭa --
Rebus: large furnace, fireplace: kang कंग् । आवसथ्यो &1;ग्निः m. the fire-receptacle or fire-place, kept burning in former times in the courtyard of a Kāshmīrī house for the benefit of guests, etc., and distinct from the three religious domestic fires of a Hindū; (at the present day) a fire-place or brazier lit in the open air on mountain sides, etc., for the sake of warmth or for keeping off wild beasts. nāra-kang, a fire-receptacle; hence, met. a shower of sparks (falling on a person) (Rām. 182). kan:gar `portable furnace' (Kashmiri)Cf. kã̄gürü, which is the fem. of this word in a dim. sense (Gr.Gr. 33, 7). kã̄gürü काँग्् or
kã̄gürüकाँग or kã̄gar काँग््र्् । हसब्तिका f. (sg. dat. kã̄grĕ काँग्र्य or kã̄garĕ काँगर्य , abl. kã̄gri काँग्रि ), the portable brazier, or kāngrī, much used in Kashmīr (K.Pr. kángár, 129, 131, 178; káṅgrí, 5, 128, 129). For particulars see El. s.v. kángri; L. 7, 25, kangar;and K.Pr. 129. The word is a fem. dim. of kang, q.v. (Gr.Gr. 37). kã̄gri-khŏphürü kã̄gri-khŏphürü काँग्रि-ख्वफ््&above;रू&below; । भग्ना काष्ठाङ्गारिका f. a worn-out brazier. -khôru -खोरु&below; । काष्ठाङ्गारिका<-> र्धभागः m. the outer half (made of woven twigs) of a brazier, remaining after the inner earthenware bowl has been broken or removed; see khôru. -kŏnḍolu -क्वंड । हसन्तिकापात्रम् m. the circular earthenware bowl of a brazier, which contains the burning fuel. -köñü -का&above;ञू&below; । हसन्तिकालता f. the covering of woven twigs outside the earthenware bowl of a brazier.
It is an archaeometallurgical challenge to trace the Maritime Tin Route from the tin belt of the world on Mekong River delta in the Far East and trace the contributions made by seafaring merchants of Meluhha in reaching the tin mineral resource to sustain the Tin-Bronze Age which was a revolution unleashed ca. 5th millennium BCE. See: http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2015/08/indus-script-corpora-as-catalogus.html
kã̄gürü
It is an archaeometallurgical challenge to trace the Maritime Tin Route from the tin belt of the world on Mekong River delta in the Far East and trace the contributions made by seafaring merchants of Meluhha in reaching the tin mineral resource to sustain the Tin-Bronze Age which was a revolution unleashed ca. 5th millennium BCE. See: http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2015/08/indus-script-corpora-as-catalogus.html
8. A pair of fishes ayo 'fish' (Mu.); rebus: ayo 'metal, iron' (Gujarati); ayas 'metal' (Sanskrit)
9.A pair of buffaloes tethered to a post-standard kāṛā ‘buffalo’ கண்டி kaṇṭi buffalo bull (Tamil); rebus: kaṇḍ 'stone ore'; kāṇḍa ‘tools, pots and pans and metal-ware’; kaṇḍ ‘furnace, fire-altar, consecrated fire’.
ṭhaṭera ‘buffalo horns’. ṭhaṭerā ‘brass worker’ (Punjabi)
Pe. kaṇga (pl. -ŋ, kaṇku) eye. Rebus: kanga ' large portable brazier, fire-place' (Kashmiri).Thus the stylized standard is read rebus: Hieroglyph components:kanga + ṭhaṭerā 'one eye + buffalo horn' Rebus: kanga 'large portable barzier' (Kashmiri) + ṭhaṭerā ‘brass worker’ (Punjabi)
Ta. kaṇ eye, aperture, orifice, star of a peacock's tail. Ma. kaṇ, kaṇṇu eye, nipple, star in peacock's tail, bud. Ko. kaṇ eye. To. koṇ eye, loop in string.Ka. kaṇ eye, small hole, orifice. Koḍ. kaṇṇï id. Tu. kaṇṇů eye, nipple, star in peacock's feather, rent, tear. Te. kanu, kannu eye, small hole, orifice, mesh of net, eye in peacock's feather. Kol. kan (pl. kanḍl) eye, small hole in ground, cave. Nk. kan (pl. kanḍḷ) eye, spot in peacock's tail. Nk. (Ch.) kan (pl. -l) eye. Pa.(S. only) kan (pl. kanul) eye. Ga. (Oll.) kaṇ (pl. kaṇkul) id.; kaṇul maṭṭa eyebrow; kaṇa (pl. kaṇul) hole; (S.) kanu (pl. kankul) eye. Go. (Tr.) kan (pl.kank) id.; (A.) kaṛ (pl. kaṛk) id. Konḍa kaṇ id. Pe. kaṇga (pl. -ŋ, kaṇku) id. Manḍ. kan (pl. -ke) id. Kui kanu (pl. kan-ga), (K.) kanu (pl. kaṛka) id. Kuwi(F.) kannū (pl. kar&nangle;ka), (S.) kannu (pl. kanka), (Su. P. Isr.) kanu (pl. kaṇka) id. Kur. xann eye, eye of tuber; xannērnā (of newly born babies or animals) to begin to see, have the use of one's eyesight (for ērnā, see 903). Malt. qanu eye. Br. xan id., bud. (DEDR 1159) kāṇá ʻ one -- eyed ʼ RV. Pa. Pk. kāṇa -- ʻ blind of one eye, blind ʼ; Ash. kã̄ṛa, °ṛī f. ʻ blind ʼ, Kt. kãŕ, Wg. kŕãmacrdotdot;, Pr. k&schwatildemacr;, Tir. kāˊna, Kho. kāṇu NTS ii 260,kánu BelvalkarVol 91; K. kônu ʻ one -- eyed ʼ, S. kāṇo, L. P. kāṇã̄; WPah. rudh. śeu. kāṇā ʻ blind ʼ; Ku. kāṇo, gng. kã̄&rtodtilde; ʻ blind of one eye ʼ, N. kānu;A. kanā ʻ blind ʼ; B. kāṇā ʻ one -- eyed, blind ʼ; Or. kaṇā, f. kāṇī ʻ one -- eyed ʼ, Mth. kān, °nā, kanahā, Bhoj. kān, f. °ni, kanwā m. ʻ one -- eyed man ʼ, H. kān,°nā, G. kāṇũ; M. kāṇā ʻ one -- eyed, squint -- eyed ʼ; Si. kaṇa ʻ one -- eyed, blind ʼ. -- Pk. kāṇa -- ʻ full of holes ʼ, G. kāṇũ ʻ full of holes ʼ, n. ʻ hole ʼ (< ʻ empty eyehole ʼ? Cf. ã̄dhḷũ n. ʻ hole ʼ < andhala -- ).S.kcch. kāṇī f.adj. ʻ one -- eyed ʼ; WPah.kṭg. kaṇɔ ʻ blind in one eye ʼ, J. kāṇā; Md. kanu ʻ blind ʼ.(CDIAL 3019) Ko. kāṇso ʻ squint -- eyed ʼ.(Konkani)
Paš. ainċ -- gánik ʻ eyelid ʼ(CDIAL 3999) Phonetic reinforcement of the gloss: Pe. kaṇga (pl. -ŋ, kaṇku) eye.
See also: nimišta kanag 'to write' (SBal): *nipēśayati ʻ writes ʼ. [√piś] Very doubtful: Kal.rumb. Kho. nivḗš -- ʻ to write ʼ more prob. ← EPers. Morgenstierne BSOS viii 659. <-> Ir. pres. st. *nipaiš -- (for *nipais -- after past *nipišta -- ) in Yid. nuviš -- , Mj. nuvuš -- , Sang. Wkh. nəviš -- ; -- Aś. nipista<-> ← Ir. *nipista -- (for *nipišta -- after pres. *nipais -- ) in SBal. novīsta or nimišta kanag ʻ to write ʼ.(CDIAL 7220)
Pe. kaṇga (pl. -ŋ, kaṇku) eye. Rebus: kanga ' large portable brazier, fire-place' (Kashmiri).
Thus the stylized standard is read rebus: Hieroglyph components:kanga + ṭhaṭerā 'one eye + buffalo horn' Rebus: kanga 'large portable barzier' (Kashmiri) + ṭhaṭerā ‘brass worker’ (Punjabi)
Ta. kaṇ eye, aperture, orifice, star of a peacock's tail. Ma. kaṇ, kaṇṇu eye, nipple, star in peacock's tail, bud. Ko. kaṇ eye. To. koṇ eye, loop in string.Ka. kaṇ eye, small hole, orifice. Koḍ. kaṇṇï id. Tu. kaṇṇů eye, nipple, star in peacock's feather, rent, tear. Te. kanu, kannu eye, small hole, orifice, mesh of net, eye in peacock's feather. Kol. kan (pl. kanḍl) eye, small hole in ground, cave. Nk. kan (pl. kanḍḷ) eye, spot in peacock's tail. Nk. (Ch.) kan (pl. -l) eye. Pa.(S. only) kan (pl. kanul) eye. Ga. (Oll.) kaṇ (pl. kaṇkul) id.; kaṇul maṭṭa eyebrow; kaṇa (pl. kaṇul) hole; (S.) kanu (pl. kankul) eye. Go. (Tr.) kan (pl.kank) id.; (A.) kaṛ (pl. kaṛk) id. Konḍa kaṇ id. Pe. kaṇga (pl. -ŋ, kaṇku) id. Manḍ. kan (pl. -ke) id. Kui kanu (pl. kan-ga), (K.) kanu (pl. kaṛka) id. Kuwi(F.) kannū (pl. kar&nangle;ka), (S.) kannu (pl. kanka), (Su. P. Isr.) kanu (pl. kaṇka) id. Kur. xann eye, eye of tuber; xannērnā (of newly born babies or animals) to begin to see, have the use of one's eyesight (for ērnā, see 903). Malt. qanu eye. Br. xan id., bud. (DEDR 1159) kāṇá ʻ one -- eyed ʼ RV. Pa. Pk. kāṇa -- ʻ blind of one eye, blind ʼ; Ash. kã̄ṛa, °ṛī f. ʻ blind ʼ, Kt. kãŕ, Wg. kŕãmacrdotdot;, Pr. k&schwatildemacr;, Tir. kāˊna, Kho. kāṇu NTS ii 260,kánu BelvalkarVol 91; K. kônu ʻ one -- eyed ʼ, S. kāṇo, L. P. kāṇã̄; WPah. rudh. śeu. kāṇā ʻ blind ʼ; Ku. kāṇo, gng. kã̄&rtodtilde; ʻ blind of one eye ʼ, N. kānu;A. kanā ʻ blind ʼ; B. kāṇā ʻ one -- eyed, blind ʼ; Or. kaṇā, f. kāṇī ʻ one -- eyed ʼ, Mth. kān, °nā, kanahā, Bhoj. kān, f. °ni, kanwā m. ʻ one -- eyed man ʼ, H. kān,°nā, G. kāṇũ; M. kāṇā ʻ one -- eyed, squint -- eyed ʼ; Si. kaṇa ʻ one -- eyed, blind ʼ. -- Pk. kāṇa -- ʻ full of holes ʼ, G. kāṇũ ʻ full of holes ʼ, n. ʻ hole ʼ (< ʻ empty eyehole ʼ? Cf. ã̄dhḷũ n. ʻ hole ʼ < andhala -- ).S.kcch. kāṇī f.adj. ʻ one -- eyed ʼ; WPah.kṭg. kaṇɔ ʻ blind in one eye ʼ, J. kāṇā; Md. kanu ʻ blind ʼ.(CDIAL 3019) Ko. kāṇso ʻ squint -- eyed ʼ.(Konkani)
Paš. ainċ -- gánik ʻ eyelid ʼ(CDIAL 3999) Phonetic reinforcement of the gloss: Pe. kaṇga (pl. -ŋ, kaṇku) eye.
See also: nimišta kanag 'to write' (SBal): *nipēśayati ʻ writes ʼ. [√piś] Very doubtful: Kal.rumb. Kho. nivḗš -- ʻ to write ʼ more prob. ← EPers. Morgenstierne BSOS viii 659. <-> Ir. pres. st. *nipaiš -- (for *nipais -- after past *nipišta -- ) in Yid. nuviš -- , Mj. nuvuš -- , Sang. Wkh. nəviš -- ; -- Aś. nipista<-> ← Ir. *nipista -- (for *nipišta -- after pres. *nipais -- ) in SBal. novīsta or nimišta kanag ʻ to write ʼ.(CDIAL 7220)
Paš. ainċ -- gánik ʻ eyelid ʼ(CDIAL 3999) Phonetic reinforcement of the gloss: Pe. kaṇga (pl. -ŋ, kaṇku) eye.
See also: nimišta kanag 'to write' (SBal): *nipēśayati ʻ writes ʼ. [√piś] Very doubtful: Kal.rumb. Kho. nivḗš -- ʻ to write ʼ more prob. ← EPers. Morgenstierne BSOS viii 659. <-> Ir. pres. st. *nipaiš -- (for *nipais -- after past *nipišta -- ) in Yid. nuviš -- , Mj. nuvuš -- , Sang. Wkh. nəviš -- ; -- Aś. nipista<-> ← Ir. *nipista -- (for *nipišta -- after pres. *nipais -- ) in SBal. novīsta or nimišta kanag ʻ to write ʼ.(CDIAL 7220)
Alternative: dol ‘eye’; Rebus: dul ‘to cast metal in a mould’ (Santali)Alternative: kandi ‘hole, opening’ (Ka.)[Note the eye shown as a dotted circle on many Dilmun seals.]; kan ‘eye’ (Ka.); rebus: kandi (pl. –l) necklace, beads (Pa.);kaṇḍ 'stone ore' Alternative: kã̄gsī f. ʻcombʼ (Gujarati); rebus 1: kangar ‘portable furnace’ (Kashmiri); rebus 2: kamsa 'bronze'.
khuṇḍ ʻtethering peg or post' (Western Pahari) Rebus: kūṭa ‘workshop’; kuṭi= smelter furnace (Santali); Rebus 2: kuṇḍ 'fire-altar'
Why are animals shown in pairs?
dula ‘pair’ (Kashmiri); rebus: dul ‘cast metal’ (Mu.)
khuṇḍ ʻtethering peg or post' (Western Pahari) Rebus: kūṭa ‘workshop’; kuṭi= smelter furnace (Santali); Rebus 2: kuṇḍ 'fire-altar'
Why are animals shown in pairs?
dula ‘pair’ (Kashmiri); rebus: dul ‘cast metal’ (Mu.)
Thus, all the hieroglyphs on the gold disc can be read as Indus writing related to one bronze-age artifact category: metalware catalog entries.
S. Kalyanaraman
Sarasvati Research Center
January 28, 2016









 Mithun or Gayal
Mithun or Gayal












 Mithun in Thrissur zoo
Mithun in Thrissur zoo


 Written by
Written by 


















 Subramanian Swamy
Subramanian Swamy  Ishkaran S. Bhandari
Ishkaran S. Bhandari