Toy animals made for the Pola festival especially celebrated by the Dhanoje Kunbis. (Bemrose, Colo. Derby - Russell, Robert Vane (1916). The Tribes and Castes of the Central Provinces of India: volume IV. Descriptive articles on the principal castes and tribes of the Central Provinces. London: Macmillan and Co., limited. p. 40).
Toy animals made for the Pola festival especially celebrated by the Dhanoje Kunbis. (Bemrose, Colo. Derby - Russell, Robert Vane (1916). The Tribes and Castes of the Central Provinces of India: volume IV. Descriptive articles on the principal castes and tribes of the Central Provinces. London: Macmillan and Co., limited. p. 40). Ox-drawn, Daimabad bronze chariot. c. 1500 BCE. 22X52X17.5 cm. ca. 1400 BCE
Ox-drawn, Daimabad bronze chariot. c. 1500 BCE. 22X52X17.5 cm. ca. 1400 BCEBanawali kammaṭa ayaskāṇḍa 'iron (metal) implements from mint. PLUS semantic determinant: पोळा [ pōḷā ] rebus: पोळा [ pōḷā ] 'magnetite, Fe3O4'
m1406 Hieroglyphs: thread of three stands + drummer + tumblers dhollu ‘drummer’ (Western Pahari) dolutsu 'tumble' Rebus: dul ‘cast metal’
dhAtu, dhAv 'strands of rope' Rebus: dhAtu 'mineral, metal, ore'
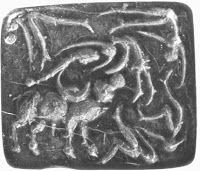
Mehrgarh. Terracotta circular button seal. (Shah, SGM & Parpola, A., 1991, Corpus of Indus Seals and Inscriptions 2: Collections in Pakistan, Helsinki: Suomalainen Tiedeakatemia, MR-17. A humped bull (water buffalo?) and abstract forms (one of which is like a human body) around the bull. The human body is tossed from the horns of the bovine.
Mokkhacika (m. or ˚ā f.) [see on attempt at etym. Morris in J.P.T.S. 1885, 49 who takes mokkha as fr. muc "tumbling"& cika="turning" fr. cak=cik. The word remains obscure, it must be a dialectical expression, distorted by popular analogy & taken perhaps from a designation of a place where these feats or toys had their origin. More probable than Morris' etym. is an analysis of the word (if it is Aryan) as mokkha= mokkha2 , in meaning "head, top," so that it may mean "head over," top -- first"& we have to separate *mokkhac -- ika the ˚ika representing ˚iya "in the manner of, like"& -- ac being the adv. of direction as contained in Sk. prāñc=pra -- añc.] tumbling, turning somersaults, an acrobatic feat; in list of forbidden amusements at D i. 6 (cp. DA i. 86; samparivattaka -- kīḷanaŋ, i. e. playing with something that rolls along, continuously turning? The foll. sentence however seems to imply turning head over heels: "ākāse vā daṇḍaŋ gahetvā bhūmiyaŋ vā sīsaŋ ṭhapetvā heṭṭh -- upariya (so read!) -- bhāvena parivattana -- kīḷanaŋ"; i. e. trapeze -- performing. Cp. Dial.i. 10 & Vin. Texts ii. 184). The list re -- occurs at Vin ii. 10 (˚āya: f.! kīḷanti); iii. 180; M i. 266≈and A v. 203 (with important v. l. mokkhaṭika, which would imply mokkha& ending tiya, and not ˚cika at all. The Cy. on this passage expls as: daṇḍakaŋ gahetvā heṭṭh -- uppariya (sic. as DA i. 86; correct to upariya?) -- bhāvena parivattana -- kīḷanaŋ). The word is found also at Vin i. 275, where the boy of a Seṭṭhi in Bārāṇasī contracts injuries to his intestines by "mokkhacikāya kīḷanto," playing (with a) m. -- According to its use with kīḷati & in instr. mokkhacikena (Nd2 219) may be either a sort of game or an instrument (toy), with which children play.
mokkhacikāya kīḷanto, mokka 'tumbling' rebus: mukha 'copper''chief'
 Impression of a steatite stamp seal (2300-1700 BCE) with a water-buffalo and acrobats. Buffalo attack or bull-leaping scene, Banawali (after UMESAO 2000:88, cat. no. 335). A figure is impaled on the horns of the buffalo; a woman acrobat wearing bangles on both arms and a long braid flowing from the head, leaps over the buffalo bull. The action narrative is presented in five frames of the acrobat getting tossed by the horns, jumping and falling down.Two Indus script glyphs are written in front of the buffalo. (ASI BNL 5683).
Impression of a steatite stamp seal (2300-1700 BCE) with a water-buffalo and acrobats. Buffalo attack or bull-leaping scene, Banawali (after UMESAO 2000:88, cat. no. 335). A figure is impaled on the horns of the buffalo; a woman acrobat wearing bangles on both arms and a long braid flowing from the head, leaps over the buffalo bull. The action narrative is presented in five frames of the acrobat getting tossed by the horns, jumping and falling down.Two Indus script glyphs are written in front of the buffalo. (ASI BNL 5683).Rebus readings of hieroglyphs: ‘1. arrow, 2. jag/notch, 3. buffalo, 4.acrobatics’:
1. kaṇḍa ‘arrow’ (Skt.) H. kãḍerā m. ʻ a caste of bow -- and arrow -- makers (CDIAL 3024). Or. kāṇḍa, kã̄ṛ ʻstalk, arrow ʼ(CDIAL 3023). ayaskāṇḍa ‘a quantity of iron, excellent iron’ (Pāṇ.gaṇ)
2. खांडा [ khāṇḍā ] m A jag, notch, or indentation (as upon the edge of a tool or weapon). (Marathi) Rebus: khāṇḍā ‘tools, pots and pans, metal-ware’.
3. rāngo ‘water buffalo bull’ (Ku.N.)(CDIAL 10559)
Rebus: rango ‘pewter’. ranga, rang pewter is an alloy of tin, lead, and antimony (anjana) (Santali).
4. ḍullu to fall off; ḍollu to roll over (DEDR 2698) Te. ḍul(u)cu, ḍulupu to cause to fall; ḍollu to fall; ḍolligillu to fall or tumble over (DEDR 2988) డొలుచు [ḍolucu] or ḍoluṭsu. [Tel.] v. n. To tumble head over heels as dancing girls do (Telugu) Rebus 1: dul ‘to cast in a mould’; dul mẽṛhẽt, dul meṛeḍ, 'cast iron'; koṭe meṛeḍ ‘forged iron’ (Santali) Bshk. ḍōl ʻ brass pot (CDIAL 6583). Rebus 2: WPah. ḍhōˋḷ m. ʻstoneʼ, ḍhòḷṭɔ m. ʻbig stone or boulderʼ, ḍhòḷṭu ʻsmall id.ʼ Him.I 87(CDIAL 5536). Rebus: K. ḍula m. ʻ rolling stoneʼ(CDIAL 6582).
Rebus: M. dhāū, dhāv m.f. ʻ a partic. soft red stone ʼ (whence dhā̆vaḍ m. ʻ a caste of iron -- smelters ʼ, dhāvḍī ʻ composed of or relating to iron ʼ); dhāˊtu n. ʻ substance ʼ RV., m. ʻ element ʼ MBh., ʻ metal, mineral, ore (esp. of a red colour) ʼ; Pk. dhāu -- m. ʻ metal, red chalk ʼ; N. dhāu ʻ ore (esp. of copper) ʼ; Or. ḍhāu ʻ red chalk, red ochre ʼ (whence ḍhāuā ʻ reddish ʼ; (CDIAL 6773) धातु primary element of the earth i.e. metal , mineral, ore (esp. a mineral of a red colour) Mn. MBh. &c element of words i.e. grammatical or verbal root or stem Nir. Pra1t. MBh. &c (with the southern Buddhists धातु means either the 6 elements [see above] Dharmas. xxv ; or the 18 elementary spheres [धातु-लोक] ib. lviii ; or the ashes of the body , relics L. [cf. -गर्भ]) (Monier-Williams. Samskritam).
मृदु mṛdu: (page 1287) A kind of iron.-कार्ष्णायसम्,-कृष्णायसम् soft-iron, lead. (Apte. Samskritam) This gloss could link with the variant lexis of Indian sprachbund with the semantics 'iron': Bj. <i>merhd</i>(Hunter) `iron'. Sa. <i>mE~R~hE~'d</i> `iron'. ! <i>mE~RhE~d</i>(M).
Origin of the gloss med 'copper' in Uralic languages may be explained by the word meD (Ho.) of Munda family of Meluhha language stream:
Sa. <i>mE~R~hE~'d</i> `iron'. ! <i>mE~RhE~d</i>(M).
Ma. <i>mErhE'd</i> `iron'.
Mu. <i>mERE'd</i> `iron'.
~ <i>mE~R~E~'d</i> `iron'. ! <i>mENhEd</i>(M).
Ho <i>meD</i> `iron'.
Bj. <i>merhd</i>(Hunter) `iron'.
KW <i>mENhEd</i>
@(V168,M080)
— Slavic glosses for 'copper'
Мед [Med]Bulgarian
Bakar Bosnian
Медзь [medz']Belarusian
Měď Czech
Bakar Croatian
KòperKashubian
Бакар [Bakar]Macedonian
Miedź Polish
Медь [Med']Russian
Meď Slovak
BakerSlovenian
Бакар [Bakar]Serbian
Мідь [mid'] Ukrainian[unquote]
Miedź, med' (Northern Slavic, Altaic) 'copper'.
One suggestion is that corruptions from the German "Schmied", "Geschmeide" = jewelry. Schmied, a smith (of tin, gold, silver, or other metal)(German) result in med ‘copper’.
Buffalo attack scenes: a. bull attack scene, circular button seal, Mehrgarh (MR-17); b. buffalo attack scene, Mohenjo-daro (M-312); c. buffalo attack or bull-leaping scene, Banawali (after UMESAO 2000:88, cat. no. 335)
ṭhaṭera 'buffalo horns'. Rebus: ṭhaṭerā 'brass worker'
meḍha 'polar star' (Marathi). Rebus: meḍ 'iron' (Ho.Mu.)
dolutsu 'tumble' Rebus: dul 'cast metal'
Jallikattu Written Arguements by Srini Kalyanaraman on Scribd