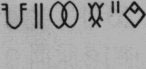Mirror: http://tinyurl.com/zh3pl7q
Jean-François Champollion (1790-1832)..."The main breakthrough in his decipherment was when he was also able to read the verb MIS related to birth, by comparing the Coptic verb for birth with the phonetic signs MS and the appearance of references to birthday celebrations in the Greek text. It was on September 14, 1822, while comparing his readings to a set of new texts from Abu Simbel that he made the realization. Running down the street to find his brother he yelled "Je tiens mon affaire!" (I've got it!) but collapsed from the excitement." (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jean-François_Champollion
loc.ci. Robinson, Andrew (2012). Cracking the Egyptian Code: The Revolutionary Life of Jean-Francois Champollion. Oxford University Press, p.142;Adkins, Lesley; Adkins, Roy (2000). The Keys of Egypt: The Obsession to Decipher Egyptian Hieroglyphs. Harper Collins Publishers, p.181.).
I remembered Jean-François Champollion's exclamation: "Je tiens mon affaire!" (I've got it!) when Prakritam gloss: kamad.ha, kamat.ha, kamad.haka,
kamad.haga, kamad.haya= a type of penance is recognized in sets of hieroglyph-multiplexes on ten inscriptions of Indus Script Corpora. These inscriptions and decipherment are presented.
Glyphs on a broken molded tablet, Ganweriwala. The reverse includes the 'rim-of-jar' glyph in a 3-glyph text. Observe shows a person seated on a stool and a kneeling adorant below.
Hieroglyph: kamadha '
kAru 'crocodile' Rebus: kAru 'artisan'.
Rebus: meD 'iron' (Mundari. Remo.)
![clip_image026]() Slide 207 Tablet with inscription. Twisted terra cotta tablet (H2000-4441/2102-464) with a mold-made inscription and narrative motif from the Trench 54 area. In the center is the depiction of what is possibly a deity with a horned headdress in so-called yogic position seated on a stool under an arch.
Slide 207 Tablet with inscription. Twisted terra cotta tablet (H2000-4441/2102-464) with a mold-made inscription and narrative motif from the Trench 54 area. In the center is the depiction of what is possibly a deity with a horned headdress in so-called yogic position seated on a stool under an arch.![]()
![clip_image006]() m0305AC
m0305AC ![clip_image008]() 2235 Pict-80: Three-faced, horned person (with a three-leaved pipal branch on the crown with two stars on either side), wearing bangles and armlets. Two stars adorn the curved buffalo horns of the seated person with a plaited pigtail. The pigtail connotes a pit furnace:
2235 Pict-80: Three-faced, horned person (with a three-leaved pipal branch on the crown with two stars on either side), wearing bangles and armlets. Two stars adorn the curved buffalo horns of the seated person with a plaited pigtail. The pigtail connotes a pit furnace:
Text on obverse of the tablet m453A: Text 1629. m453BC Seated in penance, the person is flanked on either side by a kneeling adorant, offering a pot and a hooded serpent rearing up.
Glyph: kaṇḍo ‘stool’. Rebus; kaṇḍ ‘furnace’. Vikalpa: kaṇḍ ‘stone (ore) metal’. Rebus: kamaḍha ‘penance’. Rebus 1: kaṇḍ ‘stone ore’. Rebus 2: kampaṭṭa ‘mint’. Glyph: ‘serpent hood’: paṭa. Rebus: pata ‘sharpness (of knife), tempered (metal). padm ‘tempered iron’ (Ko.) kulA 'hood of serpent' Rebus: kolle 'blacksmith'.
m453B. Scarf as pigtail of seated person.Kneeling adorant and serpent on the field.
khaṇḍiyo [cf. khaṇḍaṇī a tribute] tributary; paying a tribute to a superior king (Gujarti) Rebus 1: khaṇḍaran, khaṇḍrun ‘pit furnace’ (Santali) Rebus 2: khaNDa 'metal implements'![]() Santali glosses.
Santali glosses.
paṭa. 'serpent hood' Rebus: pata ‘sharpness (of knife), tempered (metal). padm ‘tempered iron’ (Kota) kulA 'hood of serpent' Rebus: kolle 'blacksmith'.
Jean-François Champollion (1790-1832)..."The main breakthrough in his decipherment was when he was also able to read the verb MIS related to birth, by comparing the Coptic verb for birth with the phonetic signs MS and the appearance of references to birthday celebrations in the Greek text. It was on September 14, 1822, while comparing his readings to a set of new texts from Abu Simbel that he made the realization. Running down the street to find his brother he yelled "Je tiens mon affaire!" (I've got it!) but collapsed from the excitement." (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jean-François_Champollion
loc.ci. Robinson, Andrew (2012). Cracking the Egyptian Code: The Revolutionary Life of Jean-Francois Champollion. Oxford University Press, p.142;Adkins, Lesley; Adkins, Roy (2000). The Keys of Egypt: The Obsession to Decipher Egyptian Hieroglyphs. Harper Collins Publishers, p.181.).
I remembered Jean-François Champollion's exclamation: "Je tiens mon affaire!" (I've got it!) when Prakritam gloss: kamad.ha, kamat.ha, kamad.haka,
kamad.haga, kamad.haya= a type of penance is recognized in sets of hieroglyph-multiplexes on ten inscriptions of Indus Script Corpora. These inscriptions and decipherment are presented.
(Haragovindadāsa Trikamacanda Seṭha, 1963,Prakrit-Sanskrit-Hindi dictionary, Motilal Banarsidass, Dehi,p.223)
Proto-Elamite seal impressions, Susa. Seated bulls in penance posture. (After Amiet 1980: nos. 581, 582).
Hieroglyph: kamaDha 'penance' (Prakritam) Rebus: kammaTTa 'coiner, mint'
Hieroglyph: dhanga 'mountain range' Rebus: dhangar 'blacksmith'
Hieroglyph: rango 'buffalo' Rebus: rango 'pewter'
Hieroglyph: rango 'buffalo' Rebus: rango 'pewter'
Ganweriwala tablet. Ganeriwala or Ganweriwala (Urdu: گنےریوالا Punjabi: گنیریوالا) is a Sarasvati-Sindhu civilization site in Cholistan, Punjab, Pakistan.
gumat.a, gumut.a, gumuri, gummat.a, gummut.a a copula or dome (Ka.); ghumat.a (M.); gummat.a, gummad a dome; a paper lantern; a fire-baloon (H.Te.); kummat.t.a arch, vault, arched roof, pinnacle of a pagoda; globe, lantern made of paper (Ta.)(Ka.lex.); gummaṭ m. ‘dome’ (P.) CDIAL 4217
Other glyphs (glyphemes): gúlma— m. ‘clump of trees’ VS., gumba— m. ‘cluster, thicket’ (Pali); gumma— m.n. ‘thicket’ (Pkt.); S. gūmbaṭu m. ‘bullock’s hump’; gumbaṭ m., gummaṭ f. ‘bullock’s hump’ (L.) CDIAL 4217
rebus: kumpat.i = ban:gala = an:ga_ra s’akat.i_ = a chafing dish, a portable stove, a goldsmith’s portable furnace (Te.lex.) kumpiṭu-caṭṭichafing-dish, port- able furnace, potsherd in which fire is kept by goldsmiths; kumutam oven, stove; kummaṭṭi chafing-dish (Ta.).kuppaḍige, kuppaṭe, kum- paṭe, kummaṭa, kummaṭe id. (Ka.)kumpaṭi id. (Te.) DEDR 1751. kummu smouldering ashes (Te.); kumpōḍsmoke.(Go) DEDR 1752.
Glyphs on a broken molded tablet, Ganweriwala. The reverse includes the 'rim-of-jar' glyph in a 3-glyph text. Observe shows a person seated on a stool and a kneeling adorant below.
Hieroglyph: kamadha '
Reading rebus three glyphs of text on Ganweriwala tablet: brass-worker, scribe, turner:
1. kuṭila ‘bent’; rebus: kuṭila, katthīl = bronze (8 parts copper and 2 parts tin) [cf. āra-kūṭa, ‘brass’ (Skt.) (CDIAL 3230)
2. Glyph of ‘rim of jar’: kárṇaka m. ʻ projection on the side of a vessel, handle ʼ ŚBr. [kárṇa -- ]Pa. kaṇṇaka -- ʻ having ears or corners ʼ; (CDIAL 2831) kaṇḍa kanka; Rebus: furnace account (scribe). kaṇḍ = fire-altar (Santali); kan = copper (Tamil) khanaka m. one who digs , digger , excavator Rebus: karanikamu. Clerkship: the office of a Karanam or clerk. (Telugu) káraṇa n. ʻ act, deed ʼ RV. [√kr̥1] Pa. karaṇa -- n. ʻdoingʼ; NiDoc. karana, kaṁraṁna ʻworkʼ; Pk. karaṇa -- n. ʻinstrumentʼ(CDIAL 2790)
3. khareḍo = a currycomb (G.) Rebus: kharādī ‘ turner’ (G.)
Hieroglyph: मेढा [mēḍhā] A twist or tangle arising in thread or cord, a curl or snarl (Marathi). Rebus: meḍ 'iron, copper' (Munda. Slavic) mẽṛhẽt, meD 'iron' (Mu.Ho.Santali)
meď 'copper' (Slovak)
Mohenjo-daro. Sealing. Surrounded by fishes, lizard and snakes, a horned person sits in 'yoga' on a throne with hoofed legs. One side of a triangular terracotta amulet (Md 013); surface find at Mohenjo-daro in 1936, Dept. of Eastern Art, Ashmolean Museum, Oxford. [seated person penance, crocodile?] Brief memoranda: kamaḍha ‘penance’ Rebus: kammaṭa ‘mint, coiner’; kaṇḍo ‘stool, seat’ Rebus: kāṇḍa ‘metalware’ kaṇḍa ‘fire-altar’.
Hieroglyphs (allographs):
kamaḍha 'penance' (Prakriam)
kamḍa, khamḍa 'copulation' (Santali)
kamaṭha crab (Skt.)
kamaṛkom = fig leaf (Santali.lex.) kamarmaṛā (Has.), kamaṛkom (Nag.); the petiole or stalk of a leaf (Mundari.lex.) kamat.ha = fig leaf, religiosa (Sanskrit)
kamāṭhiyo = archer; kāmaṭhum = a bow; kāmaḍ, kāmaḍum = a chip of bamboo (G.) kāmaṭhiyo a bowman; an archer (Sanskrit)
Rebus: kammaṭi a coiner (Ka.); kampaṭṭam coinage, coin, mint (Ta.) kammaṭa = mint, gold furnace (Te.) kamaṭa = portable furnace for melting precious metals (Telugu); kampaṭṭam = mint (Tamil)
Glyph: meD 'to dance' (F.)[reduplicated from me-]; me id. (M.) in Remo (Munda)(Source: D. Stampe's Munda etyma) meṭṭu to tread, trample, crush under foot, tread or place the foot upon (Te.); meṭṭu step (Ga.); mettunga steps (Ga.). maḍye to trample, tread (Malt.)(DEDR 5057) మెట్టు (p. 1027) [ meṭṭu ] meṭṭu. [Tel.] v. a. &n. To step, walk, tread. అడుగుపెట్టు, నడుచు, త్రొక్కు . "మెల్ల మెల్లన మెట్టుచుదొలగి అల్లనల్లనతలుపులండకు జేరి ." BD iv. 1523. To tread on, to trample on. To kick, to thrust with the foot.మెట్టిక meṭṭika. n. A step , మెట్టు, సోపానము (Telugu)
Harappa. Two tablets. Seated figure or deity with reed house or shrine at one side. Left: H95-2524; Right: H95-2487.
Harappa. Planoconvex molded tablet found on Mound ET. A. Reverse. a female deity battling two tigers and standing above an elephant and below a six-spoked wheel; b. Obverse. A person spearing with a barbed spear a buffalo in front of a seated horned deity wearing bangles and with a plumed headdress. The person presses his foot down the buffalo’s head. An alligator with a narrow snout is on the top register. “We have found two other broken tablets at Harappa that appear to have been made from the same mold that was used to create the scene of a deity battling two tigers and standing above an elephant. One was found in a room located on the southern slope of Mount ET in 1996 and another example comes from excavations on Mound F in the 1930s. However, the flat obverse of both of these broken tablets does not show the spearing of a buffalo, rather it depicts the more well-known scene showing a tiger looking back over its shoulder at a person sitting on the branch of a tree. Several other flat or twisted rectangular terracotta tablets found at Harappa combine these two narrative scenes of a figure strangling two tigers on one side of a tablet, and the tiger looking back over its shoulder at a figure in a tree on the other side.” [JM Kenoyer, 1998, p. 115].
m1181A![clip_image012]() 2222 Pict-80: Three-faced, horned person (with a three-leaved pipal branch on the crown), wearing bangles and armlets and seated, in a yogic posture, on a hoofed platform
2222 Pict-80: Three-faced, horned person (with a three-leaved pipal branch on the crown), wearing bangles and armlets and seated, in a yogic posture, on a hoofed platform
Mohenjo-daro. Square seal depicting a nude male deity with three faces, seated in yogic position on a throne, wearing bangles on both arms and an elaborate headdress. Five symbols of the Indus script appear on either side of the headdress which is made of two outward projecting buffalo style curved horns, with two upward projecting points. A single branch with three pipal leaves rises from the middle of the headdress.
Seven bangles are depicted on the left arm and six on the right, with the hands resting on the knees. The heels are pressed together under the groin and the feet project beyond the edge of the throne. The feet of the throne are carved with the hoof of a bovine as is seen on the bull and unicorn seals. The seal may not have been fired, but the stone is very hard. A grooved and perforated boss is present on the back of the seal.
Material: tan steatite Dimensions: 2.65 x 2.7 cm, 0.83 to 0.86 thickness Mohenjo-daro, DK 12050
Islamabad Museum, NMP 50.296 Mackay 1938: 335, pl. LXXXVII, 222
Material: tan steatite Dimensions: 2.65 x 2.7 cm, 0.83 to 0.86 thickness Mohenjo-daro, DK 12050
Islamabad Museum, NMP 50.296 Mackay 1938: 335, pl. LXXXVII, 222
Hieroglyph: kamaḍha ‘penance’ (Pkt.) Rebus 1: kampaṭṭa ‘mint’ (Ma.) kamaṭa = portable furnace for melting precious metals (Te.);Rebus 2: kaṇḍa ‘fire-altar' (Santali); kan ‘copper’ (Ta.)
Hieroglyph: karã̄ n. pl. ʻwristlets, bangles ʼ (Gujarati); kara 'hand' (Rigveda) Rebus: khAr 'blacksmith' (Kashmiri)
The bunch of twigs = ku_di_, ku_t.i_ (Skt.lex.) ku_di_ (also written as ku_t.i_ in manuscripts) occurs in the Atharvaveda (AV 5.19.12) and Kaus’ika Su_tra (Bloomsfield’s ed.n, xliv. cf. Bloomsfield, American Journal of Philology, 11, 355; 12,416; Roth, Festgruss an Bohtlingk,98) denotes it as a twig. This is identified as that of Badari_, the jujube tied to the body of the dead to efface their traces. (See Vedic Index, I, p. 177).[Note the twig adoring the head-dress of a horned, standing person]
Horned deity seals, Mohenjo-daro: a. horned deity with pipal-leaf headdress, Mohenjo-daro (DK12050, NMP 50.296) (Courtesy of the Department of Archaeology and Museums, Government of Pakistan); b. horned deity with star motifs, Mohenjo-daro (M-305) (PARPOLA 1994:Fig. 10.9); courtesy of the Archaeological Survey of India; c. horned deity surrounded by animals, Mohenjo-daro (JOSHI – PARPOLA 1987:M-304); courtesy of the Archaeological Survey of India.
Glyph: kamad.ha, kamat.ha, kamad.haka, kamad.haga, kamad.haya = a type of penance (Pkt.lex.)
kamat.amu, kammat.amu = a portable furnace for melting precious metals; kammat.i_d.u = a goldsmith, a silversmith (Te.lex.) ka~pr.aut.,kapr.aut. jeweller’s crucible made of rags and clay (Bi.); kapr.aut.i_wrapping in cloth with wet clay for firing chemicals or drugs, mud cement (H.)[cf. modern compounds: kapar.mit.t.i_ wrapping in cloth and clay (H.);kapad.lep id. (H.)](CDIAL 2874). kapar-mat.t.i clay and cowdung smeared on a crucible (N.)(CDIAL 2871).
kampat.t.tam coinage, coin (Ta.); kammat.t.am, kammit.t.am coinage, mint (Ma.); kammat.i a coiner (Ka.)(DEDR 1236) kammat.a = coinage, mint (Ka.M.) kampat.t.a-k-ku_t.am mint; kampat.t.a-k-ka_ran- coiner; kampat.t.a- mul.ai die, coining stamp (Ta.lex.)
Seated person in penance. Wears a scarf as pigtail and curved horns with embedded stars and a twig.
mēḍha The polar star. (Marathi) Rebus: meḍ ‘iron’ (Ho.) dula ‘pair’ (Kashmiri); Rebus: dul ‘cast (metal)’(Santali) ḍabe, ḍabea ‘large horns, with a sweeping upward curve, applied to buffaloes’ (Santali) Rebus: ḍab, ḍhimba, ḍhompo ‘lump (ingot?)’, clot, make a lump or clot, coagulate, fuse, melt together (Santali) kūtī = bunch of twigs (Skt.) Rebus: kuṭhi = (smelter) furnace (Santali) The narrative on this metalware catalog is thus: (smelter) furnace for iron and for fusing together cast metal. kamaḍha ‘penance’.Rebus 1: kaṇḍ ‘stone (ore) metal’.Rebus 2: kampaṭṭa‘mint’.
mēḍha The polar star. (Marathi) Rebus: meḍ ‘iron’ (Ho.) dula ‘pair’ (Kashmiri); Rebus: dul ‘cast (metal)’(Santali) ḍabe, ḍabea ‘large horns, with a sweeping upward curve, applied to buffaloes’ (Santali) Rebus: ḍab, ḍhimba, ḍhompo ‘lump (ingot?)’, clot, make a lump or clot, coagulate, fuse, melt together (Santali) kūtī = bunch of twigs (Skt.) Rebus: kuṭhi = (smelter) furnace (Santali) The narrative on this metalware catalog is thus: (smelter) furnace for iron and for fusing together cast metal. kamaḍha ‘penance’.Rebus 1: kaṇḍ ‘stone (ore) metal’.Rebus 2: kampaṭṭa‘mint’.
ṭhaṭera 'buffalo horns'. Rebus: ṭhaṭerā 'brass worker'
kamadha '
karã̄ n. pl. wristlets, banglesRebus: khAr 'blacksmith, iron worker'
rango 'buffalo' Rebus:rango 'pewter'
kari 'elephant' ibha 'elephant' Rebus: karba 'iron' ib 'iron'
kola 'tiger' Rebus: kol 'working in iron'
gaNDA 'rhinoceros' Rebus: kaNDa 'im;lements'
mlekh 'antelope, goat' Rebus: milakkha 'copper'
meD 'body' Rebus: meD 'iron''copper'
dhatu 'scarf' Rebus: dhatu 'mineral
Text on obverse of the tablet m453A: Text 1629. m453BC Seated in penance, the person is flanked on either side by a kneeling adorant, offering a pot and a hooded serpent rearing up.
Glyph: kaṇḍo ‘stool’. Rebus; kaṇḍ ‘furnace’. Vikalpa: kaṇḍ ‘stone (ore) metal’. Rebus: kamaḍha ‘penance’. Rebus 1: kaṇḍ ‘stone ore’. Rebus 2: kampaṭṭa ‘mint’. Glyph: ‘serpent hood’: paṭa. Rebus: pata ‘sharpness (of knife), tempered (metal). padm ‘tempered iron’ (Ko.) kulA 'hood of serpent' Rebus: kolle 'blacksmith'.
Glyph: rimless pot: baṭa. Rebus: bhaṭa ‘smelter, furnace’. It appears that the message of the glyphics is about a mint or metal workshop which produces sharpened, tempered iron (stone ore) using a furnace.
Rebus readings of glyphs on text of inscription:
koṇḍa bend (Ko.); Tu. Kōḍi corner; kōṇṭu angle, corner, crook. Nk. Kōnṭa corner (DEDR 2054b) G. khū̃ṭṛī f. ʻangleʼRebus: kõdā ‘to turn in a lathe’(B.) कोंद kōnda ‘engraver, lapidary setting or infixing gems’ (Marathi) koḍ ‘artisan’s workshop’ (Kuwi) koḍ = place where artisans work (G.) ācāri koṭṭya ‘smithy’ (Tu.) कोंडण [kōṇḍaṇa] f A fold or pen. (Marathi) B. kõdā ‘to turn in a lathe’; Or.kū̆nda ‘lathe’, kũdibā, kū̃d ‘to turn’ (→ Drav. Kur. Kū̃d ’ lathe’) (CDIAL 3295)
aṭar ‘a splinter’ (Ma.) aṭaruka ‘to burst, crack, sli off,fly open; aṭarcca ’ splitting, a crack’; aṭarttuka ‘to split, tear off, open (an oyster) (Ma.); aḍaruni ‘to crack’ (Tu.) (DEDR 66) Rebus: aduru ‘native, unsmelted metal’ (Kannada)
ãs = scales of fish (Santali); rebus: aya ‘metal, iron’ (Gujarati.) cf. cognate to amśu 'soma' in Rigveda: ancu 'iron' (Tocharian)
Glyph of ‘rim of jar’: kárṇaka m. ʻ projection on the side of a vessel, handle ʼ ŚBr. [kárṇa -- ]Pa. kaṇṇaka -- ʻ having ears or corners ʼ; (CDIAL 2831) kaṇḍa kanka; Rebus: furnace account (scribe). kaṇḍ = fire-altar (Santali); kan = copper (Tamil) khanaka m. one who digs , digger , excavator Rebus: karanikamu. Clerkship: the office of a Karanam or clerk. (Telugu) káraṇa n. ʻ act, deed ʼ RV. [√kr̥1] Pa. karaṇa -- n. ʻdoingʼ; NiDoc. karana, kaṁraṁna ʻworkʼ; Pk. karaṇa -- n. ʻinstrumentʼ(CDIAL 2790)
The suggested rebus readings indicate that the Indus writing served the purpose of artisans/traders to create metalware, stoneware, mineral catalogs -- products with which they carried on their life-activities in an evolving Bronze Age.
Rebus readings of glyphs on text of inscription:
koṇḍa bend (Ko.); Tu. Kōḍi corner; kōṇṭu angle, corner, crook. Nk. Kōnṭa corner (DEDR 2054b) G. khū̃ṭṛī f. ʻangleʼRebus: kõdā ‘to turn in a lathe’(B.) कोंद kōnda ‘engraver, lapidary setting or infixing gems’ (Marathi) koḍ ‘artisan’s workshop’ (Kuwi) koḍ = place where artisans work (G.) ācāri koṭṭya ‘smithy’ (Tu.) कोंडण [kōṇḍaṇa] f A fold or pen. (Marathi) B. kõdā ‘to turn in a lathe’; Or.kū̆nda ‘lathe’, kũdibā, kū̃d ‘to turn’ (→ Drav. Kur. Kū̃d ’ lathe’) (CDIAL 3295)
aṭar ‘a splinter’ (Ma.) aṭaruka ‘to burst, crack, sli off,fly open; aṭarcca ’ splitting, a crack’; aṭarttuka ‘to split, tear off, open (an oyster) (Ma.); aḍaruni ‘to crack’ (Tu.) (DEDR 66) Rebus: aduru ‘native, unsmelted metal’ (Kannada)
ãs = scales of fish (Santali); rebus: aya ‘metal, iron’ (Gujarati.) cf. cognate to amśu 'soma' in Rigveda: ancu 'iron' (Tocharian)
G.karã̄ n. pl. ‘wristlets, bangles’; S. karāī f. ’wrist’ (CDIAL 2779). Rebus: khār खार् ‘blacksmith’ (Kashmiri)
dula ‘pair’; rebus dul ‘cast (metal)’
Glyph of ‘rim of jar’: kárṇaka m. ʻ projection on the side of a vessel, handle ʼ ŚBr. [kárṇa -- ]Pa. kaṇṇaka -- ʻ having ears or corners ʼ; (CDIAL 2831) kaṇḍa kanka; Rebus: furnace account (scribe). kaṇḍ = fire-altar (Santali); kan = copper (Tamil) khanaka m. one who digs , digger , excavator Rebus: karanikamu. Clerkship: the office of a Karanam or clerk. (Telugu) káraṇa n. ʻ act, deed ʼ RV. [√kr̥1] Pa. karaṇa -- n. ʻdoingʼ; NiDoc. karana, kaṁraṁna ʻworkʼ; Pk. karaṇa -- n. ʻinstrumentʼ(CDIAL 2790)
The suggested rebus readings indicate that the Indus writing served the purpose of artisans/traders to create metalware, stoneware, mineral catalogs -- products with which they carried on their life-activities in an evolving Bronze Age.
khaṇḍiyo [cf. khaṇḍaṇī a tribute] tributary; paying a tribute to a superior king (Gujarti) Rebus 1: khaṇḍaran, khaṇḍrun ‘pit furnace’ (Santali) Rebus 2: khaNDa 'metal implements'
 Santali glosses.
Santali glosses.paṭa. 'serpent hood' Rebus: pata ‘sharpness (of knife), tempered (metal). padm ‘tempered iron’ (Kota) kulA 'hood of serpent' Rebus: kolle 'blacksmith'.
S. Kalyanaraman
Sarasvati Research Center
January 23, 2016