In view of the unique expression attested in Pashto dialect, and reading two earlier monographs together, the following conclusions are drawn from a review of Indus Script Corpora which now exceed 8000 inscriptions:
1. Most frequent Indus Script expression signifies, 'wealth-accounting ledger of blacksmith,scribe';
2. most frequent hypertext ' 'unicorn' signifies the blacksmith's professional title: کار کنده kār-kunda, 'manager scribe'.
This is an addendum to:
1. खर-अंशुः 'Soma, metaphor of wealth, of sun's rays'. Meluhha Indus Script Citragupta 'pictographic cipher' expressions 1) lohakaraṇika 'metal engraver', 2) khār karṇī kharaḍā 'blacksmith, supercargo, engraver, daybook (of metalwork)'. https://tinyurl.com/y37svtye
2.Unicorn, Indus Script hypertext kunda-kara karaṇī is a goldsmith, smelter blacksmith, lapidary, supercargo, scribe https://tinyurl.com/y5wneaqr
کار کنده kār-kunda 'manager, director, adroit, clever, experienced' (Pashto) This Pashto expression finds mention on two distinct categories of Indus Script Corpora:
2.The most frequent expression of Indus Script Corpora is a text composed of three signs:
From r. to l.:
1. Hieroglyph: khāra 2 खार 'backbone, spine' rebus: khār खार् । 'blacksmith'
2. Hieroglyph: karṇīka, kanka 'rim of jar' rebus: kaṇḍa kanka 'smelting furnace account (scribe), karṇī, supercargo'
3. khareḍo 'a currycomb (Gujarati) Rebus: karaḍā खरडें 'daybook, wealth-accounting ledger'. Rebus: kharādī ' turner' (Gujarati) Thus, together, the message reads: khār karṇī karaḍā 'blacksmith, scribe, daybook' or 'wealth-accounting ledger of blacksmith,scribe'.
1. On the hypertext signified by the 'one-horned young bull'. It has been noted that the 'unicorn' is an Indus Script hypertext signifying kunda-kara karaṇī. This has to be modified to signify کار کنده kār-kunda karaṇī 'manager goldsmith,smelter blacksmith,lapidary, supercargo,scribe (cf. the monograph at https://tinyurl.com/y5wneaqr)
This monograph reconstructs two ancient Meluhha (Indian sprachbund, 'language union') expressions which signify wealth-accounting for a nation by merchant-/artisan-guilds of Sarasvati Civilization. Cognates of the word khār has two meanings: 1. blacksmith; 2. खर-अंशुः the sun. अंशुः is a synonym of Soma and is cognate with ancu.'iron' (Tocharian). The processing of Soma or अंशुः is the central, sacred metaphor of R̥gveda.
![Image result for gold pectoral bharatkalyan97]()
![Image result for gold pectoral bharatkalyan97]() m1656 Pectoral. Gold Pendant. Harappa. National Museum, New Delhi
m1656 Pectoral. Gold Pendant. Harappa. National Museum, New Delhi
Sun's rays arka 'sun, rays of sun' rebus: arka 'copper, gold' eraka 'moltencast'.
Orthography of the young bull clearly shows sun’s rays on the belly of the bovine.
अंशु m. a filament (especially of the सोम plant); a kind of सोम libation (शतपथ-ब्राह्मण); a ray , sunbeam; end of a thread , a minute particle; a point, end (Monier-Williams); aṃśuḥ अंशुः [अंश्-मृग˚ कु.] 1 A ray, beam of light; चण्ड˚, घर्मं˚ hot-rayed the sun; सूर्यांशुभिर्भिन्नमिवारविन्दम् Ku.1.32; Iustre, brilliance चण्डांशुकिरणाभाश्च हाराः Rām.5.9.48; Śi.1.9. रत्न˚, नख˚ &c. -2 A point or end. -3 A small or minute particle. - 4 End of a thread. -5 A filament, especially of the Soma plant (Ved.) -6 Garment; decoration. -7 N. of a sage or of a prince. -8 Speed, velocity (वेग). -9 Fine thread -Comp. -उदकम् dew-water. -जालम् a collection of rays, a blaze or halo of light. -धरः -पतिः -भृत्-बाणः -भर्तृ-स्वामिन् the sun, (bearer or lord of rays). -पट्टम् a kind of silken cloth (अंशुना सूक्ष्मसूत्रेणयुक्तं पट्टम्); सश्रीफलैरंशुपट्टम् Y. 1.186; श्रीफलैरंशुपट्टानां Ms.5.12. -माला a garland of light, halo. -मालिन् m. [अंशवो मालेव, ततः अस्त्यर्थे इनि] 1 the sun (wreathed with, surrounded by, rays). -2 the number twelve. -हस्तः [अंशुः हस्त इव यस्य] the sun (who draws up water from the earth by means of his 1 hands in the form of rays)(Apte).
This is an addendum to:
1. Uniquely ligatured ficus hieroglyph signifies lohakāra 'coppersmith, ironsmith' (Pali) lohakaraṇika 'metal engraver' https://tinyurl.com/y3sdsz7g
![]() Sign 327
Sign 327![]()
![]() V326 (Orthographic variants of Sign 326)
V326 (Orthographic variants of Sign 326) ![]() V327 (Orthographic variants of Sign 327) loa = a species of fig tree, ficus glomerata, the fruit of ficus glomerata(Santali)
V327 (Orthographic variants of Sign 327) loa = a species of fig tree, ficus glomerata, the fruit of ficus glomerata(Santali)

 m1656 Pectoral. Gold Pendant. Harappa. National Museum, New Delhi
m1656 Pectoral. Gold Pendant. Harappa. National Museum, New DelhiOrthography of the young bull clearly shows sun’s rays on the belly of the bovine.
अंशु m. a filament (especially of the सोम plant); a kind of सोम libation (शतपथ-ब्राह्मण); a ray , sunbeam; end of a thread , a minute particle; a point, end (Monier-Williams); aṃśuḥ अंशुः [अंश्-मृग˚ कु.] 1 A ray, beam of light; चण्ड˚, घर्मं˚ hot-rayed the sun; सूर्यांशुभिर्भिन्नमिवारविन्दम् Ku.1.32; Iustre, brilliance चण्डांशुकिरणाभाश्च हाराः Rām.5.9.48; Śi.1.9. रत्न˚, नख˚ &c. -2 A point or end. -3 A small or minute particle. - 4 End of a thread. -5 A filament, especially of the Soma plant (Ved.) -6 Garment; decoration. -7 N. of a sage or of a prince. -8 Speed, velocity (वेग). -9 Fine thread -Comp. -उदकम् dew-water. -जालम् a collection of rays, a blaze or halo of light. -धरः -पतिः -भृत्-बाणः -भर्तृ-स्वामिन् the sun, (bearer or lord of rays). -पट्टम् a kind of silken cloth (अंशुना सूक्ष्मसूत्रेणयुक्तं पट्टम्); सश्रीफलैरंशुपट्टम् Y. 1.186; श्रीफलैरंशुपट्टानां Ms.5.12. -माला a garland of light, halo. -मालिन् m. [अंशवो मालेव, ततः अस्त्यर्थे इनि] 1 the sun (wreathed with, surrounded by, rays). -2 the number twelve. -हस्तः [अंशुः हस्त इव यस्य] the sun (who draws up water from the earth by means of his 1 hands in the form of rays)(Apte).
अंशुः, पुं, (अंशयति इति अंश विभाजने । मृग-ष्वादित्वात् कुः ।) किरणः ॥ प्रभा ॥ इति मेदि-नी ॥ वेशः ॥ इति धरणी ॥ सूत्रादिसूक्ष्मांशः ।इति हेमचन्द्रः ॥ लेशः ॥ सूर्य्यः ॥ इति विश्वः ॥(ऋषिविशेषः । लतावयवः । सोमलतावयवः ।भागः ।) https://sa.wikisource.org/wiki/शब्दकल्पद्रुमः
अंशु पु० अंश--मृग० कु । किरणे सूत्रे सूक्ष्मांशे प्रकाशेप्रभायां वेगे च “अंशवोऽत्र पतिता रवेः किमु”? इत्युद्भटः“सूर्य्यांशुभिर्भिन्नमिवारविन्दमिति” कुमा० । तत्र स्वपर-प्रकाशकस्य तेजःपदार्थस्य समन्तात् प्रसृतः स्पर्शयोग्यःकिञ्चिन्निविडः सूक्ष्मांशविशेषः किरणः, स च प्रायशःसूर्य्यस्य, तस्य तेजसा प्रदीप्तचन्द्रादेश्च । तदपेक्षया अल्प-स्थानप्रसारी किञ्चिद्विरलः स्पर्शायोग्यः तेजःसूक्ष्मांशःप्रभा, सा च रत्नादिवस्तुनः । चन्द्रादेस्तु अन्यापेक्षयाऽधिक-प्रसृतत्वात् किरणसम्भवः अतएव तत्र शीतांशुः सितकिरणइत्यादिप्रयोगः । स्पर्शयोग्यः तेजःपदार्थस्य किरणादपिनिविडः सूक्ष्मांशः आतपः, किरणापेक्षया अतिविरल-प्रसारी स्पर्शायोग्यः परप्रकाशसाधनमतिसूक्ष्मांशविशेषःआलोकः । प्रभायाम् आलोके वा न र्शोऽनुभूयते ।तत्र अंशुशब्दस्य किरणवाचित्वे सहस्रांशुः उष्णांशुःशीतांशुरित्यादयः । प्रभापरत्वे रत्नांशुः नखांशुरित्या-दयः । अजस्रमाश्रावितवल्लकीगुणक्षतोज्ज्वलाङ्गुष्ठनखांशु-भिन्नयेति” “द्विजावलीबालनिशाकरांशुभिरिति” चमाघः । सूत्रांशपरत्वे अंशुकं पट्टांशुकं चीना-शुकमित्यादयः । प्रकाशपरत्वे उपांशु उपहृतप्रकाश-त्वाच्चास्य गुप्तत्वं प्रतीयते तच्चार्थिकम् । सूक्ष्मविभागपरत्वेप्रांशुः प्रोन्नतावयवत्वा च्चास्य दीर्घत्वं प्रतीयते तच्चा-र्थिकम् इति । https://sa.wikisource.org/wiki/वाचस्पत्यम्
This is an addendum to:
1. Uniquely ligatured ficus hieroglyph signifies lohakāra 'coppersmith, ironsmith' (Pali) lohakaraṇika 'metal engraver' https://tinyurl.com/y3sdsz7g
2. Citragupta, accountant, kāyastha 'merchant-guilds' on sculptues signify Indus Script hypertexts, signifiers of wealth-accounting https://tinyurl.com/y3dwju97

 V326 (Orthographic variants of Sign 326)
V326 (Orthographic variants of Sign 326)  V327 (Orthographic variants of Sign 327) loa = a species of fig tree, ficus glomerata, the fruit of ficus glomerata(Santali)
V327 (Orthographic variants of Sign 327) loa = a species of fig tree, ficus glomerata, the fruit of ficus glomerata(Santali) Vikalpa: kamaṛkom ‘ficus’ (Santali); rebus: kampaṭṭam ‘mint’ (Ta.) patra ‘leaf’ (Skt.); rebus: paṭṭarai ‘workshop’ (Ta.) Rebus: lo ‘iron’ (Assamese, Bengali); loa ‘iron’ (Gypsy) lauha = made of copper or iron (Gr.S'r.); metal, iron (Skt.); lohakāra = coppersmith, ironsmith (Pali); lohāra = blacksmith (Pt.); lohal.a (Or.); loha = metal, esp. copper or bronze (Pali); copper (VS.); loho, lo_ = metal, ore, iron (Si.) loha luṭi = iron utensils and implements (Santali)
Analogous to the reading of the expression of Sign 327 as
lohakaraṇika 'metal engraver', it is possible to interpret the most frequently used Indus Script expression as khār karṇī kharaḍā 'blacksmith, supercargo, engraver,daybook (of metalwork)'.
Etymology of Khar from Sanskrit "Svar", meaning Sun, which changes in northwestern Indian languages to "Khar". खर khara खर a. [opp. मृदु, श्लक्ष्ण, द्रव) 1
Hard, rough, solid-Comp. खर-अंशुः, -करः, -रश्मिः the sun (Apte). खर--मयूख = खरा* ंशु "hot-rayed" , the sun (धूर्तनर्तक)(Monier-Williams) ![]() Sign 48 and variants One reading is barado 'spine' rebus: bharata 'alloy metal oc copper, pewter, tin'. It also signifies khār
Sign 48 and variants One reading is barado 'spine' rebus: bharata 'alloy metal oc copper, pewter, tin'. It also signifies khār खार् 'spine'. کار کنده kār-kunda ' 'manager, director, adroit, clever, experienced' (Pashto) kuṇḍa n. ʻ clump ʼ e.g. darbha-- kuṇḍa-- Pāṇ.(CDIAL 3236). kundār turner (A.)(CDIAL 3295). : kundār turner (A.); kũdār, kũdāri (B.); kundāru (Or.); kundau to turn on a lathe, to carve, to chase; kundau dhiri = a hewn stone; kundau murhut = a graven image (Santali) kunda a turner's lathe (Skt.)(CDIAL 3295) Vikalpa: kūdī, kūṭī 'bunch of twigs' (Skt.) Rebus: kuṭhi ‘smelter furnace’ (Santali) kō̃da कोँद । कुलालादिकन्दुः f. a kiln; a potter's kiln; blacksmith and engraver-lapidary setting or infixing gems. (Kashmiri) kundana ‘fine gold’ (Kannada). कुन्द [p= 291,2] one of कुबेर's nine treasures (N. of a गुह्यक Gal. ) L. کار کند kār-kund (corrup. of P کار کن ) adj. Adroit, clever, experienced. 2. A director, a manager; (Fem.) کار کنده kār-kundaʿh. (Pashto) P کار kār, s.m. (2nd) Business, action, affair, work, labor, profession, operation. Pl. کارونه kārūnah. (E.) کار آرموده .چار kār āzmūdah. adj. Experienced, practised, veteran. کار و بار kār-o-bār, s.m. (2nd) Business, affair. Pl. کار و بارونه kār-o-bārūnah. کار خانه kār- ḵẖānaʿh, s.f. (3rd) A manufactory, a dock- yard, an arsenal, a workshop. Pl. يْ ey. کاردیده kār-dīdah, adj. Experienced, tried, veteran. کار روائي kār-rawā-ī, s.f. (3rd) Carrying on a business, management, performance. Pl. ئِي aʿī. کار زار kār-zār, s.m. (2nd) Battle, conflict. Pl. کار زارونه kār-zārūnah. کار ساز kār-sāz, adj. Adroit, clever; (Fem.) کار سازه kār-sāzaʿh. کار ساري kār-sāzī, s.f. (3rd) Cleverness, adroitness. Pl. ئِي aʿī. کار کند kār-kund (corrup. of P کار کن ) adj. Adroit, clever, experienced. 2. A director, a manager; (Fem.) کار کنده kār-kundaʿh. کار کول kār kawul, verb trans. To work, to labor, to trade. په کار راتلل pah kār rā-tʿlal or راغلل rāg̠ẖ-lal, verb intrans. To be fit, to come into use, to be of use, to be proper or useful. په کار راوړل pah kār rā-wʿṟṟal, verb trans. To bring to use, to make use of, to expend. په کار دي pah kār daey, It is useful. په کار نه دي pah kār nah daey, It is useless. P کارستان kār-istān, s.m. (2nd) A place of work, a manufactory, an arsenal. Pl. کارستانونه kār-istānūnah.(Pashto) Khar or Khor is the Persian word Khordad, which means "Given by Sun". The Skt. expressions ˚सूदनः the sun. -मणिः the sun. -मध्यम् the central point of the sky, the zenith are cognate with khar 'sun'. खर m. a quadrangular mound of earth for receiving the sacrificial vessels (शतपथ-ब्राह्मण v , 1 , 2 , 15); (?) m. xiv (आश्वलायन-श्रौत-सूत्र, कात्यायन-श्रौत-सूत्र)
Hieroglyph: G. khũṭṛɔ m. ʻ entire bull used for agriculture but not for breeding ʼ, (Kathiawar) khũṭ m. ʻ Brahmani bull ʼ.(CDIAL 3899) Rebus: कारकुन kārakuna m ( P A factor, agent, or business-man.) A clerk, scribe, writer. सवा हात लेखणीचा का0 A term of ironical commendation for a clerk.
Hieroglyph 1: khāra 2 Hieroglyph 2: खार khāra 'squirrel'; खारी khārī f (Usually खार) A squirrel. (Kashmiri)
Longest inscription m0314 of Indus Script Corpora is catalogue of a guild-master. The guild master is signified by Indus Script hypertext 'squirrel' hieroglyph 'khāra, šē̃ṣṭrĭ̄' Rebus: plaintext: khār 'blacksmith' śrēṣṭhin 'guild-master' (Aitareya Brāhmaṇa).
palm squirrel,Sciurus palmarum'
svar स्वर् ind. 1 Heaven, paradise; as in स्वर्लोक, स्वर्वेश्या, स्वर्भानुः, &c.; त्वं कर्मणां मङ्गलमङ्गलानां कर्तुः स्म लोकं तनुषे स्वः परं वा Bhāg.4.6.45. -2 The heaven of Indra and the temporary abode of the virtuous after death. -3 The sky, ether. -4 The space above the sun or between the sun and the polar star. -5 The third of the three Vyāhṛitis, pronounced by every Brāhmaṇa in his daily prayers; see व्याहृति. -6 Radiance, splendour. -7 Water. ind. (used in nom., acc., gen., or loc. case); स्वलंकृतैर्भ- वनवरैविभूषितां पुरंदरः स्वरिव यथामरावतीम् Rām.7.11.5; साधोरपि स्वः खलु गामिताधो गमी स तु स्वर्गमितः प्रयाणे N.6. 99 (herein abl. case, स्वर् = स्वर्गात्). -Comp. -अतिक्रमः reaching Vaikuṇṭha (beyond heaven). -आपगा, -गङ्गा 1 the celestial Ganges. -2 the galaxy or milky way. -इङ्गणः a strong wind. -गत a. dead. -गतिः f., -गमनम् 1 going to heaven, future felicity. -2 death. -गिरिः Sumeru. -जित् m. a kind of sacrifice; यजेत वाश्वमेधेन स्वर्जिता गोसवेन वा Ms.11.74. -तरुः (स्वस्तरुः) a tree of paradise. -दृश् m. 1 an epithet of Indra. -2 of Agni. -3 of Soma. -धुनी, -नदी (forming स्वर्णदी) the celestial Ganges; सद्यः पुनन्त्युपस्पृष्टाः स्वर्धुन्यापोनुसेवया Bhāg.1.1.15. -भानवः a kind of precious stone. -भानुः Name of Rāhu; तुल्ये$पराधे स्वर्भानुर्भानुमन्तं चिरेण यत् । हिमांशुमाशु ग्रसते तन्म्रदिम्नः स्फुटं फलम् Ś.i.2.49. ˚सूदनः the sun. -मणिः the sun. -मध्यम् the central point of the sky, the zenith. -यात a. dead. -यातृ a. dying. -यानम् dying, death. -योषित a celestial woman, apsaras. -लोकः the celestial world, heaven. -वधूः f. a celestial damsel, an apsaras. -वापी the Ganges. -वारवामभ्रू (see -वधू above); स्वर्वारवामभ्रुवः नृत्यं चक्रुः Cholachampū p.22, Verse 51. -वेश्या 'a courtezan of heaven', acelestial nymph, an apsaras. -वैद्य m. du. an epithet of the two Aśvins. -षा 1 an epithet of Soma. -2 of the thunderbolt of Indra. -सिन्धु = स्वर्गङ्गा q. v. (Apte)
sanskritdictionary.com/svar/35038/4
https://tinyurl.com/ycgtthuz
The most frequently used Indus Script hypertext expression in Indus Script corpora consists of three unique hieroglyph: 1. khār 'backbone'; 2. karṇaka, 'rim-of-jar' 3. kharaḍā, 'currycomb'.
This triplet of hieroglyphs in Indus Script hypertext signifies wealth-accounting ledger of blacksmith's metalwork products:
1. khār खार् 'blacksmith',
2. karṇī, scribe/supercargo (a representative of the ship's owner on board a merchant ship, responsible for overseeing the cargo and its sale), [Note: kul-- karṇī m. ʻ village accountant ʼ(Marathi)]
3. (scribed in) karaḍā खरडें 'daybook, wealth-accounting ledger of khār खार् 'blacksmith' (Kashmiri)
At the outset, it should be noted that many of these Indus Script expressions are unique to Harappa where tablets (inclduing sealings as tablets) are used to record works in process for subsequent compilation of shipment info. of metalwork catalogues on seals.
Decipherment of variants of the most-frequently used expression (shown on venn diagram) relate to yields from three types of furnaces: 1. smithy, 2. cast metal, 3. implements. The outputs from the furnaces are meant for 1. supercargo (consignments to be shipped by seafaring merchants, helmsmen) and 2. for further work by kharādī turners and for entry in daybook of the scribe: karaḍā खरडें 'daybook, wealth-accounting ledger'.
Seal published by Omananda Saraswati. In Pl. 275: Omananda Saraswati 1975. Ancient Seals of Haryana (in Hindi). Rohtak.
Harappa. Prism tablet. H94-2177/4999-01: Molded faience tablet, Period 3B/3C. Rebus reading:
Two 'ingot' hieroglyphs: dul ḍ̠aḇ 'cast ingot'
'Backbone' hieroglyph:karaṁḍa ʻbackboneʼ Rebus: karaḍa 'hard alloy'
'crocodile' hieroglyph: kāru 'crocodile' (Telugu) Rebus: kāruvu 'artisan' (Telugu) khār 'blacksmith' (Kashmiri)
'two' hieroglyph + 'rimless pot' hieroglyph: dula 'two' Rebus: dul 'cast metal' + baTa 'rimless pot' Rebus: baTa 'furnace'. Thus metal-casting furnace.
Rebus reading of incised Kalibangan potsherd: ayo 'fish' Rebus: aya 'iron, metal' PLUS karaṁḍa ʻbackboneʼ Rebus: karaḍa 'hard alloy' PLUS kanka, karṇaka ‘rim of jar’ Rebus: karṇaka ‘accountscribe’.
kārṇī m. ʻsuper cargo of a ship ʼ(Marathi)
Incised potsherd from Kalibangan. The overriding of the signs shows that the direction of writing was from right to left.
Map showing Khao Sam Kaeo on the east coast and the complex of Phu Khao Thong/Bang Kluai Nok on the west coast [Drawing by the Thai-French archaeological mission].in: "The development of coastal polities in the Upper Thai-Malay Peninsula" by Berenice Bellina et al (2014) in: Before Siam: Essays in Art and Archaeology. (pp. 69-89). River Books http://discovery.ucl.ac.
Apart from etched beads which echo Sarasvati Civilization lapidary work, there are 1) ornaments found in Khao Sam Kaeo which signify Indus Script hieroglyphs and 2) potsherd with Indus Script epigraph found in Phu Khao Thong. Indus Script hieroglyphs on the Khao Sam Kaeo ornaments are:
 The Phu Khao Thong potsherd inscription has hieroglyphs which read rebus: karaṇḍa'backbone' rebus: karaḍa 'hard alloy' PLUS mũhe 'ingot' (Santali) mũhã̄ = the quantity of iron produced at one time in a native smelting furnace of the Kolhes; iron produced by the Kolhes and formed like a four-cornered piece a little pointed at each end. Thus the inscription reads: karaḍa mũhe 'hard metal alloy ingot'.
The Phu Khao Thong potsherd inscription has hieroglyphs which read rebus: karaṇḍa'backbone' rebus: karaḍa 'hard alloy' PLUS mũhe 'ingot' (Santali) mũhã̄ = the quantity of iron produced at one time in a native smelting furnace of the Kolhes; iron produced by the Kolhes and formed like a four-cornered piece a little pointed at each end. Thus the inscription reads: karaḍa mũhe 'hard metal alloy ingot'.Slide 33. Early Harappan zebu figurine with incised spots from Harappa.
Decipherment of the Harappa figurine on Slide 33:
पोळ [pōḷa], 'zebu' Rebus: magnetite, citizen.(See: http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2015/08/zebu-archaeometallurgy-legacy-of-india.html )
mūhā mẽṛhẽt = iron smelted by the Kolhes and formed into an equilateral lump a little pointed at each of four ends (Santali)
खोट (p. 212) [ khōṭa ] f A mass of metal (unwrought or of old metal melted down); an ingot or wedge. (Marathi)
The figurine signifies ingots of पोळ [pōḷa], ‘magnetite’. This is a metalwork catalogue message in Indus Script Corpora.
पोळ [pōḷa], 'zebu' Rebus: magnetite, citizen.(See: http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2015/08/zebu-archaeometallurgy-legacy-of-india.html )
mūhā mẽṛhẽt = iron smelted by the Kolhes and formed into an equilateral lump a little pointed at each of four ends (Santali)
खोट (p. 212) [ khōṭa ] f A mass of metal (unwrought or of old metal melted down); an ingot or wedge. (Marathi)
The figurine signifies ingots of पोळ [pōḷa], ‘magnetite’. This is a metalwork catalogue message in Indus Script Corpora.
Hieroglyph: sãgaḍ, 'lathe' Rebus: sãgaṛh , 'fortification' Rebus: jangad 'invoicing on approval basis'
Hieroglyph: kõdā 'young bull calf' Rebus: kõdā 'turner-joiner' (forge);kundana 'fine gold'
eraka 'nave of wheel' Rebus: eraka 'molten cast, copper' arā 'spokes' rebus: āra 'brass'
sal 'splinter' Rebus: sal 'workshop'
karaṇḍa 'backbone' rebus: karaḍa 'hard alloy'
aḍar 'harrow' Rebus: aduru 'native metal'
bhaṭa 'warrior' Rebus: bhaṭa 'furnace'
karṇaka, 'rim of jar' Rebus: karṇī 'supercargo, scribe'.
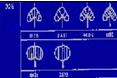
This high-frequency of the expression is highlighted by the venn diagram presented by Nisha Yadav using a limited set of 235 Harappa tablets from the Corpora (Mahadevan concordance):
Yadav, Nisha, 2013, Sensitivity of Indus Script to type of object, SCRIPTA, Vol. 5 (Sept. 2013), pp. 67-103
From r. to l.:
1. Hieroglyph: khāra 2 खार 'backbone, spine' rebus: khār खार् । 'blacksmith'
2. Hieroglyph: karṇīka, kanka 'rim of jar' rebus: kaṇḍa kanka 'smelting furnace account (scribe), karṇī, supercargo'
3. khareḍo 'a currycomb (Gujarati) Rebus: karaḍā खरडें 'daybook, wealth-accounting ledger'. Rebus: kharādī ' turner' (Gujarati)
Thus, the Indus Script hypertext signifies: 1. blacksmith, 2. supercargo (a representative of the ship's owner on board a merchant ship, responsible for overseeing the cargo and its sale.), 3. wealth-accounting ledger
Onager shown on Standard of Ur (2600 BCE) is also shown on Indus Script inscriptions. An example is the seal from Mohenjo-daro (m290)(ca. 2500 BCE) which is a documentation of metalwork wealth by smelters' guild.

DETAIL FROM THE PANEL ON THE BULL-HEADED LYRE showing an 8-stringed bovine lyre being played. At the top of the lyre, braided material is wrapped around the crossbar under the tuning sticks. The small fox-like animal facing the front of the lyre holds a sistrum, or rattle. UPM 817694. Detail of neg. 735-110
The Indus Script hypertext message of the narrative on the Ur lyre: pōḷa, 'zebu' rebus: pōḷa 'magnetite, ferrite ore' PLUS khōṇḍa 'young bull' rebus: kundaṇa 'fine gold' PLUS kolhā, 'jackal' rebus: kolhe 'iron smelter' PLUS tambur 'harp' rebus: tambra 'copper' PLUS khara 'onager' rebus: khār खार् 'blacksmith'.
Rebus: karaḍā खरडें 'daybook, wealth-accounting ledger'. Thus, the message is: daybook (wealth-accounting ledger) of blacksmith working with iron smelter, copper, gold, magnetite ore.
Hieroglyph: पोळ pōḷa, 'Zebu, bos indicus' Rebus: पोळ pōḷa, 'magnetite, ferrite ore' खोंड [ khōṇḍa ] m A young bull, a bullcalf. Rebus: kõdā 'to turn in a lathe' (B.) कोंद kōnda. 'engraver, lapidary setting or infixing gems' (Marathi) कोंडण [
Hieroglyph: jackal: kolhā: krōṣṭŕ̊ ʻ crying ʼ BhP., m. ʻ jackal ʼ RV. = krṓṣṭu -- m. Pāṇ. [√kruś ]Pa. koṭṭhu -- , °uka -- and kotthu -- , °uka -- m. ʻ jackal ʼ, Pk. koṭṭhu -- m.; Si. koṭa ʻ jackal ʼ, koṭiya ʻ leopard ʼ GS 42; -- Pk. kolhuya -- , kulha -- m. ʻ jackal ʼ < *kōḍhu -- ; H. kolhā, °lā m. ʻ jackal ʼ, adj. ʻ crafty ʼ; G. kohlũ, °lũ n. ʻ jackal ʼ, M. kolhā, °lā m.(CDIAL 3615) Rebus: kol 'working in iron'; kolle 'blacksmith'; kolhe 'smelter'
Hieroglyph: tambura 'harp/lyre' rebus: tambra 'copper'
Hieroglyph: khara1 m. ʻ donkey ʼ KātyŚr., °rī -- f. Pāṇ.NiDoc. Pk. khara -- m., Gy. pal. ḳăr m., kắri f., arm. xari, eur. gr. kher, kfer, rum. xerú, Kt. kur, Pr. korūˊ, Dm. khar m., °ri f., Tir. kh*l r, Paš. lauṛ. khar m., khär f., Kal. urt. khār, Phal. khār m., khári f., K. khar m., khürü f., pog. kash. ḍoḍ. khar, S. kharu m., P. G. M. khar m., OM. khari f.; -- ext. Ash. kərəṭék, Shum. xareṭá; <-> L. kharkā m., °kī f. -- Kho. khairánu ʻ donkey's foal ʼ (+?).*kharapāla -- ; -- *kharabhaka -- . Addenda: khara -- 1 : Bshk. Kt. kur ʻ donkey ʼ (for loss of aspiration Morgenstierne ID 334).(CDIAL 3818) Rebus: khār खार् । 'blacksmith' (Kashmiri)
Rebus: karaḍā खरडें 'daybook, wealth-accounting ledger'.
Thus, the symbolic ensemble is a documentation of metalwork in Indus Script Cipher.
 m290 Mohenjo-daro seal. Decipherment: kola 'tiger' Rebus; kolle 'blacksmith' kol 'working in iron' kole.l 'smithy, temple' kolimi 'smithy, forge' PLUS pattar 'trough' Rebus: pattar 'guild of goldsmiths'. panja 'feline paw' rebus: panja 'kiln, furnace'
m290 Mohenjo-daro seal. Decipherment: kola 'tiger' Rebus; kolle 'blacksmith' kol 'working in iron' kole.l 'smithy, temple' kolimi 'smithy, forge' PLUS pattar 'trough' Rebus: pattar 'guild of goldsmiths'. panja 'feline paw' rebus: panja 'kiln, furnace'khar 'ass, onager' (Kashmiri) rebus: khār खार् 'blacksmith' khāra-- basta f. ʻ blacksmith's skin bellows ʼ (Kashmiri)(CDIAL 9424)
kharkhara खर््खर । अश्वादिकण्डूयनयन्त्रम् m. a curry-comb (K.Pr. 15). -- karun -- करुन् । अश्वादिकण्डूयनकरणम् m.inf. to use a curry-comb, to curry (a horse), to groom (a horse).(Kashmiri) kharedo = a currycomb (Gujarati) rebus: kharādī ‘ turner’ (Gujarati) Rebus: daybook: karaḍā m The arrangement of bars or embossed lines (plain or fretted with little knobs) raised upon a तार of gold by pressing and driving it upon the ... 4 also खरडें n A rude sketch; a rough draught; a foul copy; a waste-book; a day-खार् 'blacksmith' (Kashmiri)
Hieroglyph: khāra 2 खार (= खार् (L.V. 96, K.Pr. 47, Śiv. 827) । द्वेषः m. (for 1, see khār 1 ), a thorn, prickle, spine (K.Pr. 47; Śiv. 827, 153)(Kashmiri) Pk. karaṁḍa -- m.n. ʻ bone shaped like a bamboo ʼ, karaṁḍuya -- n. ʻ backbone ʼ.*kaṇṭa3 ʻ backbone, podex, penis ʼ. 2. *kaṇḍa -- . 3. *karaṇḍa -- 4 . (Cf. *kāṭa -- 2 , *ḍākka -- 2 : poss. same as káṇṭa -- 1 ]1. Pa. piṭṭhi -- kaṇṭaka -- m. ʻ bone of the spine ʼ; Gy. eur. kanro m. ʻ penis ʼ (or < káṇṭaka -- ); Tir. mar -- kaṇḍḗ ʻ back (of the body) ʼ; S. kaṇḍo m. ʻ back ʼ, L. kaṇḍ f., kaṇḍā m. ʻ backbone ʼ, awāṇ. kaṇḍ, °ḍī ʻ back ʼ; P. kaṇḍ f. ʻ back, pubes ʼ; WPah. bhal. kaṇṭ f. ʻ syphilis ʼ; N. kaṇḍo ʻ buttock, rump, anus ʼ, kaṇḍeulo ʻ small of the back ʼ; B. kã̄ṭ ʻ clitoris ʼ; Or. kaṇṭi ʻ handle of a plough ʼ; H. kã̄ṭā m. ʻ spine ʼ, G. kã̄ṭɔ m., M. kã̄ṭā m.; Si. äṭa -- kaṭuva ʻ bone ʼ, piṭa -- k° ʻ backbone ʼ.2. Pk. kaṁḍa -- m. ʻ backbone ʼ.(CDIAL 2670) కరాళము karāḷamu karāḷamu. [Skt.] n. The backbone. వెన్నెముక (Telugu)
खार् । लोहकारः m. (sg. abl. khāra 1 खार ; the pl. dat. of this word is khāran 1 खारन् , which is to be distinguished from khāran 2, q.v., s.v.), a blacksmith, an iron worker (cf. bandūka-khār, p. 111b, l. 46; K.Pr. 46; H. xi, 17); a farrier (El.). This word is often a part of a name, and in such case comes at the end (W. 118) as in Wahab khār, Wahab the smith (H. ii, 12; vi, 17). khāra-basta खार -बस््त । चर्मप्रसेविका f. the skin bellows of a blacksmith. -büṭhü -ब&above;ठू&below; । लोहकारभित्तिः f. the wall of a blacksmith's furnace or hearth. -bāy-बाय् । लोहकारपत्नी f. a blacksmith's wife (Gr.Gr. 34). -dŏkuru । लोहकारायोघनः m. a blacksmith's hammer, a sledge-hammer.; । लोहकारचुल्लिः f. a blacksmith's furnace or hearth. -hāl -हाल् । लोहकारकन्दुः f. , a blacksmith's smelting furnace; cf. hāl । लोहकारकन्या f. a blacksmith's daughter. । लोहकारपुत्रः m. the son of a blacksmith, esp. a skilful son, who can work at the same profession. । लोहकारकन्या f. a blacksmith's daughter, esp. one who has the virtues and qualities properly belonging to her father's profession or caste. -më˘ʦü 1 -म्य&above;च&dotbelow;ू&below; । लोहकारमृत्तिका f. (for 2, see [khāra 3] ), 'blacksmith's earth,' i.e. iron-ore.; । लोहकारात्मजः m. a blacksmith's son. -nay -नय् । लोहकारनालिका f. (for khāranay 2, see [khārun] ), the trough into which the blacksmith allows melted iron to flow after smelting. -ʦañĕ -च्&dotbelow;ञ । लोहकारशान्ताङ्गाराः f.pl. charcoal used by blacksmiths in their furnaces. -wān वान् । लोहकारापणः m. a blacksmith's shop, a forge, smithy (K.Pr. 3). -waṭh -वठ् । आघाताधारशिला m. (sg. dat. -waṭas -वटि ), the large stone used by a blacksmith as an anvil. (Kashmiri)Rebus: khara 'sharp-edged' Kannada); pure, unalloyed (Kashmiri) khára2 ʻ hard, sharp, pungent ʼ MBh., ʻ solid ʼ Pān., ʻ hot (of wind) ʼ Suśr. [Cf. karkara -- 1 , karkaśá -- , kakkhaṭa -- ]Pa. Pk. khara -- ʻ hard, rough, cruel, sharp ʼ; K. khoru ʻ pure, genuine ʼ, S. kharo, L. P. kharā (P. also ʻ good of weather ʼ); WPah. bhad. kharo ʻ good ʼ, paṅ. cur. cam. kharā ʻ good, clean ʼ; Ku. kharo ʻ honest ʼ; N. kharo ʻ real, keen ʼ; A. khar ʻ quick, nimble ʼ, m. ʻ dry weather ʼ, kharā ʻ dry, infertile ʼ, khariba ʻ to become dry ʼ; B. kharā ʻ hot, dry ʼ, vb. ʻ to overparch ʼ; Or. kharā ʻ sunshine ʼ; OAw. khara ʻ sharp, notched ʼ; H. kharā ʻ sharp, pure, good ʼ; G. khar ʻ sharp, hot ʼ, °rũ ʻ real, good, well parched or baked, well learnt ʼ; M. khar ʻ sharp, biting, thick (of consistency) ʼ, °rā ʻ pure, good, firm ʼ; Ko. kharo ʻ true ʼ; Si. kara -- räs ʻ hot -- rayed, i.e. sun ʼ. -- Ext. Pk. kharaḍia -- ʻ rough ʼ; Or. kharaṛā ʻ slightly parched ʼ. <-> X kṣārá -- 1 : Or. khārā ʻ very sharp, pure, true ʼ. <-> X paruṣá -- 1 : Bshk. khärúṣ ʻ rough, rugged ʼ; Si. karahu ʻ hard ʼ.
kharapattrā -- , kharayaṣṭikā -- , *kharasrōtas -- .Addenda: khara -- 2 : WPah.kṭg. (kc.) khɔ́rɔ ʻ great, good, excessive ʼ; J. kharā ʻ good, well ʼ; OMarw. kharaü ʻ extreme ʼ.(CDIAL 3819)
Rebus: karaḍā खरडें 'daybook, wealth-accounting ledger'.
Rebus: Ta. karaṭu roughness, unevenness, churlish temper; karaṭṭu rugged, uneven, unpolished; karaṇ uneven surface in vegetables and fruits, scar; karu prong, barb, spike; karumai, karil severity, cruelty; karukkuteeth of a saw or sickle, jagged edge of palmyra leaf-stalk, sharpness. Ma. karaṭu what is rough or uneven; kaṟu rough; kaṟuppu roughness; karuma sharpness of sword; karukku teeth of a saw or file, thorns of a palmyra branch, irregular surface; karukarukka to be harsh, sharp, rough, irritating; karikku edge of teeth; kari-muḷ hard thorn; projecting parts of the skin of custard-apples, jack-fruits, etc.; kari-maṭal rind of jack-fruits. Ko. karp keenness or harshness (of wind); ? kako·ṭ hoe with sharp, broad blade (for -ko·ṭ, see 2064). Ka. karaḍu that is rough, uneven, unpolished, hard, or waste, useless, or wicked; kaṟaku, karku, kakku, gaṟaku, garaku, garku, garasu a jag, notch, dent, toothed part of a file or saw, rough part of a millstone, irregular surface, sharpness. Tu. karaḍů, karaḍu rough, coarse, worn out; wastage, loss, wear; kargōṭa hardness, hard-heartedness; hard, hard-hearted; garu rough; garime severity, strictness; gargāsů a saw. Te. kara sharp; karagasamu a saw; karakasa roughness; karusu rough, harsh; harsh words; kaṟaku, kaṟuku harshness, roughness, sharpness; rough, harsh, sharp; gari hardness, stiffness, sharpness; (B.) karaṭi stubborn, brutish, villainous; kakku a notch or dent, toothed part of a saw, file, or sickle, roughness of a millstone. Go. (Ma.) karkara sharp (Voc. 543). Kur. karcnā to be tough, (Hahn) be hardened. ? Cf. 1260 Ka. garasu. / Cf. Skt. karaṭa- a low, unruly, difficult person; karkara- hard, firm; karkaśa- rough, harsh, hard; krakaca-, karapattra-saw; khara- hard, harsh, rough, sharp-edged; kharu- harsh, cruel; Pali kakaca- saw; khara- rough; saw; Pkt. karakaya- saw; Apabhraṃśa (Jasaharacariu) karaḍa- hard. Cf. esp. Turner, CDIAL, no. 2819. Cf. also Skt. karavāla- sword (for second element, cf. 5376 Ta. vāḷ).(DEDR 1265)

Faience tablet (H2001-5082/2920-02) made from two colors of faience was found eroding from the Trench 54 South workshop area. Identical tablets made from two colors of faience were recovered in Area J, at the south end of Mound AB, in the excavations of Vats during the 1930s. gaNDa 'four' rebus: khaNDa 'implements' baṭa 'rimless pot' rebus: bhaṭa 'furnace' PLUS ayo 'fish' rebus: aya 'iron' ayas 'metal'.
4305 Pict-90: Standing person with horns and bovine features holding a staff or mace on his shoulder. Hieroglyph: ḍhangar 'bull' Rebus: dhangar 'blacksmith' (Maithili) damgar, tamkāru 'merchant' (
bhaṭa 'warrior' Rebus: bhaṭa 'furnace' sal 'splinter' rebus: sal 'workshop' PLUS karṇīka, kanka 'rim of jar' rebus: kaṇḍa kanka 'smelting furnace account (scribe), karṇī, supercargo' Thus, the three-sided Harappa tablet signifies blacksmith, merchant, supercargo (handling products from) furnace workshop.
 Stone seal. h179. National Museum, India. Carved seal. Scan 27418 Tongues of flame decorate the flaming pillar, further signified by two 'star' hieroglyphs on either side of the bottom of the flaming arch.
Stone seal. h179. National Museum, India. Carved seal. Scan 27418 Tongues of flame decorate the flaming pillar, further signified by two 'star' hieroglyphs on either side of the bottom of the flaming arch.Front
khār 'blacksmith' emerges out of the tree or flaming pillar (skambha) identified by the 'star' hieroglyph'. The wristlets he wears and headdress signify that he is khār working with kuṭhi 'tree' Rebus: kuṭhi 'smelting furnace'. He is a smith engaged in smelting.
Hieroglyph:मेढा [ mēḍhā ] 'polar star' Rebus: mẽṛhẽt, meḍ 'iron' (Santali.Mu.Ho.) dula'two' rebus: dul 'metal casting' Thus, signifying a cast iron smelter.
![]() Santali glosses.
Santali glosses.
Hieroglyph: karã̄ n. pl. wristlets, bangles' rebus: khār 'blacksmith'
Hieroglyph: head-dress: kūdī, kūṭī bunch of twigs (Sanskrit) kuṭhi 'tree' Rebus: kuṭhi 'smelting furnace' (Santali) (Phonetic determinative of skambha, 'flaming pillar', rebus:kammaTa 'mint, coiner, coinage'). Skambha, flamiung pillar is the enquiry in Atharva veda Skambha Sukta (AV X.7,8)
Hieroglyph:मेढा [ mēḍhā ] 'polar star' Rebus: mẽṛhẽt, meḍ 'iron' (Santali.Mu.Ho.) dula'two' rebus: dul 'metal casting' Thus, signifying a cast iron smelter.
 Santali glosses.
Santali glosses.Hieroglyph: karã̄ n. pl. wristlets, bangles' rebus: khār 'blacksmith'
Hieroglyph: head-dress: kūdī, kūṭī bunch of twigs (Sanskrit) kuṭhi 'tree' Rebus: kuṭhi 'smelting furnace' (Santali) (Phonetic determinative of skambha, 'flaming pillar', rebus:kammaTa 'mint, coiner, coinage'). Skambha, flamiung pillar is the enquiry in Atharva veda Skambha Sukta (AV X.7,8)
Huntington Archive Scan 27419.
|
Hieroglyphs: backbone + four short strokes
Signs 47, 48: Four ribs of backbone: gaṇḍa ‘four’ Rebus: kaṇḍ ‘fire-altar’. Pk. karaṁḍa -- m.n. ʻbone shaped like a bambooʼ, karaṁḍuya -- n. ʻ backbone ʼ.( (CDIAL 2670) rebus: karaḍa 'hard alloy'. Alternative: baraḍo = spine; backbone (Tulu) Rebus: baran, bharat ‘mixed alloys’ (5 copper, 4 zinc and 1 tin) (Punjabi) + rebus: bharat kaṇḍ ‘fire-altar’, furnace for mixed alloy called bharat(copper, zinc, tin alloy).
bhāthī m. ʻ warrior ʼ bhaṭa 'warrior' Rebus: bhaTa 'furnace', thus reinforcing the smelting process in the fire-altars. Smelters might have used bhaThi 'bellows'. bhástrā f. ʻ leathern bag ʼ ŚBr., ʻ bellows ʼ Kāv., bhastrikā -- f. ʻ little bag ʼ Daś. [Despite EWA ii 489, not from a √bhas ʻ blow ʼ (existence of which is very doubtful). -- Basic meaning is ʻ skin bag ʼ (cf. bakura <-> ʻ bellows ʼ ~ bākurá -- dŕ̊ti -- ʻ goat's skin ʼ), der. from bastá -- m. ʻ goat ʼ RV. (cf.bastājina -- n. ʻ goat's skin ʼ MaitrS. = bāstaṁ carma Mn.); with bh -- (and unexpl. -- st -- ) in Pa. bhasta -- m. ʻ goat ʼ, bhastacamma -- n. ʻ goat's skin ʼ. Phonet. Pa. and all NIA. (except S. with a) may be < *bhāsta -- , cf. bāsta -- above (J. C. W.)]With unexpl. retention of -- st -- : Pa. bhastā -- f. ʻ bellows ʼ (cf. vāta -- puṇṇa -- bhasta -- camma -- n. ʻ goat's skin full ofwind ʼ), biḷāra -- bhastā -- f. ʻ catskin bag ʼ, bhasta -- n. ʻ leather sack (for flour) ʼ; K. khāra -- basta f. ʻ blacksmith's skin bellows ʼ; -- S. bathī f. ʻ quiver ʼ (< *bhathī); A. Or. bhāti ʻ bellows ʼ, Bi. bhāthī, (S of Ganges) bhã̄thī; OAw. bhāthā̆ ʻ quiver ʼ; H. bhāthā m. ʻ quiver ʼ, bhāthī f. ʻ bellows ʼ; G. bhāthɔ,bhātɔ, bhāthṛɔ m. ʻ quiver ʼ (whence bhāthī m. ʻ warrior ʼ); M. bhātā m. ʻ leathern bag, bellows, quiver ʼ, bhātaḍ n. ʻ bellows, quiver ʼ; <-> (X bhráṣṭra -- ?) N. bhã̄ṭi ʻ bellows ʼ, H. bhāṭhī f.Addenda: bhástrā -- : OA. bhāthi ʻ bellows ʼ .(CDIAL 9424) bhráṣṭra n. ʻ frying pan, gridiron ʼ MaitrS. [√bhrajj ]
Pk. bhaṭṭha -- m.n. ʻ gridiron ʼ; K. büṭh
kanda kanka 'rim of jar' (Santali) Rebus: kanda kanka 'fire-trench account, karṇi supercargo' karṇīka 'helmsman, merchantman, scribe, account'.

Harappa tablets showing a pair of 'ingots' flanking 'backbone' hieroglyph
dula 'pair' rebus: dul 'metal casting' PLUS hieroglyph: oval (lozenge) shape:
mũhe 'ingot' (Santali) mũhã̄ = the quantity of iron produced at one time in a native smelting furnace of the Kolhes; iron produced by the Kolhes and formed like a four-cornered piece a little pointed at each end; mūhā mẽṛhẽt = iron smelted by the Kolhes and formed into an equilateral lump a little pointed at each of four ends;kolhe tehen mẽṛhẽt ko mūhā akata = the Kolhes have to-day produced pig iron (Santali). Thus, the message of the Indus Script hypertext with three hieroglyphs is: cast metal ingot of karaḍa 'hard alloy'. करडा [karaḍā] Hard from alloy--iron, silver &c. (Marathi) kharādī ' turner, a person who fashions or shapes objects on a lathe' (Gujarati)
Alternative reading of ingot: ḍhālako = a large metal ingot (G.) ḍhālakī = a metal heated and poured into a mould; a solid piece of metal; an ingot (Gujarati).
 Persian gulf seal. mr̤eka, melh 'goat' rebus: milakkhu, mleccha-mukha 'copper' eraka 'raisedhand' rebus: eraka 'moltencast, copper'
Persian gulf seal. mr̤eka, melh 'goat' rebus: milakkhu, mleccha-mukha 'copper' eraka 'raisedhand' rebus: eraka 'moltencast, copper'karaḍū or ṅkaraḍēṃ ] n A kid. कराडूं (p. 137) [ karāḍūṃ ] n (Commonly करडूं ) A kid. (Marathi) Rebus: करडा (p. 137) [ karaḍā ] 'hard alloy' PLUS dula 'two' rebus: dul 'metal casting'. Thus copper metal casters.
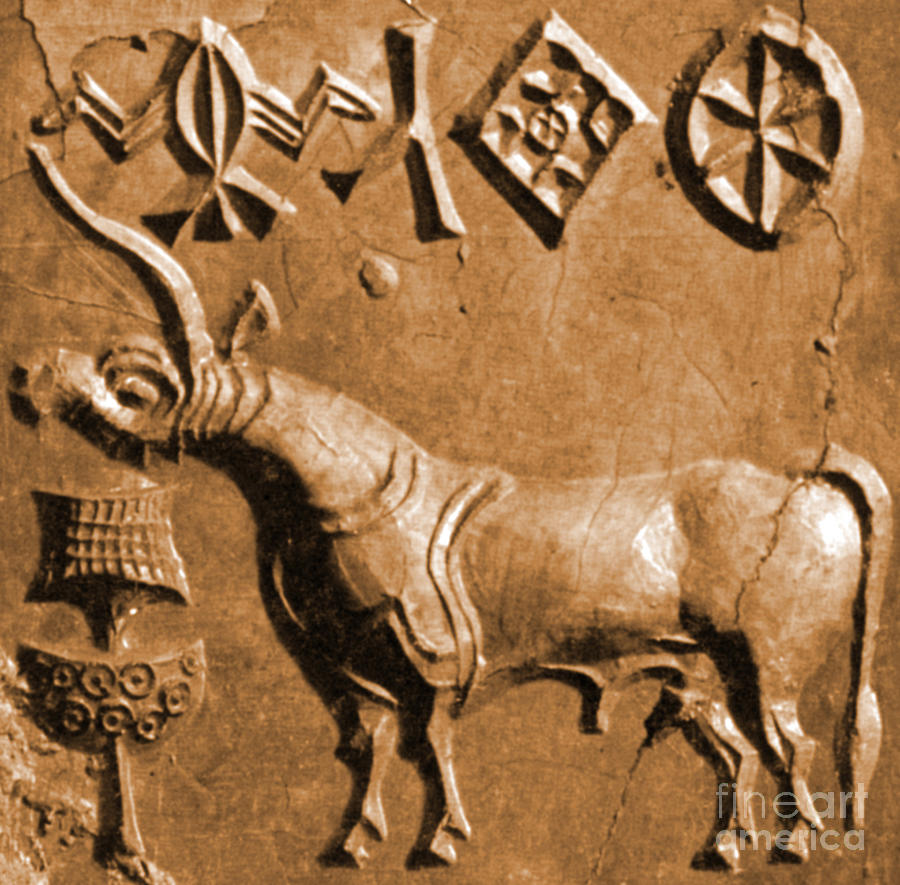
Unicorn, Indus Script hypertext kunda-kara karaṇī is a goldsmith, smelter blacksmith, lapidary, supercargo, scribe
https://tinyurl.com/y5wneaqr
-- Unicorn, Indus Script hieroglyphs read Meluhha rebus as kō̃da-khār-karaṇī'smelter blacksmith, supercargo, scribe', kunda-kara'turner, lapidary', kunda'treasure'kundaṇa'fine gold'
-- Unicorn, Indus Script hieroglyphs read Meluhha rebus as kō̃da-khār-karaṇī'smelter blacksmith, supercargo, scribe', kunda-kara'turner, lapidary', kunda'treasure'kundaṇa'fine gold'
-- Unicorn, composite animal खोंड khōṇḍa'young bull' PLUS khara'onager' read rebus: kunda-kara'turner, lapidary', kō̃da-khār'smelter blacksmith'; kunda'one of the nine treasures of Kubera'; kundaṇa 'fine gold'; karṇī 'ear' rebus: karaṇī 'supercargo, scribe'
-- Unicorn of Indus Script is a composite animal with body of young bull, head & ear of onager, crumpled horn
Identifying hieroglyph components of unicorn, as a composite animal of Indus Script
On the pattern of ligaturing technique to create a composite animal, the 'unicorn' pictorial motif of Indus Script can be seen as a hypertext composition with distinct hieroglyphic ligatures. See Annex:Harappan chimaera analysed by Dennys Frenez and Massimo Vidale.
On seal m008 of Mohenjo-daro, such ligatures or component hieroglyphs are idenified as: 1. one wavy, serrated, crumpled horn; 2. ear; 3. head, including face; 4. pannier; 5. the body of the animal is a young bull.
Each of these five hieroglyph components of the composition is read rebus in Meluhha:
1. mer̥ha deren'crumpled horn' rebus: meḍ'iron' (Mu.Ho.),med'copper' (Slavic) PLUS tiṟ(u) 'trade, exchange, barter.'
2. karṇī 'ear' rebus: karaṇī 'supercargo, scribe' [supercargo in charge as 'a representative of the ship's owner on board a merchant ship, responsible for overseeing the cargo and its sale.'
3.Head of onager: khara'onager' rebus: khār खार् 'blacksmith'(Kashmiri) kāruvu 'artisan' (Telugu)
4. Pannier: khōṇḍa 'sack, pannier'khōṇḍī 'pannier sack'खोंडी (Marathi) Rebus: kunda 'nidhi'; kō̃daकोँद 'kiln, furnace for smelting' This is a semantic determinative of the body of the animal.
5. Body of the animal: खोंड khōṇḍa m A young bull, a bullcalf. (Marathi) rebus: kō̃da कोँद 'kiln, furnace for smelting'; kunda 'a treasure of Kubera'Rebus: Ta. kuntaṉam interspace for setting gems in a jewel; fine gold (< Te.). Ka. kundaṇa setting a precious stone in fine gold; fine gold; kundana fine gold.Tu. kundaṇa pure gold. Te. kundanamu fine gold used in very thin foils in setting precious stones; setting precious stones with fine gold. (DEDR 1725).
Thus, the body of the young bull PLUS face/head of onager is read together: khara'onager' rebus: खोंड khōṇḍa'young bull' rebus: kō̃daकोँद 'kiln, furnace for smelting'PLUS khār खार् 'blacksmith'. The expression read together rebus is: kundakara, 'turner, lapidary'.
The animal is in front of a standard device.The standard device has two hieroglyph components: 1. lathe; 2. portable furnace.
Component 1. Lathe: kunda1 m. ʻ a turner's lathe ʼ lex. [Cf. *cunda -- 1 ] N. kũdnu ʻ to shape smoothly, smoothe, carve, hew ʼ, kũduwā ʻ smoothly shaped ʼ; A. kund ʻ lathe ʼ, kundiba ʻ to turn and smooth in a lathe ʼ, kundowā ʻ smoothed and rounded ʼ; B. kũd ʻ lathe ʼ, kũdā, kõdā ʻ to turn in a lathe ʼ; Or. kū˘nda ʻ lathe ʼ, kũdibā, kū̃d° ʻ to turn ʼ (→ Drav. Kur. kū̃d ʻ lathe ʼ); Bi.kund ʻ brassfounder's lathe ʼ; H. kunnā ʻ to shape on a lathe ʼ, kuniyā m. ʻ turner ʼ, kunwā m. (CDIAL 3295). kundakara m. ʻ turner ʼ W. [Cf. *cundakāra -- : kunda -- 1 , kará -- 1 ] A. kundār, B. kũdār, °ri, Or. kundāru; H. kũderā m. ʻ one who works a lathe, one who scrapes ʼ, °rī f., kũdernā ʻ to scrape, plane, round on a lathe ʼ.(CDIAL 3297).
Component 2. Portable furnace: kammatamu'portable gold furnace' rebus: kammaṭa'mint, coiner coinage'.The bottom portion, the portable furnace is: కమటము (p. 246) kamaṭamu kamaṭamu. [Tel.] n. A portable furnace for melting the precious metals. అగసాలెవాని కుంపటి. "చ కమటము కట్లెసంచి
Thus, together, the standard device signifies kammaṭa kunda 'mint treasure'.
 m008 "This unicorn seal was also discovered during the late 1927-31 excavations at Mohenjo-daro. One theory holds that the bull actually has two horns, but that these have been stylized to one because of the complexity of depicting three dimensions. However the manufacturing and design process behind seals was so sophisticated that the depiction of three dimensions might not necessarily have been a problem." -- Omar Khan https://www.harappa.com/seal/11.html Slide 46 https://slideplayer.com/slide/15162906/
m008 "This unicorn seal was also discovered during the late 1927-31 excavations at Mohenjo-daro. One theory holds that the bull actually has two horns, but that these have been stylized to one because of the complexity of depicting three dimensions. However the manufacturing and design process behind seals was so sophisticated that the depiction of three dimensions might not necessarily have been a problem." -- Omar Khan https://www.harappa.com/seal/11.html Slide 46 https://slideplayer.com/slide/15162906/khār 1 खार् । लोहकारः m. (sg. abl. khāra 1 खार ; the pl. dat. of this word is khāran 1 खारन् , which is to be distinguished from khāran 2, q.v., s.v.), a blacksmith, an iron worker (cf. bandūka-khār, p. 111b, l. 46; K.Pr. 46; H. xi, 17); a farrier (El.). This word is often a part of a name, and in such case comes at the end (W. 118) as in Wahab khār, Wahab the smith (H. ii, 12; vi, 17). khāra-basta खार-बस्त । चर्मप्रसेविका f. the skin bellows of a blacksmith. -büṭhü-ब॑ठू॒ । लोहकारभित्तिः f. the wall of a blacksmith's furnace or hearth. -bāy -बाय् । लोहकारपत्नी f. a blacksmith's wife (Gr.Gr. 34). -dŏkuru -द्वकुरु॒ । लोहकारायोघनः m. a blacksmith's hammer, a sledge-hammer. -gȧji -ग॑जि॒ or -güjü -ग॑जू॒ । लोहकारचुल्लिः f. a blacksmith's furnace or hearth. -hāl -हाल् । लोहकारकन्दुः f. (sg. dat. -höjü -हा॑जू॒ ), a blacksmith's smelting furnace; cf. hāl 5. -kūrü -कूरू॒ । लोहकारकन्या f. a blacksmith's daughter. -koṭu -क॑टु॒ । लोहकारपुत्रः m. the son of a blacksmith, esp. a skilful son, who can work at the same profession. -küṭü -क॑टू॒ । लोहकारकन्या f. a blacksmith's daughter, esp. one who has the virtues and qualities properly belonging to her father's profession or caste. -më̆ʦü 1 -म्य॑च़ू॒ । लोहकारमृत्तिका f. (for 2, see khāra 3), 'blacksmith's earth,' i.e. iron-ore. -nĕcyuwu -न्यचिवु॒ । लोहकारात्मजः m. a blacksmith's son. -nay -नय् । लोहकारनालिका f. (for khāranay 2, see khārun), the trough into which the blacksmith allows melted iron to flow after smelting. -ʦañĕ -च़्ञ । लोहकारशान्ताङ्गाराः f.pl. charcoal used by blacksmiths in their furnaces. -wān वान् । लोहकारापणः m. a blacksmith's shop, a forge, smithy (K.Pr. 30). -waṭh -वठ् । आघाताधारशिला m. (sg. dat. -waṭas -वटि ), the large stone used by a blacksmith as an anvil.(Kashmiri) S لوهار lo-hār, s.m. (5th) A blacksmith. Pl. لوهاران lo-hārān.(Pashto)1 lōhakāra m. ʻ iron -- worker ʼ, ˚rī -- f., ˚raka -- m. lex., lauhakāra -- m. Hit. [lōhá -- , kāra -- 1 ]Pa. lōhakāra -- m. ʻ coppersmith, ironsmith ʼ; Pk. lōhāra -- m. ʻ blacksmith ʼ, S. luhā̆ru m., L. lohār m., ˚rī f., awāṇ. luhār, P. WPah.khaś. bhal. luhār m., Ku. lwār, N. B. lohār, Or. lohaḷa, Bi.Bhoj. Aw.lakh. lohār, H. lohār, luh˚ m., G. lavār m., M. lohār m.; Si. lōvaru ʻ coppersmith ʼ.
Addenda: lōhakāra -- : WPah.kṭg. (kc.) lhwāˋr m. ʻ blacksmith ʼ, lhwàrkarmāˊra m. ʻ blacksmith ʼ RV. [EWA i 176 < stem *karmar -- ~ karman -- , but perh. with ODBL 668 ← Drav. cf. Tam. karumā ʻ smith, smelter ʼ whence meaning ʻ smith ʼ was transferred also to karmakāra -- ] Pa. kammāra -- m. ʻ worker in metal ʼ; Pk. kammāra -- , ˚aya -- m. ʻ blacksmith ʼ, A. kamār, B. kāmār; Or. kamāra ʻ blacksmith, caste of non -- Aryans, caste of fishermen ʼ; Mth. kamār ʻ blacksmith ʼ, Si. kam̆burā.*karmāraśālā -- .Addenda: karmāˊra -- : Md. kan̆buru ʻ blacksmith ʼ. *karmāraśālā ʻ smithy ʼ. [karmāˊra -- , śāˊlā -- ]Mth. kamarsārī; -- Bi. kamarsāyar?(CDIAL 2898, 2899)
m0008a ![]() 1038 Field symbol: kõda ‘young bull-calf’. Rebus: kũdār ‘turner’.sangaḍa ‘lathe, furnace’. Rebus: samgara ‘living in the same house, guild’. sãgaḍa (double-canoe, catamaran) Hence, smith guild.
1038 Field symbol: kõda ‘young bull-calf’. Rebus: kũdār ‘turner’.sangaḍa ‘lathe, furnace’. Rebus: samgara ‘living in the same house, guild’. sãgaḍa (double-canoe, catamaran) Hence, smith guild.
 1038 Field symbol: kõda ‘young bull-calf’. Rebus: kũdār ‘turner’.sangaḍa ‘lathe, furnace’. Rebus: samgara ‘living in the same house, guild’. sãgaḍa (double-canoe, catamaran) Hence, smith guild.
1038 Field symbol: kõda ‘young bull-calf’. Rebus: kũdār ‘turner’.sangaḍa ‘lathe, furnace’. Rebus: samgara ‘living in the same house, guild’. sãgaḍa (double-canoe, catamaran) Hence, smith guild.Meaning, artha of inscription: Trade (and metalwork wealth production) of kōnda sangara 'metalwork engraver'... PLUS (wealth categories cited.).
kole.l 'temple' rebus: kole.l'smithy, forge' Or, warehouse kuṭhī granary, factory (M.)(CDIAL 3546). koṭho = a warehouse.
bhaṭā 'warrior' rebus: bhaṭa 'furnace'.
baṭa 'rimless, wide-mouthed pot' rebus: bhaṭa 'furnace' PLUS ḍabu 'an iron spoon' (Santali) Rebus: ḍab, ḍhimba, ḍhompo 'lump (ingot?). Thus, together, furnace ingots.

 m008 "This unicorn seal was also discovered during the late 1927-31 excavations at Mohenjo-daro. One theory holds that the bull actually has two horns, but that these have been stylized to one because of the complexity of depicting three dimensions. However the manufacturing and design process behind seals was so sophisticated that the depiction of three dimensions might not necessarily have been a problem." -- Omar Khan https://www.harappa.com/seal/11.html Slide 46 https://slideplayer.com/slide/15162906/
m008 "This unicorn seal was also discovered during the late 1927-31 excavations at Mohenjo-daro. One theory holds that the bull actually has two horns, but that these have been stylized to one because of the complexity of depicting three dimensions. However the manufacturing and design process behind seals was so sophisticated that the depiction of three dimensions might not necessarily have been a problem." -- Omar Khan https://www.harappa.com/seal/11.html Slide 46 https://slideplayer.com/slide/15162906/ "First Unicorn seals. The splash of the new. Pictures of mysterious seals from Harappa had appeared in specialized journals, but no composite picture of seals had been offered to the masses until September 24, 1924. This set of seals from the Illustrated London News were the vehicle. From the very beginning, the face of the unicorn was the face of the Indus civilization, and that is probably how its rulers had intended it to be.Sir John Marshall, who published the findings wrote "The animal most often represented on the seals is the apparently single-horned beast . . .. There is a possibility, I think, that the artist intended to represent one horn behind the other. In other animals, however, the two horns are shown quite distinctly. In some respects the body of this beast, which is always a male, resembles that of an antelope of heavy build, such as the eland or oryx, and in others that of an ox. The long tuffed tail may belong to either class. The horn is sometimes smooth . . . sometimes it has transverse ridges. In the latter case, the possibility of the creature being an ox is ruled out. The long pointed ears are also characteristic of the antelope. Perhaps we have here a fabulous animal which is a composite of the ox and antelope. And yet to the casual eye there is nothing fantastic about it, as about some of the other animals represented on seals; nor does it in any way resemble the unicorn of heraldry, which is made up of different parts of a number of animals, though it must be noted that the traditional unicorn was supposed to have originated in India" [Mohenjo-daro and The Indus Civilization, Vol. II., p. 382]."https://www.harappa.com/blog/first-unicorn-seals
"First Unicorn seals. The splash of the new. Pictures of mysterious seals from Harappa had appeared in specialized journals, but no composite picture of seals had been offered to the masses until September 24, 1924. This set of seals from the Illustrated London News were the vehicle. From the very beginning, the face of the unicorn was the face of the Indus civilization, and that is probably how its rulers had intended it to be.Sir John Marshall, who published the findings wrote "The animal most often represented on the seals is the apparently single-horned beast . . .. There is a possibility, I think, that the artist intended to represent one horn behind the other. In other animals, however, the two horns are shown quite distinctly. In some respects the body of this beast, which is always a male, resembles that of an antelope of heavy build, such as the eland or oryx, and in others that of an ox. The long tuffed tail may belong to either class. The horn is sometimes smooth . . . sometimes it has transverse ridges. In the latter case, the possibility of the creature being an ox is ruled out. The long pointed ears are also characteristic of the antelope. Perhaps we have here a fabulous animal which is a composite of the ox and antelope. And yet to the casual eye there is nothing fantastic about it, as about some of the other animals represented on seals; nor does it in any way resemble the unicorn of heraldry, which is made up of different parts of a number of animals, though it must be noted that the traditional unicorn was supposed to have originated in India" [Mohenjo-daro and The Indus Civilization, Vol. II., p. 382]."https://www.harappa.com/blog/first-unicorn-seals![Image result for mohenjo-daro seal unicorn]() Source: Chapter Ten - Understanding Indus Seal-Carving Traditions: A Stylistic and Metric Approach
Source: Chapter Ten - Understanding Indus Seal-Carving Traditions: A Stylistic and Metric Approach
Unicorn seal found Kish, Iraq.
The Harappan riddle of 'unicorn'
Shubhangana Atre
Bulletin of the Deccan College Post-Graduate and Research Institute
Vol. 44 (1985), pp. 1-10 Published by: Vice Chancellor, Deccan College Post-Graduate and Research Institute (Deemed University), Pune



Onager shown on Standard of Ur (2600 BCE) is also shown on Indus Script inscriptions. An example is the seal from Mohenjo-daro (m290)(ca. 2500 BCE) which is a documentation of metalwork wealth by smelters' guild.

DETAIL FROM THE PANEL ON THE BULL-HEADED LYRE showing an 8-stringed bovine lyre being played. At the top of the lyre, braided material is wrapped around the crossbar under the tuning sticks. The small fox-like animal facing the front of the lyre holds a sistrum, or rattle. UPM 817694. Detail of neg. 735-110
The Indus Script hypertext message of the narrative on the Ur lyre: pōḷa, 'zebu' rebus: pōḷa 'magnetite, ferrite ore' PLUS khōṇḍa 'young bull' rebus: kundaṇa 'fine gold' PLUS kolhā, 'jackal' rebus: kolhe 'iron smelter' PLUS tambur 'harp' rebus: tambra 'copper' PLUS khara 'onager' rebus: khār खार् 'blacksmith'.
Rebus: karaḍā खरडें 'daybook, wealth-accounting ledger'. Thus, the message is: daybook (wealth-accounting ledger) of blacksmith working with iron smelter, copper, gold, magnetite ore.
Hieroglyph: पोळ pōḷa, 'Zebu, bos indicus' Rebus: पोळ pōḷa, 'magnetite, ferrite ore' खोंड [ khōṇḍa ] m A young bull, a bullcalf. Rebus: kõdā 'to turn in a lathe' (B.) कोंद kōnda. 'engraver, lapidary setting or infixing gems' (Marathi) कोंडण [
Hieroglyph: jackal: kolhā: krōṣṭŕ̊ ʻ crying ʼ BhP., m. ʻ jackal ʼ RV. = krṓṣṭu -- m. Pāṇ. [√kruś ]Pa. koṭṭhu -- , °uka -- and kotthu -- , °uka -- m. ʻ jackal ʼ, Pk. koṭṭhu -- m.; Si. koṭa ʻ jackal ʼ, koṭiya ʻ leopard ʼ GS 42; -- Pk. kolhuya -- , kulha -- m. ʻ jackal ʼ < *kōḍhu -- ; H. kolhā, °lā m. ʻ jackal ʼ, adj. ʻ crafty ʼ; G. kohlũ, °lũ n. ʻ jackal ʼ, M. kolhā, °lā m.(CDIAL 3615) Rebus: kol 'working in iron'; kolle 'blacksmith'; kolhe 'smelter'
Hieroglyph: tambura 'harp/lyre' rebus: tambra 'copper'
Hieroglyph: khara1 m. ʻ donkey ʼ KātyŚr., °rī -- f. Pāṇ.NiDoc. Pk. khara -- m., Gy. pal. ḳăr m., kắri f., arm. xari, eur. gr. kher, kfer, rum. xerú, Kt. kur, Pr. korūˊ, Dm. khar m., °ri f., Tir. kh*l r, Paš. lauṛ. khar m., khär f., Kal. urt. khār, Phal. khār m., khári f., K. khar m., khürü f., pog. kash. ḍoḍ. khar, S. kharu m., P. G. M. khar m., OM. khari f.; -- ext. Ash. kərəṭék, Shum. xareṭá; <-> L. kharkā m., °kī f. -- Kho. khairánu ʻ donkey's foal ʼ (+?).*kharapāla -- ; -- *kharabhaka -- . Addenda: khara -- 1 : Bshk. Kt. kur ʻ donkey ʼ (for loss of aspiration Morgenstierne ID 334).(CDIAL 3818) Rebus: khār खार् । 'blacksmith' (Kashmiri)
Rebus: karaḍā खरडें 'daybook, wealth-accounting ledger'.
Thus, the symbolic ensemble is a documentation of metalwork in Indus Script Cipher.
 m290 Mohenjo-daro seal. Decipherment: kola 'tiger' Rebus; kolle 'blacksmith' kol 'working in iron' kole.l 'smithy, temple' kolimi 'smithy, forge' PLUS pattar 'trough' Rebus: pattar 'guild of goldsmiths'. panja 'feline paw' rebus: panja 'kiln, furnace'
m290 Mohenjo-daro seal. Decipherment: kola 'tiger' Rebus; kolle 'blacksmith' kol 'working in iron' kole.l 'smithy, temple' kolimi 'smithy, forge' PLUS pattar 'trough' Rebus: pattar 'guild of goldsmiths'. panja 'feline paw' rebus: panja 'kiln, furnace'khar 'ass, onager' (Kashmiri) rebus: khār खार् 'blacksmith' khāra-- basta f. ʻ blacksmith's skin bellows ʼ (Kashmiri)(CDIAL 9424)
kharkhara खर््खर । अश्वादिकण्डूयनयन्त्रम् m. a curry-comb (K.Pr. 15). -- karun -- करुन् । अश्वादिकण्डूयनकरणम् m.inf. to use a curry-comb, to curry (a horse), to groom (a horse).(Kashmiri) kharedo = a currycomb (Gujarati) rebus: kharādī ‘ turner’ (Gujarati) Rebus: daybook: karaḍā m The arrangement of bars or embossed lines (plain or fretted with little knobs) raised upon a तार of gold by pressing and driving it upon the ... 4 also खरडें n A rude sketch; a rough draught; a foul copy; a waste-book; a day-खार् 'blacksmith' (Kashmiri)
Hieroglyph: khāra 2 खार (= खार् (L.V. 96, K.Pr. 47, Śiv. 827) । द्वेषः m. (for 1, see khār 1 ), a thorn, prickle, spine (K.Pr. 47; Śiv. 827, 153)(Kashmiri) Pk. karaṁḍa -- m.n. ʻ bone shaped like a bamboo ʼ, karaṁḍuya -- n. ʻ backbone ʼ.*kaṇṭa3 ʻ backbone, podex, penis ʼ. 2. *kaṇḍa -- . 3. *karaṇḍa -- 4 . (Cf. *kāṭa -- 2 , *ḍākka -- 2 : poss. same as káṇṭa -- 1 ]1. Pa. piṭṭhi -- kaṇṭaka -- m. ʻ bone of the spine ʼ; Gy. eur. kanro m. ʻ penis ʼ (or < káṇṭaka -- ); Tir. mar -- kaṇḍḗ ʻ back (of the body) ʼ; S. kaṇḍo m. ʻ back ʼ, L. kaṇḍ f., kaṇḍā m. ʻ backbone ʼ, awāṇ. kaṇḍ, °ḍī ʻ back ʼ; P. kaṇḍ f. ʻ back, pubes ʼ; WPah. bhal. kaṇṭ f. ʻ syphilis ʼ; N. kaṇḍo ʻ buttock, rump, anus ʼ, kaṇḍeulo ʻ small of the back ʼ; B. kã̄ṭ ʻ clitoris ʼ; Or. kaṇṭi ʻ handle of a plough ʼ; H. kã̄ṭā m. ʻ spine ʼ, G. kã̄ṭɔ m., M. kã̄ṭā m.; Si. äṭa -- kaṭuva ʻ bone ʼ, piṭa -- k° ʻ backbone ʼ.2. Pk. kaṁḍa -- m. ʻ backbone ʼ.(CDIAL 2670) కరాళము karāḷamu karāḷamu. [Skt.] n. The backbone. వెన్నెముక (Telugu)
खार् । लोहकारः m. (sg. abl. khāra 1 खार ; the pl. dat. of this word is khāran 1 खारन् , which is to be distinguished from khāran 2, q.v., s.v.), a blacksmith, an iron worker (cf. bandūka-khār, p. 111b, l. 46; K.Pr. 46; H. xi, 17); a farrier (El.). This word is often a part of a name, and in such case comes at the end (W. 118) as in Wahab khār, Wahab the smith (H. ii, 12; vi, 17). khāra-basta खार -बस््त । चर्मप्रसेविका f. the skin bellows of a blacksmith. -büṭhü -ब&above;ठू&below; । लोहकारभित्तिः f. the wall of a blacksmith's furnace or hearth. -bāy-बाय् । लोहकारपत्नी f. a blacksmith's wife (Gr.Gr. 34). -dŏkuru । लोहकारायोघनः m. a blacksmith's hammer, a sledge-hammer.; । लोहकारचुल्लिः f. a blacksmith's furnace or hearth. -hāl -हाल् । लोहकारकन्दुः f. , a blacksmith's smelting furnace; cf. hāl । लोहकारकन्या f. a blacksmith's daughter. । लोहकारपुत्रः m. the son of a blacksmith, esp. a skilful son, who can work at the same profession. । लोहकारकन्या f. a blacksmith's daughter, esp. one who has the virtues and qualities properly belonging to her father's profession or caste. -më˘ʦü 1 -म्य&above;च&dotbelow;ू&below; । लोहकारमृत्तिका f. (for 2, see [khāra 3] ), 'blacksmith's earth,' i.e. iron-ore.; । लोहकारात्मजः m. a blacksmith's son. -nay -नय् । लोहकारनालिका f. (for khāranay 2, see [khārun] ), the trough into which the blacksmith allows melted iron to flow after smelting. -ʦañĕ -च्&dotbelow;ञ । लोहकारशान्ताङ्गाराः f.pl. charcoal used by blacksmiths in their furnaces. -wān वान् । लोहकारापणः m. a blacksmith's shop, a forge, smithy (K.Pr. 3). -waṭh -वठ् । आघाताधारशिला m. (sg. dat. -waṭas -वटि ), the large stone used by a blacksmith as an anvil. (Kashmiri)Rebus: khara 'sharp-edged' Kannada); pure, unalloyed (Kashmiri) khára2 ʻ hard, sharp, pungent ʼ MBh., ʻ solid ʼ Pān., ʻ hot (of wind) ʼ Suśr. [Cf. karkara -- 1 , karkaśá -- , kakkhaṭa -- ]Pa. Pk. khara -- ʻ hard, rough, cruel, sharp ʼ; K. khoru ʻ pure, genuine ʼ, S. kharo, L. P. kharā (P. also ʻ good of weather ʼ); WPah. bhad. kharo ʻ good ʼ, paṅ. cur. cam. kharā ʻ good, clean ʼ; Ku. kharo ʻ honest ʼ; N. kharo ʻ real, keen ʼ; A. khar ʻ quick, nimble ʼ, m. ʻ dry weather ʼ, kharā ʻ dry, infertile ʼ, khariba ʻ to become dry ʼ; B. kharā ʻ hot, dry ʼ, vb. ʻ to overparch ʼ; Or. kharā ʻ sunshine ʼ; OAw. khara ʻ sharp, notched ʼ; H. kharā ʻ sharp, pure, good ʼ; G. khar ʻ sharp, hot ʼ, °rũ ʻ real, good, well parched or baked, well learnt ʼ; M. khar ʻ sharp, biting, thick (of consistency) ʼ, °rā ʻ pure, good, firm ʼ; Ko. kharo ʻ true ʼ; Si. kara -- räs ʻ hot -- rayed, i.e. sun ʼ. -- Ext. Pk. kharaḍia -- ʻ rough ʼ; Or. kharaṛā ʻ slightly parched ʼ. <-> X kṣārá -- 1 : Or. khārā ʻ very sharp, pure, true ʼ. <-> X paruṣá -- 1 : Bshk. khärúṣ ʻ rough, rugged ʼ; Si. karahu ʻ hard ʼ.kharapattrā -- , kharayaṣṭikā -- , *kharasrōtas -- .Addenda: khara -- 2 : WPah.kṭg. (kc.) khɔ́rɔ ʻ great, good, excessive ʼ; J. kharā ʻ good, well ʼ; OMarw. kharaü ʻ extreme ʼ.(CDIAL 3819)
Rebus: karaḍā खरडें 'daybook, wealth-accounting ledger'.
Rebus: Ta. karaṭu roughness, unevenness, churlish temper; karaṭṭu rugged, uneven, unpolished; karaṇ uneven surface in vegetables and fruits, scar; karu prong, barb, spike; karumai, karil severity, cruelty; karukkuteeth of a saw or sickle, jagged edge of palmyra leaf-stalk, sharpness. Ma. karaṭu what is rough or uneven; kaṟu rough; kaṟuppu roughness; karuma sharpness of sword; karukku teeth of a saw or file, thorns of a palmyra branch, irregular surface; karukarukka to be harsh, sharp, rough, irritating; karikku edge of teeth; kari-muḷ hard thorn; projecting parts of the skin of custard-apples, jack-fruits, etc.; kari-maṭal rind of jack-fruits. Ko. karp keenness or harshness (of wind); ? kako·ṭ hoe with sharp, broad blade (for -ko·ṭ, see 2064). Ka. karaḍu that is rough, uneven, unpolished, hard, or waste, useless, or wicked; kaṟaku, karku, kakku, gaṟaku, garaku, garku, garasu a jag, notch, dent, toothed part of a file or saw, rough part of a millstone, irregular surface, sharpness. Tu. karaḍů, karaḍu rough, coarse, worn out; wastage, loss, wear; kargōṭa hardness, hard-heartedness; hard, hard-hearted; garu
rough; garime severity, strictness; gargāsů asaw. Te. kara sharp; karagasamu a saw; karakasa roughness; karusu rough, harsh; harsh words; kaṟaku, kaṟuku harshness, roughness, sharpness; rough, harsh, sharp; gari hardness, stiffness, sharpness; (B.) karaṭi stubborn, brutish, villainous; kakku a notch or dent, toothed part of a saw, file, or sickle, roughness of a millstone. Go. (Ma.) karkara sharp (Voc. 543). Kur. karcnā to be tough, (Hahn) be hardened. ? Cf. 1260 Ka. garasu. / Cf. Skt. karaṭa- a low, unruly, difficult person; karkara- hard, firm; karkaśa- rough, harsh, hard; krakaca-, karapattra-saw; khara- hard, harsh, rough, sharp-edged; kharu- harsh, cruel; Pali kakaca- saw; khara- rough; saw; Pkt. karakaya- saw; Apabhraṃśa (Jasaharacariu) karaḍa- hard. Cf. esp. Turner, CDIAL, no. 2819. Cf. also Skt. karavāla- sword (for second element, cf. 5376 Ta. vāḷ).(DEDR 1265)
See:
235 Harappa Indus Script tablets deciphered: भरत 'alloy of pewter, copper, tin' ready as supercargo & for turners, from 1. smithy, 2. cast metal, 3. implements furnaces (workshops) http://tinyurl.com/h45ex2j
 Dwaraka. Turbinella pyrum, s'ankha seal with सांगड [sāṅgaḍa] 'a body formed with combination of parts of animals' Rebus: sanghāḍiyo, a worker on a lathe (Gujarati). Rebus: sangar 'fortification'; jangadiyo 'military guards carrying treasure into the treasury' (Gujarati) The mercantile agents who were jangadiyo received goods on jangad 'entrusted for approval'. An ancient Near East accounting system was jangaḍ. The system of jangaḍ simply meant 'goods on approval' with the agent -- like the Meluhhan merchant-agents or brokers living in settlements in ancient near East -- merely responsible for showing the goods to the intended buyers. సంగడము (p. 1272) saṅgaḍamu sangaḍamu. [from Skt. సంగతమ్.] n. Dumb-bells, సాముచేయువారు తిప్పేలోడు. Help, assistance, aid, సహాయము. Friendship, త, స్నేహము. Meeting, చేరిక. Nearness, సమీపము. A retinue, పరిచారము. Service, సేవ. An army, సేన. "అనవుడు వాడునగుచు నీవిక్రమంబునకు నా వెరపు సంగడంబుగాదె." M. VII. iv. 59. "ఉ అంచెలుగట్టి కాలి తొడుసైచనననీవుగదమ్మప్రోదిరా, యంచలివేటి సంగడములయ్యెను." Swa. v. 72. Trouble, annoyance, ంాటము, సంకటము. సంగడమువాడు sangaḍamu-vāḍu. n. A friend or companion. చెలికాడు, నేస్తకాడు. సంగడి sangaḍi. n. A couple, pair, ంట త, ోడు. Friendship, స్నేహము. A friend, a fellow, a playmate, నేస్తకాడు. A raft or boat made of two canoes fastened side by side.
Dwaraka. Turbinella pyrum, s'ankha seal with सांगड [sāṅgaḍa] 'a body formed with combination of parts of animals' Rebus: sanghāḍiyo, a worker on a lathe (Gujarati). Rebus: sangar 'fortification'; jangadiyo 'military guards carrying treasure into the treasury' (Gujarati) The mercantile agents who were jangadiyo received goods on jangad 'entrusted for approval'. An ancient Near East accounting system was jangaḍ. The system of jangaḍ simply meant 'goods on approval' with the agent -- like the Meluhhan merchant-agents or brokers living in settlements in ancient near East -- merely responsible for showing the goods to the intended buyers. సంగడము (p. 1272) saṅgaḍamu sangaḍamu. [from Skt. సంగతమ్.] n. Dumb-bells, సాముచేయువారు తిప్పేలోడు. Help, assistance, aid, సహాయము. Friendship, త, స్నేహము. Meeting, చేరిక. Nearness, సమీపము. A retinue, పరిచారము. Service, సేవ. An army, సేన. "అనవుడు వాడునగుచు నీవిక్రమంబునకు నా వెరపు సంగడంబుగాదె." M. VII. iv. 59. "ఉ అంచెలుగట్టి కాలి తొడుసైచనననీవుగదమ్మప్రోదిరా, యంచలివేటి సంగడములయ్యెను." Swa. v. 72. Trouble, annoyance, ంాటము, సంకటము. సంగడమువాడు sangaḍamu-vāḍu. n. A friend or companion. చెలికాడు, నేస్తకాడు. సంగడి sangaḍi. n. A couple, pair, ంట త, ోడు. Friendship, స్నేహము. A friend, a fellow, a playmate, నేస్తకాడు. A raft or boat made of two canoes fastened side by side.The animal heads ligatured are:
1. markhor: Tor. miṇḍ 'ram', miṇḍā́ l 'markhor' (CDIAL 10310) mẽḍha ‘antelope,markhor’; rebus: meḍ ‘iron’ (Ho.)
2. barad, balad 'ox' Rebus: bharata 'metal alloy' (5 copper, 4 zinc and 1 tin).
3. khōṇḍa 'young bull' Rebus: kunda 'nidhi'; kō̃da कोँद 'kiln, furnace for smelting'
Annex
Harappan chimaera analysed by Dennys Frenez and Massimo Vidale
Above: Harappan chimaera and its hypertextual components.
Harappan chimera and its hypertextual components. The 'expression' summarizes the syntax of Harappan chimeras within round brackets, creatures with body parts used in their correct anatomic position (tiger, unicorn, markhor goat, elephant, zebu, and human); within square brackets, creatures with body parts used to symbolize other anatomic elements (cobra snake for tail and human arm for elephant proboscis); the elephant icon as exonent out of the square brackets symbolizes the overall elephantine contour of the chimeras; out of brackes, scorpion indicates the animal automatically perceived joining the lineate horns, the human face, and the arm-like trunk of Harappan chimeras. (After Fig. 6 in: Harappan chimaeras as 'symbolic hypertexts'. Some thoughts on Plato, Chimaera and the Indus Civilization (Dennys Frenez & Massimo Vidale, 2012) A paper by Dennys Frenez and Massimo Vidale on composite Indus creatures and their meaning: Harappa Chimaeras as 'Symbolic Hypertexts'. Some Thoughts on Plato, Chimaera and the Indus Civilization at http://a.harappa.com/content/harappan-chimaeras









 Source: Chapter Ten - Understanding Indus Seal-Carving Traditions: A Stylistic and Metric Approach
Source: Chapter Ten - Understanding Indus Seal-Carving Traditions: A Stylistic and Metric Approach









