Mirror: http://tinyurl.com/hmzobq7
Goat, fin, fin of fish are recurring images of Ancient Near East and also on Indus Script Corpora. These three significant hieroglyphs relate to minwork catalogues. Variant ligatures on 'fish' hieroglyph are also explained in positional analyses describing the processes involved in working with aya 'iron' ayas 'metal'.
Steven Bonta (2010) has presented a semiologic approach on the Indus Valley Script and offers some insights: “What is beyond reasonable dispute is that the Harappan signary is a sophisticated system of signs that represent, possibly quite elliptically, the language or languages employed by the Harappans…Whatever the irretrievable details of their culture and history, the preliminary evidence from their inscriptions appears to suggest that their voice may have been Indo-Aryan.”
Michael Korvink presents a positional anaysis of 'fish' signs and highlights the ligatures to derive variants of the message conveyed by the basic glyph. Some ligatures are accents indicating 'fins' of fish read rebus as related to mintwork.
What are recorded as Sumerian SUHUR.MASH, Akk. suhurmashu/i sometimes interpreted as 'sea-goat' and kulullû fish-man may relate to two Meluhha expressions:1. mr̤ēka'goat': Ka. mēke she-goat; mē the bleating of sheep or goats. Te. mē̃ka, mēka goat. Kol. me·ke id. Nk. mēke id. Pa. mēva, (S.) mēya she-goat. Ga. (Oll.) mēge, (S.) mēge goat. Go. (M) mekā, (Ko.) mēka id. ? Kur. mēxnā (mīxyas) to call, call after loudly, hail. Malt. méqe to bleat. [Te. mr̤ēka (so correct) is of unknown meaning. Br. mēḻẖ is without etymology; see MBE 1980a.] / Cf. Skt. (lex.) meka- goat. (DEDR 5087) Rebus: milakkhu, mleccha, mlecchamukha 'copper' (Pali. Samskrtam) 2. ayo, ayu 'fish' rebus: aya 'iron' ayas 'metal' (Samskrtam) 3. kammaṭa'mint': khambhaṛā ʻfinʼ rebus: kammaṭṭam, kammiṭṭam coinage, mint Ta. kampaṭṭam coinage, coin. Ma. kammaṭṭam, kammiṭṭam coinage, mint. Ka. kammaṭa id.; kammaṭi a coiner. (DEDR 1236) Thus, the goat-fish message relates to copper, iron mintwork.
A person ligatured to a fish w/fin is ayaskara 'metalsmith' -- working in khambhaṛā ʻfinʼ rebus: kammaṭṭam, kammiṭṭam coinage, mint. కమ్మటము (p. 0247) [ kammaṭamu ] Same as కమటము . కమ్మటీడు kammaṭīḍu. [Tel.] A man of the goldsmith caste. He wears a bracelet with a safflower hieroglyph. करडी [ karaḍī ] f (See करडई) Safflower Rebus: करड [ karaḍa ] 'hard alloy'.
![A fish-apkallu drawn by A.H. Layard from a stone relief, one of a pair flanking a doorway in the Temple of Ninurta at Kalhu. British Museum.
Reproduced in Schlomo Izre'el, Adapa and the South Wind: Language Has the Power of Life and Death, Eisenbrauns, 2001.
https://books.google.co.th/books?id=MbwwROVGl7UC&pg=PA3&source=gbs_selected_pages&cad=3#v=onepage&q&f=false]() A fish-apkallu drawn by AH Layard from a stone relief, one of a pair flanking a doorway in the Temple of Ninurta at Kalhu. British Museum. Reproduced in Schlomo Izre'el, Adpa and the South Wind, Language has the power of life and death, Eisenbrauns, 2001.
A fish-apkallu drawn by AH Layard from a stone relief, one of a pair flanking a doorway in the Temple of Ninurta at Kalhu. British Museum. Reproduced in Schlomo Izre'el, Adpa and the South Wind, Language has the power of life and death, Eisenbrauns, 2001.
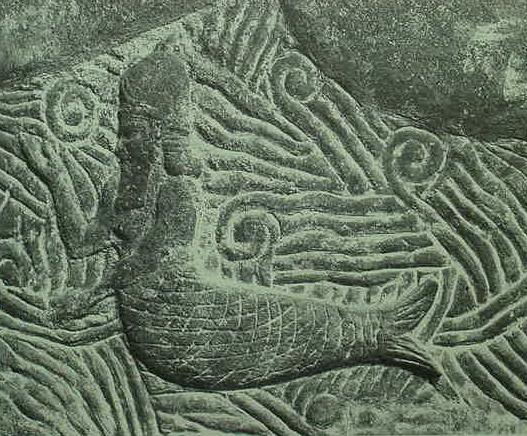
Below, a fish-man in a sea from a bas-relief in the palace of the Assyrian king Sargon II, ca. 721-705 BCE at Dur-Sharken, modern Khorsabad. (p. 131. fig. 107. "merman and mermaid." Jeremy Black and Anthony Green. Gods, Demons and Symbols of Ancient Mesopotamia, An Illustrated Dictionary. London, British Museum, in association with the University of Texas Press. Austin. 1992. ISBn 0-292-70794-0. paperback)![]()
Below, sun-dried clay figures. Upper: a goat-fish (Greek: Capricorn) emblem of the god Enki (Ea) of Eridu. Lower: a fishman. Placed in a building to ward off evil in the Assyrian period (p. 92. figure 70. "goat-fish." Jeremy Black and Anthony Green. Gods, Demons and Symbols of Ancient Mesopotamia, An Illustrated Dictionary. London, British Museum, in association with the University of Texas Press. Austin. 1992. ISBn 0-292-70794-0. paperback). Note: I understand that Ea (Enki) who gave his servant Adapa wisdom or knowledge but denied him immortality has been recast as Yahweh in the Garden of Eden. Please click here for the details.![]()
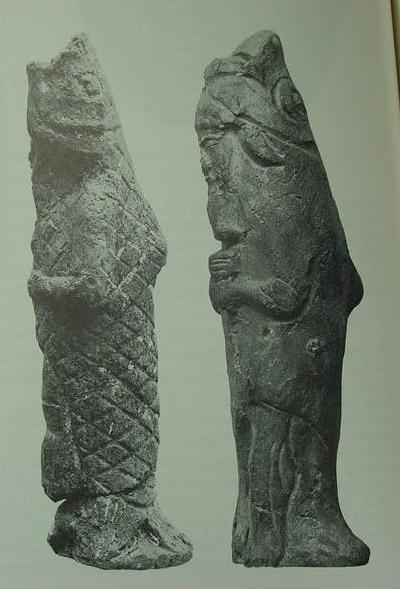
Below, fish-men figurines, the so-called "seven sages"
(apkallu), sun-dried clay, from the foundations of a priest's house in Asshur ca. 721-705 BCE (p. 18. Jeremy Black and Anthony Green.Gods, Demons and Symbols of Ancient Mesopotamia, An Illustrated Dictionary. London, British Museum, in association with the University of Texas Press. Austin. 1992. ISBN 0-292-70794-0. paperback).
![]()
Below, p. 131. fig. 108. "merman and mermaid." Jeremy Black and Anthony Green. Gods, Demons and Symbols of Ancient Mesopotamia, An Illustrated Dictionary. London, British Museum, in association with the University of Texas Press. Austin. 1992. ISBN 0-292-70794-0. paperback).
![]()
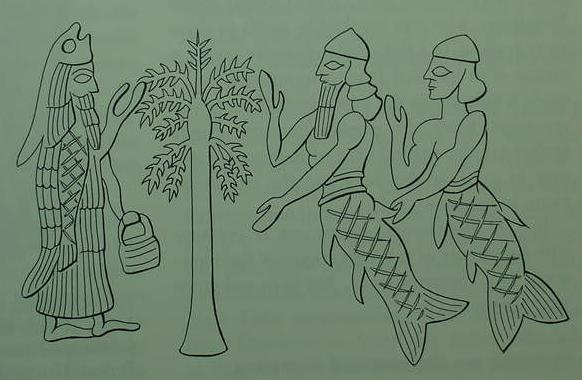
Below, a cylinder seal showing "fishmen" holding pine cones (?) and pollen-buckets (?), adoring a sacred tree. Above the tree is the sun-god with eagle wings and tail (perhaps Utu, Shamash or Asshur?). This tree appears in other Neo-Assyrian art forms as a highly stylized Date-palm with a vine lattice and leaves, sometimes bearing fruits such as grapes (?). To this day, Arabs in Lower Mesopotamia drape grapevines about Date-palms in their gardens. Could the Neo-Assyrian highly stylized grapevine tendril motif associated with the Date-palm be what is represented in this art form? In the Epic of Gilgamesh, a plant of rejuvenation lies at the bottom of the sea, could this be the plant the Fishmen are adoring? Or are they adoring the Mesu tree or Kiskanu tree at Eridu where Adapa and the apkallu served? (For the below picture cf. p. 15. figure 7. "Fish Gods at the Tree pf Life; Assyria, c. 700 BC." Joseph Campbell. The Masks of God: Creative Mythology. New York. Viking Penguin. 1968. Reprinted 1976)
kuTi 'tree' rebus: kuThi 'smelter'.
![]() Below, sun-dried clay figures. Upper: a goat-fish (Greek: Capricorn) emblem of the god Enki (Ea) of Eridu. Lower: a fishman. Placed in a building to ward off evil in the Assyrian period (p. 92. figure 70. "goat-fish." Jeremy Black and Anthony Green. Gods, Demons and Symbols of Ancient Mesopotamia, An Illustrated Dictionary. London, British Museum, in association with the University of Texas Press. Austin. 1992. ISBn 0-292-70794-0. paperback). Note: I understand that Ea (Enki) who gave his servant Adapa wisdom or knowledge but denied him immortality has been recast as Yahweh in the Garden of Eden. Please click here for the details.
Below, sun-dried clay figures. Upper: a goat-fish (Greek: Capricorn) emblem of the god Enki (Ea) of Eridu. Lower: a fishman. Placed in a building to ward off evil in the Assyrian period (p. 92. figure 70. "goat-fish." Jeremy Black and Anthony Green. Gods, Demons and Symbols of Ancient Mesopotamia, An Illustrated Dictionary. London, British Museum, in association with the University of Texas Press. Austin. 1992. ISBn 0-292-70794-0. paperback). Note: I understand that Ea (Enki) who gave his servant Adapa wisdom or knowledge but denied him immortality has been recast as Yahweh in the Garden of Eden. Please click here for the details.


Below, fish-men figurines, the so-called "seven sages"
(apkallu), sun-dried clay, from the foundations of a priest's house in Asshur ca. 721-705 BCE (p. 18. Jeremy Black and Anthony Green.Gods, Demons and Symbols of Ancient Mesopotamia, An Illustrated Dictionary. London, British Museum, in association with the University of Texas Press. Austin. 1992. ISBN 0-292-70794-0. paperback).

Below, p. 131. fig. 108. "merman and mermaid." Jeremy Black and Anthony Green. Gods, Demons and Symbols of Ancient Mesopotamia, An Illustrated Dictionary. London, British Museum, in association with the University of Texas Press. Austin. 1992. ISBN 0-292-70794-0. paperback).
Below, a cylinder seal showing "fishmen" holding pine cones (?) and pollen-buckets (?), adoring a sacred tree. Above the tree is the sun-god with eagle wings and tail (perhaps Utu, Shamash or Asshur?). This tree appears in other Neo-Assyrian art forms as a highly stylized Date-palm with a vine lattice and leaves, sometimes bearing fruits such as grapes (?). To this day, Arabs in Lower Mesopotamia drape grapevines about Date-palms in their gardens. Could the Neo-Assyrian highly stylized grapevine tendril motif associated with the Date-palm be what is represented in this art form? In the Epic of Gilgamesh, a plant of rejuvenation lies at the bottom of the sea, could this be the plant the Fishmen are adoring? Or are they adoring the Mesu tree or Kiskanu tree at Eridu where Adapa and the apkallu served? (For the below picture cf. p. 15. figure 7. "Fish Gods at the Tree pf Life; Assyria, c. 700 BC." Joseph Campbell. The Masks of God: Creative Mythology. New York. Viking Penguin. 1968. Reprinted 1976)
kuTi 'tree' rebus: kuThi 'smelter'.
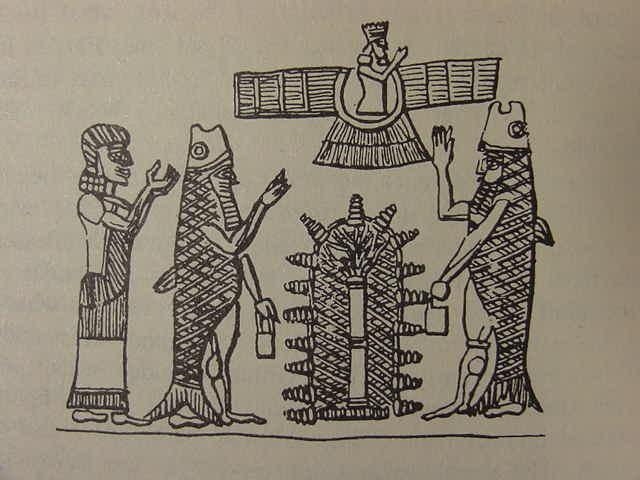 Below, sun-dried clay figures. Upper: a goat-fish (Greek: Capricorn) emblem of the god Enki (Ea) of Eridu. Lower: a fishman. Placed in a building to ward off evil in the Assyrian period (p. 92. figure 70. "goat-fish." Jeremy Black and Anthony Green. Gods, Demons and Symbols of Ancient Mesopotamia, An Illustrated Dictionary. London, British Museum, in association with the University of Texas Press. Austin. 1992. ISBn 0-292-70794-0. paperback). Note: I understand that Ea (Enki) who gave his servant Adapa wisdom or knowledge but denied him immortality has been recast as Yahweh in the Garden of Eden. Please click here for the details.
Below, sun-dried clay figures. Upper: a goat-fish (Greek: Capricorn) emblem of the god Enki (Ea) of Eridu. Lower: a fishman. Placed in a building to ward off evil in the Assyrian period (p. 92. figure 70. "goat-fish." Jeremy Black and Anthony Green. Gods, Demons and Symbols of Ancient Mesopotamia, An Illustrated Dictionary. London, British Museum, in association with the University of Texas Press. Austin. 1992. ISBn 0-292-70794-0. paperback). Note: I understand that Ea (Enki) who gave his servant Adapa wisdom or knowledge but denied him immortality has been recast as Yahweh in the Garden of Eden. Please click here for the details.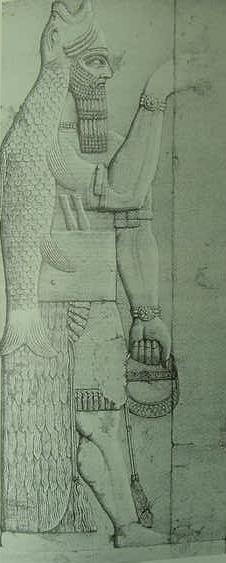 Fish-garbed priest bas-relief on temple of the god Ninurta (Saturn) at Kalhu (biblical Calah), ca. 883-859 BCE Assurnasirpal II (p. 83. fig. 65.) Fish-men figurines, the so-called "seven sages" (apkallu), sun-dried clay, from the foundations of a priest's house in Asshur ca. 721-705 BCE (p. 18.) Fish-man in a sea from a bas-relief in the palace of the Assyrian king Sargon II, ca. 721-705 BCE at Dur-Sharken, modern Khorsabad. (p. 131. fig. 107. "merman and mermaid." Jeremy Black and Anthony Green. Gods, Demons and Symbols of Ancient Mesopotamia, An Illustrated Dictionary. London, British Museum, in association with the University of Texas Press. Austin. 1992.
Fish-garbed priest bas-relief on temple of the god Ninurta (Saturn) at Kalhu (biblical Calah), ca. 883-859 BCE Assurnasirpal II (p. 83. fig. 65.) Fish-men figurines, the so-called "seven sages" (apkallu), sun-dried clay, from the foundations of a priest's house in Asshur ca. 721-705 BCE (p. 18.) Fish-man in a sea from a bas-relief in the palace of the Assyrian king Sargon II, ca. 721-705 BCE at Dur-Sharken, modern Khorsabad. (p. 131. fig. 107. "merman and mermaid." Jeremy Black and Anthony Green. Gods, Demons and Symbols of Ancient Mesopotamia, An Illustrated Dictionary. London, British Museum, in association with the University of Texas Press. Austin. 1992.Reading of Text 1401: karaNika 'rim of jar' rebus: karNi 'supercargo' bhaTa 'warrior' rebus: bhaTa 'furnace' goTa 'round' rebus: khoTa 'ingot' PLUS kolom 'rice plant' rebus: kolami 'smithy, forge' tutha 'goad' rebus: tutha 'pewter' PLUS kolom 'three' rebus: kolami 'smithy, forge' khambhaṛā ʻfinʼ rebus: kammaṭṭam, kammiṭṭam coinage, mint PLUS ayo 'fish' rebus: aya 'iron' ayas 'metal'.
Last three hieroglyphs as a distinct string: tutha 'goad' rebus: tutha 'pewter' PLUS kolom 'three' rebus: kolami 'smithy, forge' khaNDa 'notch' rebus: khaNDa 'implements' arA 'spoke' rebus: Ara 'brass' eraka 'nave of wheel' rebus: eraka 'moltencast, copper'.
 See m1429C
See m1429COn many sculptural friezes of Ancient Near East, a 'fin' is also signified by the short linear stroke at the fish-tail, the word signified is khambhaṛā ʻfinʼ (Lahnda Punjabi)(CDIAL 13640) rebus: kammaṭṭam, kammiṭṭam coinage, mint. (Malayalam)(DEDR 1236). Crocodile hieroglyph: kharA 'crocodie' rebus: khara 'blacksmith'. Thus, togethr ayaskara'metalsmith'. This is a Pali expression.
A person ligatured to a fish PLUS fins is ayaskara 'metalsmith'.
Also attested in Panini: अयस्--कार [p= 85,1]m. id. Pa1n2. 2-4 , 10 Sch. and viii , 3 , 46 Sch.अयस्--काम [p= 85,1] m. a blacksmith Pa1n2. 8-3 , 46 Sch.अयस् [p= 85,1]n. iron , metal RV. &can iron weapon (as an axe , &c ) RV. vi , 3 ,5 and 47 , 10 gold Naigh.steel L. ; ([cf. Lat. aes , aer-is for as-is ; Goth. ais , Thema aisa ; Old Germ. e7r , iron ; Goth. eisarn ; Mod. Germ. Eisen.]) See: aya 'iron' (Gujarati)
Munda etyma related to ayo, ayu:
beḍa hako (ayo) ‘fish’ (Santali); beḍa ‘either of the sides of a hearth’ (G.) Munda: So. ayo `fish'. Go. ayu `fish'. Go <ayu> (Z), <ayu?u> (Z),, <ayu?> (A) {N} ``^fish''. Kh. kaDOG `fish'. Sa. Hako `fish'. Mu. hai (H) ~ haku(N) ~ haikO(M) `fish'. Ho haku `fish'. Bj. hai `fish'. Bh.haku `fish'. KW haiku ~ hakO |Analyzed hai-kO, ha-kO (RDM). Ku. Kaku`fish'.@(V064,M106) Mu. ha-i, haku `fish' (HJP). @(V341) ayu>(Z), <ayu?u> (Z) <ayu?>(A) {N} ``^fish''. #1370. <yO>\\<AyO>(L) {N} ``^fish''. #3612. <kukkulEyO>,,<kukkuli-yO>(LMD) {N} ``prawn''. !Serango dialect. #32612. <sArjAjyO>,,<sArjAj>(D) {N} ``prawn''. #32622. <magur-yO>(ZL) {N} ``a kind of ^fish''. *Or.<>. #32632. <ur+GOl-Da-yO>(LL) {N} ``a kind of ^fish''. #32642.<bal.bal-yO>(DL) {N} ``smoked fish''. #15163.
Vikalpa: Munda: <aDara>(L) {N} ``^scales of a fish, sharp bark of a tree''.#10171. So<aDara>(L) {N} ``^scales of a fish, sharp bark of a tree''.
khambhaṛā ʻfinʼ rebus: kammaṭṭam, kammiṭṭam coinage, mint.
Indian mackerel Ta. ayirai, acarai, acalai loach, sandy colour, Cobitis thermalis; ayilai a kind of fish. Ma.ayala a fish, mackerel, scomber; aila, ayila a fish; ayira a kind of small fish, loach (DEDR 191) aduru native metal (Ka.); ayil iron (Ta.) ayir, ayiram any ore (Ma.); ajirda karba very hard iron (Tu.)(DEDR 192). Ta. ayil javelin, lance, surgical knife, lancet.Ma. ayil javelin, lance; ayiri surgical knife, lancet. (DEDR 193). aduru = gan.iyinda tegadu karagade iruva aduru = ore taken from the mine and not subjected to melting in a furnace (Ka. Siddhānti Subrahmaṇya’ Śastri’s new interpretation of the AmarakoŚa, Bangalore, Vicaradarpana Press, 1872, p.330); adar = fine sand (Ta.); ayir – iron dust, any ore (Ma.) Kur. adar the waste of pounded rice, broken grains, etc. Malt. adru broken grain (DEDR 134). Ma. aśu thin, slender;ayir, ayiram iron dust.Ta. ayir subtlety, fineness, fine sand, candied sugar; ? atar fine sand, dust. அய.ர³ ayir, n. 1. Subtlety, fineness; நணசம. (த_வ_.) 2. [M. ayir.] Fine sand; நணமணல. (மலசலப. 92.) ayiram, n. Candied sugar; ayil, n. cf. ayas. 1. Iron; 2. Surgical knife, lancet; Javelin, lance; ayilavaṉ, Skanda, as bearing a javelin (DEDR 341).Tu. gadarů a lump (DEDR 1196)
Fish ligatured to a crocodile. Mohenjodaro tablet. Decoding of the two Indus Script glyphs of fish and crocodile read rebus:
fish fins khambhaṛā 'fin' rebus: kammaTa 'mint'
Ayo ‘fish’ (Mu.) aya = iron (G.);
ayah, ayas = metal (Skt.)
kāru a wild crocodile or alligator (Te.) ghariyal id. (H.)
khār a blacksmith, an iron worker (Kashmiri)
ayakāra ‘iron-smith’ (Pali)
While the goat-fish enters into myths of Sumer and later Assyrian traditions, the hieroglyphs of goat and fish on Indus script have been decoded in the context of metallurgy [metal (milakkhu, 'copper'(Pali)and cast metal -- ayas, perhaps bronze].
The emphatic depiction of fish ligatured with a crocodile on Indus Script (on a Mohenjodaro tablet) is decoded asayakara 'metalsmith' (aya 'fish'; kara 'crocodile' of the underlying Meluhha (Mleccha) lexemes of Indian linguistic area).
[Anthony Green, A Note on the Assyrian "Goat-Fish", "Fish-Man" and "Fish-Woman", Iraq, Vol. 48 (1986), pp. 25-30; After Plate X, b, on seal. BM 119918. 2.5X2.5X2.5cm. Late Babylonian stamp seal depicting kulullu and kuliltu(?); streams flow from a vase at top left;top centre, a crescent. Previously published: Van Buren 1933: Pl. XX:70, p. 116, with earlier references cited in n.3, to which may be added Munter 1827: Tab. II:18, p. 139. Cf. also Unger 1957: 71, Nr. 2; Unger 1966.)
In Fig. 1 in the following embedded document, a pair of goat-fish images appear, flanking a door entrance, on a Middle Assyrian seal. Sumerian SUHUR.MASH, Akk. suhurmashu/i is sometimes interpreted as 'sea-goat'.
A Note on the Assyrian “Goat-Fish”, “Fish-Man” and “Fish-Woman”
Anthony Green
In their recent edition of inscribed material from Fort Shalmaneser at Nimrud, Dalley and Postgate (1984: No. 95, pp. 159 ff., Pl. 22) have published and discussed a text recording the measurements, apparently in preparation for their covering in gold leaf, of statues for a temple of Nabu, probably the Nabu Temple at Kalḫu itself. As extant, “face B” begins with the dimensions for the statue or statues of the uridimmu (UR.ID[IM?]), which is probably to be identified as an upright figure with human head, arms and torso but the lower body and legs of lion, a type known in the Assyrian period on the palace reliefs and among the apotropaic foundation figurines (Wiggermann, in press: § VII C 5; cf. Green 1985: 77, with Fig. 1 and Pls. XIIIb, XIVa, b).
The next section (ll. 10 ff.) concerns statues of the suḫurmāšu, or “Goat-fish” (literally “Carp-goat”), and kulullû, “Fish-man”. As Dr. Dalley points out, these creatures are known among the apotropaic figurines and named in the appropriate rituals (Dalley and Postgate 1984: 162, n. to ll. 15–19; citing Rittig 1977 for the figurines). An example of the Goat-fish omitted from Rittig's catalogue is shown on Plate V; its inscription (er-ba taš-mu u ma-ga-rù), corresponding to the form prescribed in KAR, no. 298, rev. line 5 (Gurney 1935: 70 f.; Rittig 1977: 157, 167) proves the identity as the suḫurmāšu(cf. Rittig 1977: 188 f., § Ib.2; 206; Green 1983: 93, n. 54; Wiggermann, in press: § VII C 10 b). The mention of statues of the type in the Nimrud text is a significant testimony to their original presence in the repertoire of Assyrian monumental art, for which no examples are now known (notice their absence in the review by Kolbe 1981), although an example is to be found on one face of a ninth(?)-century smaller-scale stone altar from Nineveh (Plate VIa), and statues of the creature appear to be depicted on a Middle Assyrian (Fig. 1 ) and post-Assyrian (Plate Xc) seals. This fact further supports the apparent identical, or at least very close, repertoires of apotropaic figures as foundation figurines and in monumental sculpture (Green 1983).
 Example of water-carrier hieroglyph as Indus script. Seal impression, Ur (Upenn; U.16747) Seal impression, Ur (Upenn; U.16747); dia. 2.6, ht. 0.9 cm.; Gadd, PBA 18 (1932), pp. 11-12, pl. II, no. 12; Porada 1971: pl.9, fig.5; Parpola, 1994, p. 183; water carrier with a skin (or pot?) hung on each end of the yoke across his shoulders and another one below the crook of his left arm; the vessel on the right end of his yoke is over a receptacle for the water; a star on either side of the head (denoting supernatural?). The whole object is enclosed by 'parenthesis' marks. The parenthesis is perhaps a way of splitting of the ellipse (Hunter, G.R., JRAS, 1932, 476). An unmistakable example of an 'hieroglyphic' seal.
Example of water-carrier hieroglyph as Indus script. Seal impression, Ur (Upenn; U.16747) Seal impression, Ur (Upenn; U.16747); dia. 2.6, ht. 0.9 cm.; Gadd, PBA 18 (1932), pp. 11-12, pl. II, no. 12; Porada 1971: pl.9, fig.5; Parpola, 1994, p. 183; water carrier with a skin (or pot?) hung on each end of the yoke across his shoulders and another one below the crook of his left arm; the vessel on the right end of his yoke is over a receptacle for the water; a star on either side of the head (denoting supernatural?). The whole object is enclosed by 'parenthesis' marks. The parenthesis is perhaps a way of splitting of the ellipse (Hunter, G.R., JRAS, 1932, 476). An unmistakable example of an 'hieroglyphic' seal.The inscription on the Ur circular seal is deciphered goṭa dul meḍ kuṭhi 'laterite, iron (cast metal), tin smelter furnace'. [kuṭhi 'smelter' furnace for iron/ kuṭila, 'tin (bronze)metal; kuṭila, katthīl = bronze (8 parts copper and 2 parts tin) [cf. āra-kūṭa, ‘brass’ (Samskritam)]
kuṭi ‘water-carrier’ (Telugu); Rebus: kuṭhi ‘smelter furnace’ (Santali) kuṛī f. ‘fireplace’ (H.); krvṛI f. ‘granary (WPah.); kuṛī, kuṛo house, building’(Ku.)(CDIAL 3232) kuṭi ‘hut made of boughs’ (Skt.) guḍi temple (Telugu) मेढ (p. 662) [ mēḍha ] 'polar' star' Rebus: mẽṛhẽt, meḍ 'iron' (Ho.Munda)
kuṭi 'womanwater-carrier' (Telugu) kuṭhi ‘smelter furnace’ (Santali)] A pair of hieroglyphs flank the head of the water-carrier. It is read as the polar star मेढ [mēḍha](Marathi) Rebus: meḍ ‘iron’ (Ho.) dula ‘pair’ (Kashmiri); rebus: dul ‘cast (metal)’(Santali)
kuṭhi 'smelter, furnace for iron' (Santali) kūṭa कूट -पालकः a potter; a potter's kiln. (Samskritam) कुटिलिका A blacksmith's forge. (Samskritam) कुटिलक [p= 288,2] f. a tool used by a blacksmith Pa1n2. 4-4 , 18 Ka1s3.कुटी a hut , cottage , house , hall , shop MBh. R. &c kut.hi, kut.i (Or.; Sad. kot.hi) (1) the smelting furnace of the blacksmith; kut.ire bica duljad.ko talkena, they were feeding the furnace with ore; (2) the name of e_kut.i has been given to the fire which, in lac factories, warms the water bath for softening the lac so that it can be spread into sheets; to make a smelting furnace; kut.hi-o of a smelting furnace, to be made; the smelting furnace of the blacksmith is made of mud, cone-shaped, 2’ 6” dia. At the base and 1’ 6” at the top. The hole in the centre, into which the mixture of charcoal and iron ore is poured, is about 6” to 7” in dia. At the base it has two holes, a smaller one into which the nozzle of the bellow is inserted, as seen in fig. 1, and a larger one on the opposite side through which the molten iron flows out into a cavity (Mundari)
měď (copper)(Czech) mіdʹ (copper, cuprum, orichalc)(Ukrainian) medʹ (copper, cuprum, Cu), mednyy (copper, cupreous, brassy, brazen, brass), omednyatʹ (copper, coppering), sulʹfatmedi (Copper), politseyskiy (policeman, constable, peeler, policemen, redcap), pokryvatʹ medʹyu (copper), payalʹnik (soldering iron, copper, soldering pen, soldering-iron), mednyy kotel (copper), medno-krasnyy (copper), mednaya moneta (copper). медь (copper, cuprum, Cu), медный (copper, cupreous, brassy, brazen, brass), омеднять (copper, coppering), Сульфатмеди (Copper), полицейский (policeman, constable, peeler, policemen, redcap), покрывать медью (copper), паяльник (soldering iron, copper, soldering pen, soldering-iron), медный котел (copper), медно-красный (copper), медная монета (copper).(Russian)

meḍho a ram, a sheep (G.)(CDIAL 10120) Rebus: mẽṛhẽt, meḍ ‘iron’ (Mu.Ho.) mūhā mẽṛhẽt = iron smelted by the Kolhes and formed into an equilateral lump a little pointed at each of four ends (Santali) meṛha, meḍhi ‘merchant’s clerk; (Gujarati)
Sign 15 occurs togethe with a notch-in-fixed fish hieroglyph on Harappa 73 seal:![]() Harappa seal (H-73)[Note: the hieroglyph ‘water carrier’ pictorial of Ur Seal Impression becomes a hieroglyph sign] Hieroglyph: fish + notch: aya 'fish' + khāṇḍā m A jag, notch Rebus: aya 'metal'+ khāṇḍā ‘tools, pots and pans, metal-ware’. kuṭi 'water-carrier' Rebus: kuṭhi 'smelter'. खोंड (p. 216) [khōṇḍa] m A young bull, a bullcalf; खोंडा [ khōṇḍā ] m A
Harappa seal (H-73)[Note: the hieroglyph ‘water carrier’ pictorial of Ur Seal Impression becomes a hieroglyph sign] Hieroglyph: fish + notch: aya 'fish' + khāṇḍā m A jag, notch Rebus: aya 'metal'+ khāṇḍā ‘tools, pots and pans, metal-ware’. kuṭi 'water-carrier' Rebus: kuṭhi 'smelter'. खोंड (p. 216) [khōṇḍa] m A young bull, a bullcalf; खोंडा [ khōṇḍā ] m A कांबळा of which one end is formed into a cowl or hood. खोंडरूं [ khōṇḍarūṃ ] n A contemptuous form of खोंडा in the sense of कांबळा -cowl (Marathi); kōḍe dūḍabull calf (Telugu); kōṛe 'young bullock' (Konda) rebus: kõdā ‘to turn in a lathe’ (Bengali) [The characteristic pannier which is ligatured to the young bull pictorial hieroglyph is a synonym खोंडा 'cowl' or 'pannier').खोंडी [ khōṇḍī ] f An outspread shovelform sack (as formed temporarily out of a कांबळा , to hold or fend off grain, chaff &c.) ] खोंड (p. 216) [ khōṇḍa ] m A young bull, a bullcalf.(Marathi) खोंडरूं [ khōṇḍarūṃ ] n A contemptuous form of खोंडा in the sense of कांबळा -cowl.खोंडा [ khōṇḍā ] m A कांबळा of which one end is formed into a cowl or hood. खोंडी [ khōṇḍī ] f An outspread shovelform sack (as formed temporarily out of a कांबळा , to hold or fend off grain, chaff &c.)
 Harappa seal (H-73)[Note: the hieroglyph ‘water carrier’ pictorial of Ur Seal Impression becomes a hieroglyph sign] Hieroglyph: fish + notch: aya 'fish' + khāṇḍā m A jag, notch Rebus: aya 'metal'+ khāṇḍā ‘tools, pots and pans, metal-ware’. kuṭi 'water-carrier' Rebus: kuṭhi 'smelter'. खोंड (p. 216) [khōṇḍa] m A young bull, a bullcalf; खोंडा [ khōṇḍā ] m A
Harappa seal (H-73)[Note: the hieroglyph ‘water carrier’ pictorial of Ur Seal Impression becomes a hieroglyph sign] Hieroglyph: fish + notch: aya 'fish' + khāṇḍā m A jag, notch Rebus: aya 'metal'+ khāṇḍā ‘tools, pots and pans, metal-ware’. kuṭi 'water-carrier' Rebus: kuṭhi 'smelter'. खोंड (p. 216) [khōṇḍa] m A young bull, a bullcalf; खोंडा [ khōṇḍā ] m A Hieroglyph: kōḍ 'horn' Rebus: kōḍ 'place where artisans work, workshop' কুঁদন, কোঁদন [ kun̐dana, kōn̐dana ] n act of turning (a thing) on a lathe; act of carving (Bengali) कातारी or कांतारी (p. 154) [ kātārī or kāntārī ] m (कातणें ) A turner.(Marathi)
Rebus: खोदकाम [ khōdakāma ] n Sculpture; carved work or work for the carver.
खोदगिरी [ khōdagirī ] f Sculpture, carving, engraving: also sculptured or carved work.खोदणें [ khōdaṇēṃ ] v c & i (खोदणें Dug. 2 Engraved, carved, sculptured. http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2015/04/excavations-at-dholavifra-1989-2005-rs.html
The intimations of a metals turner as a scribe are also gleaned from the gloss: खोडाखोड or डी [ khōḍākhōḍa or ḍī ] f (खोडणें ) Erasing, altering, interlining &c. in numerous places: also the scratched, scrawled, and disfigured state of the paper so operated upon; खोडींव [ khōḍīṃva ] p of खोडणें v c Erased or crossed out.Marathi). खोडपत्र [ khōḍapatra ] n Commonly खोटपत्र .खोटपत्र [ khōṭapatra ] n In law or in caste-adjudication. A written acknowledgment taken from an offender of his falseness or guilt: also, in disputations, from the person confuted. (Marathi) Thus, khond 'turner' is also an engraver, scribe.
That a metals turner is engaged in metal alloying is evident from the gloss: खोट [ khōṭa ] f A mass of metal (unwrought or of old metal melted down); an ingot or wedge. Hence 2 A lump or solid bit (as of phlegm, gore, curds, inspissated milk); any concretion or clot.खोटीचा Composed or made of खोट , as खोटीचें भांडें .
See: http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2015/03/x.html
The intimations of a metals turner as a scribe are also gleaned from the gloss: खोडाखोड or डी [ khōḍākhōḍa or ḍī ] f (
That a metals turner is engaged in metal alloying is evident from the gloss: खोट [ khōṭa ] f A mass of metal (unwrought or of old metal melted down); an ingot or wedge. Hence 2 A lump or solid bit (as of phlegm, gore, curds, inspissated milk); any concretion or clot.
See: http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2015/03/x.html
'Based on cuneiform documents from Mesopotamia we know that there was at least one Meluhhan village in Akkad at that time, with people called 'Son of Meluhha' living there. The cuneiform inscription (ca. 2020 BCE) says that the cylinder seal belonged to Shu-ilishu, who was a translator of the Meluhhan language. "The presence in Akkad of a translator of the Meluhhan language suggests that he may have been literate and could read the undeciphered Indus script. This in turn suggests that there may be bilingual Akkadian/Meluhhan tablets somewhere in Mesopotamia. Although such documents may not exist, Shu-ilishu's cylinder seal offers a glimmer of hope for the future in unraveling the mystery of the Indus script." (Gregory L. Possehl,Shu-ilishu's cylinder seal, Expedition, Vol. 48, Number 1, pp. 42-43).http://www.penn.museum/documents/publications/expedition/PDFs/48-1/What%20in%20the%20World.pdf
Shu-ilishu's cylinder seal. Department des Antiquites Orienteles, Musee du Louvre, Paris.
Kannada. mēke she-goat; mē the bleating of sheep or goats. Te. mē̃ka, mēka goat. Kol. me·ke id. Nk. mēke id. Pa. mēva, (S.) mēya she-goat. Ga. (Oll.) mēge, (S.) mēge goat. Go. (M) mekā, (Ko.) mēka id. ? Kur. mēxnā (mīxyas) to call, call after loudly, hail. Malt. méqe to bleat. [Te. mr̤ēka (so correct) is of unknown meaning. Br. mēḻẖ is without etymology; see MBE 1980a.] / Cf. Skt. (lex.) meka- goat (Monier-Williams lex.) mlekh ‘goat’ (Br.); meḷh ‘goat’ (Br. mr̤eka (Te.); mēṭam (Ta.); meṣam (Samskritam) Te. mr̤eka (DEDR 5087) (DEDR 5087) Rebus: meluh.h.a (Akkadian) mleccha (Samskritam) milakkhu 'copper' (Pali)
Ht. 10 feet.Alabaster relief in the Louvre. Drawing by Saint-Elme Gautier. Illustration for A History of Art in Chaldaea and Assyria by Georges Perrot and Charles Chipiez (Chapman and Hall, 1884) The winged person, whose helmet has three sets of horns holds a raphia farinifera cone on his right palm. The person (perhaps a Meluhha) with antelope on his left arm appears to be holding a date cluster on his right hand; he is followed by a person holding a pomegrante cluster.
The relief presents a trade deal involving exchange of sharp metal tools with copper metal ingots from Meluhha.
mlekh 'goat' carried by him denotes the Meluhha merchant (dealing in) milakkhu 'copper'. The twig or sprig on his right hand: ḍhāḷā m. ʻsprig' meṛh 'merchant's assistant' carries a cluster of pomegranates: ḍ̠āṛhū̃ 'pomegranate' (Sindhi) Rebus: ḍhālako 'a large metal ingot' (Gujarati)
ḍāla1 m. ʻ branch ʼ Śīl. 2. *ṭhāla -- . 3. *ḍāḍha -- . [Poss. same as *dāla -- 1 and dāra -- 1: √dal, √d&rcirclemacr;. But variation of form supports PMWS 64 ← Mu.]1. Pk. ḍāla -- n. ʻ branch ʼ; S. ḍ̠āru m. ʻ large branch ʼ, ḍ̠ārī f. ʻ branch ʼ; P. ḍāl m. ʻ branch ʼ, °lā m. ʻ large do. ʼ, °lī f. ʻ twig ʼ; WPah. bhal. ḍā m. ʻ branch ʼ; Ku. ḍālo m. ʻ tree ʼ; N. ḍālo ʻ branch ʼ, A. B. ḍāl, Or. ḍāḷa; Mth. ḍār ʻ branch ʼ, °ri ʻ twig ʼ; Aw. lakh. ḍār ʻ branch ʼ, H. ḍāl, °lā m., G. ḍāḷi, °ḷīf., °ḷũ n.2. A. ṭhāl ʻ branch ʼ, °li ʻ twig ʼ; H. ṭhāl, °lā m. ʻ leafy branch (esp. one lopped off) ʼ.3. Bhoj. ḍāṛhī ʻ branch ʼ; M. ḍāhaḷ m. ʻ loppings of trees ʼ, ḍāhḷā m. ʻ leafy branch ʼ, °ḷī f. ʻ twig ʼ, ḍhāḷā m. ʻ sprig ʼ, °ḷī f. ʻ branch ʼ.(CDIAL 5546). Rebus: ḍhāla n. ʻ shield ʼ lex. 2. *ḍhāllā -- .1. Tir. (Leech) "dàl"ʻ shield ʼ, Bshk. ḍāl, Ku. ḍhāl, gng. ḍhāw, N. A. B.ḍhāl, Or. ḍhāḷa, Mth. H. ḍhāl m.2. Sh. ḍal (pl. °le̯) f., K. ḍāl f., S. ḍhāla, L. ḍhāl (pl. °lã) f., P. ḍhāl f., G. M. ḍhāl f.. *ḍhāllā -- : WPah.kṭg. (kc.) ḍhāˋl f. (obl. -- a) ʻ shield ʼ (a word used in salutation), J. ḍhāl f. (CDIAL 5583).
dalim 'the fruit of pomegranate, punica granatum, Linn.' (Santali) S. ḍ̠āṛhū̃ 'pomegranate'(CDIAL 6254). Gy. eur. darav ʻ pomegranate ʼ (GWZS 440).(CDIAL 14598). dāḍima m. ʻ pomegranate tree ʼ MBh., n. ʻ its fruit ʼ Suśr., dālima -- m. Amar., ḍālima -- lex. 1. Pa. dālima -- m., NiDoc. daḍ'ima, Pk. dāḍima -- , dālima -- n., dāḍimī -- f. ʻ the tree ʼ, Dm. dā̤ŕim, Shum. Gaw. dāˊṛim,Kal. dā̤ŕəm, Kho. dáḷum, Phal. dhe_ṛum, S. ḍ̠āṛhū̃ m., P. dāṛū̃, °ṛū, °ṛam m., kgr. dariūṇ (= dariū̃?) m.; WPah.bhiḍ. de_ṛũ n. ʻ sour pomegranate ʼ; (Joshi) dāṛū, OAw. dārivaṁ m., H. poet. dāriũ m., OG. dāḍimi f. ʻ the tree ʼ, G. dāṛam n., dāṛem f. ʻ the tree ʼ, Si. deḷum.2. WPah.jaun. dāṛim, Ku. dā̆ṛim, dālim, dālimo, N. dārim, A. ḍālim, B. dāṛim, dālim, Or. dāḷimba, °ima, dāṛima,
mlekh 'goat' carried by him denotes the Meluhha merchant (dealing in) milakkhu 'copper'. The twig or sprig on his right hand: ḍhāḷā m. ʻsprig' meṛh 'merchant's assistant' carries a cluster of pomegranates: ḍ̠āṛhū̃ 'pomegranate' (Sindhi) Rebus: ḍhālako 'a large metal ingot' (Gujarati)
ḍāla1 m. ʻ branch ʼ Śīl. 2. *ṭhāla -- . 3. *ḍāḍha -- . [Poss. same as *dāla -- 1 and dāra -- 1: √dal, √d&rcirclemacr;. But variation of form supports PMWS 64 ← Mu.]1. Pk. ḍāla -- n. ʻ branch ʼ; S. ḍ̠āru m. ʻ large branch ʼ, ḍ̠ārī f. ʻ branch ʼ; P. ḍāl m. ʻ branch ʼ, °lā m. ʻ large do. ʼ, °lī f. ʻ twig ʼ; WPah. bhal. ḍā m. ʻ branch ʼ; Ku. ḍālo m. ʻ tree ʼ; N. ḍālo ʻ branch ʼ, A. B. ḍāl, Or. ḍāḷa; Mth. ḍār ʻ branch ʼ, °ri ʻ twig ʼ; Aw. lakh. ḍār ʻ branch ʼ, H. ḍāl, °lā m., G. ḍāḷi, °ḷīf., °ḷũ n.2. A. ṭhāl ʻ branch ʼ, °li ʻ twig ʼ; H. ṭhāl, °lā m. ʻ leafy branch (esp. one lopped off) ʼ.3. Bhoj. ḍāṛhī ʻ branch ʼ; M. ḍāhaḷ m. ʻ loppings of trees ʼ, ḍāhḷā m. ʻ leafy branch ʼ, °ḷī f. ʻ twig ʼ, ḍhāḷā m. ʻ sprig ʼ, °ḷī f. ʻ branch ʼ.(CDIAL 5546). Rebus: ḍhāla n. ʻ shield ʼ lex. 2. *ḍhāllā -- .1. Tir. (Leech) "dàl"ʻ shield ʼ, Bshk. ḍāl, Ku. ḍhāl, gng. ḍhāw, N. A. B.ḍhāl, Or. ḍhāḷa, Mth. H. ḍhāl m.2. Sh. ḍal (pl. °le̯) f., K. ḍāl f., S. ḍhāla, L. ḍhāl (pl. °lã) f., P. ḍhāl f., G. M. ḍhāl f.. *ḍhāllā -- : WPah.kṭg. (kc.) ḍhāˋl f. (obl. -- a) ʻ shield ʼ (a word used in salutation), J. ḍhāl f. (CDIAL 5583).
dalim 'the fruit of pomegranate, punica granatum, Linn.' (Santali) S. ḍ̠āṛhū̃ 'pomegranate'(CDIAL 6254). Gy. eur. darav ʻ pomegranate ʼ (GWZS 440).(CDIAL 14598). dāḍima m. ʻ pomegranate tree ʼ MBh., n. ʻ its fruit ʼ Suśr., dālima -- m. Amar., ḍālima -- lex. 1. Pa. dālima -- m., NiDoc. daḍ'ima, Pk. dāḍima -- , dālima -- n., dāḍimī -- f. ʻ the tree ʼ, Dm. dā̤ŕim, Shum. Gaw. dāˊṛim,Kal. dā̤ŕəm, Kho. dáḷum, Phal. dhe_ṛum, S. ḍ̠āṛhū̃ m., P. dāṛū̃, °ṛū, °ṛam m., kgr. dariūṇ (= dariū̃?) m.; WPah.bhiḍ. de_ṛũ n. ʻ sour pomegranate ʼ; (Joshi) dāṛū, OAw. dārivaṁ m., H. poet. dāriũ m., OG. dāḍimi f. ʻ the tree ʼ, G. dāṛam n., dāṛem f. ʻ the tree ʼ, Si. deḷum.2. WPah.jaun. dāṛim, Ku. dā̆ṛim, dālim, dālimo, N. dārim, A. ḍālim, B. dāṛim, dālim, Or. dāḷimba, °ima, dāṛima,
ḍāḷimba,ḍarami ʻ tree and fruit ʼ; Mth. dāṛim ʻ pomegranate ʼ, daṛimī ʻ dried mango ʼ; H. dāṛimb, °im, dālim, ḍāṛim, ḍār°, ḍāl° m., M.dāḷĩb, °ḷīm, ḍāḷĩb n. ʻ the fruit ʼ, f. ʻ the tree ʼ.3. Sh.gil. daṇū m. ʻ pomegranate ʼ, daṇúi f. ʻ the tree ʼ, jij. ḍ*lṇə́i, K. dönü m., P. dānū m.
dāḍima -- . 2. dāḍimba -- : Garh. dāḷimu ʻ pomegranate ʼ, A. ḍālim (phonet. d -- ).(CDIAL 6254).Ta. mātaḷai, mātuḷai, mātuḷam pomegranate. Ma. mātaḷam id. (DEDR 4809).
தாதுமாதுளை tātu-mātuḷai, n. < id. +. Pomegranate, s. tr., Punica granatum; பூ மாதுளை. (யாழ். அக.)
தாதுமாதுளை tātu-mātuḷai, n. < id. +. Pomegranate, s. tr., Punica granatum; பூ மாதுளை. (யாழ். அக.)
Rebus: ḍhālako = a large metal ingot (G.) ḍhālakī = a metal heated and poured into a mould; a solid piece of metal; an ingot (Gujarati)
Elamite statuette showed a person (king?) carrying an antelope on his hands, the same way a Meluhhan carried an antelope on his hands.
While a composite comparable glyph has not been identified in the corpus of Indus inscriptions,there are seals which show fish glyph together with antelope glyph; fish glyph together with composite bull + heifer glyph.
Harappa seal (h330)
Seal. National Museum: 135.
The rebus readings of the hieroglyphs are: mẽḍha ‘antelope’; rebus: meḍ ‘iron’ (Ho.) aya 'fish'; rebus: aya 'cast metal' (G.).
A Susa ritual basin dated to ca. 12th or 13th century BCE depicts goat and fish ligatured into a 'fabulous' or 'composite' animal representation, clearly intended to connote the underlying hieroglyphic meaning.
Deification of glyphs: When did it happen?
At what point in time, the glyphic representations denoting native metal or cast metal artefacts and which were used to authenticate trade transactions of the civilization, using Indus script inscriptions, were deified can only be conjectured. This shift from use in trade to use in cultural/religious contexts may have occurred -- in the interaction areas such as Susa and Meluhha -- between 19th and 13th centuries BCE (i.e. between the time when the continued use of Indus Script glyphs is attested, say, 19th century BCE and the time when the same glyphs or cognate glyphic representations were deified, say, 13th century BCE).
Mohenjodaro seal (m0302).
Susa ritual basin dates from 13th or 12th cent. BCE. It is decorated with goatfish figures, flankin a hieroglyph-multiplex of reedposts, spathes, molluscs. http://www.louvre.fr/en/oeuvre-notices/ritual-basin-decorated-goatfish-figures aya 'fish' Rebus: aya 'iron' (Gujarati) ayas 'metal' (Rigveda) meḷh ‘goat’ (Br. mr̤eka (Te.); mēṭam (Ta.); meṣam (Samskritam) Te. mr̤eka (DEDR 5087) (DEDR 5087) Rebus: meluh.h.a (Akkadian) mleccha (Samskritam) milakkhu 'copper' (Pali)
Hieroglyph-multiplex or Susa ritual basin has hieroglyph components: reeds, spathe, mollusc (snail). Rebus Meluhha readings in Indus Script cipher signify this to be Hieroglyph: eruva dhatugarbha śāṅkhika,'reed, spathe, mollusc (snail)' Rebus: eruva dagoba sangha.'copper mineral core assemblage'.
Hieroglyhph: eruva 'reed' Rebus: eruva 'copper'
Hieroglyph: śāṅkhika 'relating to a shell' hö̃giñ 'shell of a mollusc' Rebus: sangha 'assemblage'
Hieroglyph: spathe "A spathe is a large bract that forms a sheath to enclose the flower cluster of certain plants such as palms, arums, Iris and dayflowers. In many arums (Araceae family), the spathe is petal-like, attracting pollinators to the flowers arranged on a type of spike called a spadix." (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bract#Spathe): Kashmiri. gab m. ʻ womb, sprout of a plant ʼ; gāb(h)ā ʻspathe of a plant (Bengali)(CDIAL 4055) Rebus: gābhā m. ʻ heart, core ʼ (Marathi) gāb(h)ā'foetus' dhātugarbha (Samskritam), dhātu gabbhā (Pali) (Sinhalese dāgoba. The expression is equivalent to dhātu relics+garbha womb, inside. Thus, dāgoba is a dome-shaped shrine containing
relics of the Buddha or a Bauddham arhant.
Hieroglyph: mollusc: śāṅkhika ʻ relating to a shell ʼ W. 2. *śāṅkhinī -- (śaṅkhinī -- f. ʻ mother -- of -- pearl ʼ Bālar.). [śaṅkhá -- 1] 1. K. hāngi ʻ snail ʼ; B. sã̄khī ʻ possessing or made of shells ʼ. 2. K. hö̃giñ f. ʻ pearl oyster shell, shell of any aquatic mollusc ʼ (CDIAL 12380). Rebus: sangha [fr. saŋ+hṛ; lit. "comprising." The quâsi pop. etym. at VvA 233 is "diṭṭhi -- sīla -- sāmaññena sanghāṭabhāvena sangha"] 1. multitude, assemblage Miln 403 (kāka˚); J i.52 (sakuṇa˚); Sn 589 (ñāti˚); 680 (deva˚); D iii.23 (miga˚); Vv 55 (accharā˚=samūha VvA 37).Sanghin (adj.) [fr. sangha] having a crowd (of followers), the head of an order D i.47, 116; S i.68; Miln 4; DA i 143. -- sanghâsanghī (pl.) in crowds, with crowds (redupl. cpd.!), with gaṇi -- bhūtā "crowd upon crowd" at D i.112, 128; ii.317; DA i.280.
Source: Source: Joan Aruz et al., 2003, Art of the First cities: the third millennium BCE from the Mediterranean to the Indus, New York, Metropolitan Museum of Art (Pages 320, 322). See also: http://ancientworldonline.blogspot.in/2012/10/kuwaiti-slovak-archaeological-mission.html
The center-piece hieroglyph-multiplex: crucible + sun hieroglyphs.
Hieoglyph: koThAri 'crucible' Rebus: koThAri 'treasurer'Hieroglyph: aru m. ʻ sun ʼ lex. Kho. yor Morgenstierne NTS ii 276 with ? <-> Whence y -- ? (CDIAL 612) arka 'sun' Rebus: araka, eraka 'copper, moltencast' (Kannada. Tulu) eraka, era, er-a = syn. erka, copper, weapons (Ka.) eruvai ‘copper’ (Ta.); ere dark red (Ka.)(DEDR 446). eraka, er-aka = any metal infusion (Ka.Tu.) Tu. eraka molten, cast (as metal); eraguni to melt (DEDR 866)
Hieroglyph: aquatic bird: karaṭa1 m. ʻ crow ʼ BhP., °aka -- m. lex. [Cf. karaṭu -- , karkaṭu -- m. ʻ Numidian crane ʼ, karēṭu -- , °ēṭavya -- , °ēḍuka -- m. lex., karaṇḍa2 -- m. ʻ duck ʼ lex: seekāraṇḍava -- ]Pk. karaḍa -- m. ʻ crow ʼ, °ḍā -- f. ʻ a partic. kind of bird ʼ; S. karaṛa -- ḍhī˜gu m. ʻ a very large aquatic bird ʼ; L. karṛā m., °ṛī f. ʻ the common teal ʼ.(CDIAL 2787). Allograph: karaṭa m. ʻ Carthamus tinctorius ʼ lex.Pk. karaḍa -- m. ʻ safflower ʼ, °ḍā -- f. ʻ a tree like the karañja ʼ; M. karḍī, °ḍaī f. ʻ safflower, Carthamus tinctorius and its seed ʼ.(CDIAL 2788). Rebus: karaḍā 'hardalloy of metals' (Marathi)
gaṇḍ 'four'. kaṇḍ 'bit'. Rebus: kaṇḍ 'fire-altar'. khaṇḍ ‘field, division’ (Skt.) Rebus: Ga. (Oll.) kanḍ, (S.) kanḍu (pl. kanḍkil) stone (DEDR 1298). खडा (Marathi) is ‘metal, nodule, stone, lump’. kaṇi ‘stone’ (Kannada) with Tadbhava khaḍu. khaḍu, kaṇ ‘stone/nodule (metal)’. Rebus: khaṇḍaran, khaṇḍrun ‘pit furnace’ (Santali) kaṇḍ ‘furnace’ (Skt.) लोहकारकन्दुः f. a blacksmith's smelting furnace (Grierson Kashmiri lex.) [khaṇḍa] A piece, bit, fragment, portion.(Marathi) Rebus 2: kandi (pl. -l) beads, necklace (Pa.); kanti (pl. -l) bead, (pl.) necklace; kandit. bead (Ga.)(DEDR 1215). Rebus 3: khaNDa 'metal implements'.
Ta. kaṇ eye, aperture, orifice, star of a peacock's tail. (DEDR 1159a) Rebus ‘brazier, bell-metal worker’: கன்னான் kaṉṉāṉ , n. < கன்¹. [M. kannān.] Brazier, bell-metal worker, one of the divisions of the Kammāḷa caste; செம்புகொட்டி. (திவா.)
ranku 'antelope' Rebus: ranku 'tin'.
The antelope + divided square is read rebus: eraka tagara kaṇḍ 'tin furnace' (merchant, damgar). The upraised arm indicates eraka 'copper': eraka ‘upraised arm’ (Telugu); eraka ‘copper’ (Telugu) Thus, the seal denotes a merchant dealing in iron, tin and copper ingots.
![]() Composition of two horned animals, sitting human playing a four-string musical instrument, a star and a moon.
Composition of two horned animals, sitting human playing a four-string musical instrument, a star and a moon.
The rebus reading of hieroglyphs are: తంబుర [tambura] or తంబురా tambura. [Tel. తంతి+బుర్ర.] n. A kind of stringed instrument like the guitar. A tambourine. Rebus: tam(b)ra 'copper' tambabica, copper-ore stones; samṛobica, stones containinggold (Mundari.lex.) tagara 'antelope'. Rebus 1: tagara 'tin' (ore) tagromi 'tin, metal alloy' (Kuwi) Rebus 2: damgar 'merchant'.
Thus the seal connotes a merchant of tin and copper.
![]() Inventory No. 8480. A seal from Dilmun, A seal from Dilmun, made of soft stone, classified as the 3rd largest seal in Failaka Island, decorated with human and zoomorphic figures. 0.16 X 4.8 cm. Site: the Ruler's Palace. 2nd millennium BCE, Dilmun civilization [NOTE: Many such seals of Failaka and Dilmun have been read rebus as Indus writing.]
Inventory No. 8480. A seal from Dilmun, A seal from Dilmun, made of soft stone, classified as the 3rd largest seal in Failaka Island, decorated with human and zoomorphic figures. 0.16 X 4.8 cm. Site: the Ruler's Palace. 2nd millennium BCE, Dilmun civilization [NOTE: Many such seals of Failaka and Dilmun have been read rebus as Indus writing.]
Hieroglyphs on this Dilmun seal are: star, tabernae montana flower, cock, two divided squares, two bulls, antelope, sprout (paddy plant), drinking (straw), stool, twig or tree branch. A person with upraised arm in front of the antelope. All these hieroglyphs are read rebus using lexemes (Meluhha, Mleccha) of Indiansprachbund.
meḍha ‘polar star’ (Marathi). Rebus: meḍ ‘iron’ (Ho.Mu.)
ṭagara (tagara) fragrant wood (Pkt.Skt.).tagara 'antelope'. Rebus 1: tagara 'tin' (ore) tagromi 'tin, metal alloy' (Kuwi) Rebus 2: damgar 'merchant'
kuṭi (-pp-, -tt-) to drink, inhale. Rebus: kuṭhi ‘smelting furnace’ (Santali)
ḍangar ‘bull’; rebus: ḍangar ‘blacksmith’ (Hindi) dula 'pair' (Kashmiri). Rebus: dul 'cast metal' (Santali) Thus, a pair of bulls connote 'cast metal blacksmith'.
khaṇḍ ‘field, division’ (Skt.) Rebus 1: Ga. (Oll.) kanḍ, (S.) kanḍu (pl. kanḍkil) stone (ore). Rebus 2: kaṇḍ 'fire-altar' (Santali) Thus, the two divided squares connote furnace for stone (ore).
kolmo ‘paddy plant’ (Santali) Rebus: kolami ‘furnace, smithy’ (Telugu)
Kur. kaṇḍō a stool. Rebus: kaṇḍ 'fire-altar' (Santali)
Tu. aḍaru twig. Rebus: aduru 'native (unsmelted) metal' (Kannada) Alternative reading: కండె [kaṇḍe] kaṇḍe. [Tel.] n. A head or ear of millet or maize. Rebus 1: kaṇḍ 'fire-altar' (Santali) Rebus 2: khānḍa ‘tools, pots and pans, metal-ware’.
eraka ‘upraised arm’ (Te.); eraka ‘copper’ (Te.)
Thus, the Dilmun seal is a metalware catalog of damgar 'merchant' dealing with copper and tin.
The two divided squares attached to the straws of two vases in the following seal can also be read as hieroglyphs:
khaṇḍ ‘field, division’ (Skt.) Rebus 1: Ga. (Oll.) kanḍ, (S.) kanḍu (pl. kanḍkil) stone (ore). Rebus 2: kaṇḍ 'fire-altar' (Santali) Thus, the two divided squares connote furnace for stone (ore).
kuṭi (-pp-, -tt-) to drink, inhale. Rebus: kuṭhi ‘smelting furnace’ (Santali)
ḍangā = small country boat, dug-out canoe (Or.); ḍõgā trough, canoe, ladle (H.)(CDIAL 5568). Rebus: ḍānro term of contempt for a blacksmith (N.); ḍangar (H.) (CDIAL 5524)
Thus, a smelting furnace for stone (ore) is connoted by the seal of a blacksmith, ḍangar
Ta. kara-tāḷam palmyra palm. Ka. kara-tāḷa fan-palm, Corypha umbraculifera Lin. Tu. karatāḷa cadjan. Te. (B.) kara-tāḷamu the small-leaved palm tree.(DEDR 1270). karukku teeth of a saw or sickle, jagged edge of palmyra leaf-stalk, sharpness (Ta.) Ka. garasu. / Cf. Skt. karaṭa- a low, unruly, difficult person; karkara- hard, firm; karkaśa- rough, harsh, hard; krakaca-, karapattra- saw; khara- hard, harsh, rough, sharp-edged; kharu- harsh, cruel; Pali kakaca- saw; khara- rough; saw; Pkt.karakaya- saw; Apabhraṃśa (Jasaharacariu) karaḍa- hard. Cf. esp. Turner, CDIAL, no. 2819. Cf. also Skt. karavāla- sword (for second element, cf. 5376 Ta. vāḷ). (DEDR 1265) Allograph: Ta. karaṭi, karuṭi, keruṭi fencing, school or gymnasium where wrestling and fencing are taught. Ka. garaḍi, garuḍi fencing school. Tu.garaḍi, garoḍi id. Te. gariḍi, gariḍī id., fencing.(DEDR 1262)
Allograph: eagle: garuḍá m. ʻ a mythical bird ʼ Mn. Pa. garuḷa -- m., Pk. garuḍa -- , °ula -- m.; P. garaṛ m. ʻ the bird Ardea argala ʼ; N. garul ʻ eagle ʼ, Bhoj. gaṛur; OAw. garura ʻ blue jay ʼ; H. garuṛ m. ʻ hornbill ʼ, garul ʻ a large vulture ʼ; Si. guruḷā ʻ bird ʼ (kurullā infl. by Tam.?). -- Kal. rumb. gōrvḗlik ʻ kite ʼ?? (CDIAL 4041). gāruḍa ʻ relating to Garuḍa ʼ MBh., n. ʻ spell against poison ʼ lex. 2. ʻ emerald (used as an antidote) ʼ Kālid. [garuḍá -- ]1. Pk. gāruḍa -- , °ula -- ʻ good as antidote to snakepoison ʼ, m. ʻ charm against snake -- poison ʼ, n. ʻ science of using such charms ʼ; H. gāṛrū, gārṛū m. ʻ charm against snake -- poison ʼ; M. gāruḍ n. ʻ juggling ʼ. 2. M. gāroḷā ʻ cat -- eyed, of the colour of cat's eyes ʼ.(CDIAL 4138). கருடக்கல் karuṭa-k-kal, n. < garuḍa. (Tamil) Rebus: karaDa 'hard alloy' (Marathi)Hieroglyph: kaNDe 'pine cone' Rebus: khaNDa 'metal implements'
Depiction of an annunaki in the Pergamon Museum in Berlin. Hieroglyph composition of an eagle-faced winged person also carried a pine-cone in his right hand; a basket or wallet is held in the left hand. Assyrian) alabaster Height: 236.2 cm (93 in). Width: 135.9 cm (53.5 in). Depth: 15.2 cm (6 in). This relief decorated the interior wall of the northwest palace of King Ashurnasirpal II at Nimrud. http://www.cuttingedge.org/articles/RC125.htm
Hieroglyph: pine-cone: கண்டபலம் kaṇṭa-palam, n. < kaṇṭa கண்டம்¹ kaṇṭam kaṇṭal 'pine-cone'; maraka 'peacock' Rebus: khaṇḍa, kaṇṭa 'temple front' smāraka, 'memorial for ancestors'., n. < khaṇḍa. A portion of the front hall, in a temple; கோயில் முக மண்டபப்பகுதி. (S. I. I. v, 236.)Ash. piċ -- kandə ʻ pine ʼ, Kt. pṳ̄ċi, piċi, Wg. puċ, püċ (pṳ̄ċ -- kəŕ ʻ pine -- cone ʼ), Pr. wyoċ, Shum. lyēwič (lyē -- ?).(CDIAL 8407). Cf. Gk. peu/kh f. ʻ pine ʼ, Lith. pušìs, OPruss. peuse NTS xiii 229. The suffix –kande in the lexeme: Ash. piċ-- kandə ʻ pine ʼ may be cognate with the bulbous glyphic related to a mangrove root: Koḍ. kaṇḍe root-stock from which small roots grow; ila·ti kaṇḍe sweet potato (ila·ti England). Tu. kaṇḍe, gaḍḍè a bulbous root; Ta. kaṇṭal mangrove, Rhizophora mucronata; dichotomous mangrove, Kandelia rheedii. Ma. kaṇṭa bulbous root as of lotus, plantain; point where branches and bunches grow out of the stem of a palm; kaṇṭal what is bulb-like, half-ripe jackfruit and other green fruits; R. candel. (DEDR 1171). Rebus: khaṇḍa, kaṇṭa 'temple front'. Rebus:khānḍa ‘tools, pots and pans, metal-ware’. Rebus 2: kaṇḍ 'fire-altar' (Santali) Hieroglyphs: kandə ʻpineʼ, ‘ear of maize’. Rebus: kaṇḍa ‘tools, pots and pans of metal’. Rebus: kāḍ ‘stone’. Ga. (Oll.) kanḍ, (S.) kanḍu (pl. kanḍkil) stone (DEDR 1298).
gaṇḍ 'four'. kaṇḍ 'bit'. Rebus: kaṇḍ 'fire-altar'.
khaṇḍ ‘field, division’ (Skt.) Rebus: Ga. (Oll.) kanḍ, (S.) kanḍu (pl. kanḍkil) stone (DEDR 1298). खडा (Marathi) is ‘metal, nodule, stone, lump’. kaṇi ‘stone’ (Kannada) with Tadbhava khaḍu. khaḍu, kaṇ ‘stone/nodule (metal)’. Rebus: khaṇḍaran, khaṇḍrun ‘pit furnace’ (Santali) kaṇḍ ‘furnace’ (Skt.) लोहकारकन्दुः f. a blacksmith's smelting furnace (Grierson Kashmiri lex.) [khaṇḍa] A piece, bit, fragment, portion.(Marathi) Rebus 2: kandi (pl. -l) beads, necklace (Pa.); kanti (pl. -l) bead, (pl.) necklace; kandit. bead (Ga.)(DEDR 1215). Rebus 3: khaNDa 'metal implements'.
 Composition of two horned animals, sitting human playing a four-string musical instrument, a star and a moon.
Composition of two horned animals, sitting human playing a four-string musical instrument, a star and a moon.The rebus reading of hieroglyphs are: తంబుర [tambura] or తంబురా tambura. [Tel. తంతి+బుర్ర.] n. A kind of stringed instrument like the guitar. A tambourine. Rebus: tam(b)ra 'copper' tambabica, copper-ore stones; samṛobica, stones containinggold (Mundari.lex.) tagara 'antelope'. Rebus 1: tagara 'tin' (ore) tagromi 'tin, metal alloy' (Kuwi) Rebus 2: damgar 'merchant'.
Thus the seal connotes a merchant of tin and copper.
 Inventory No. 8480. A seal from Dilmun, A seal from Dilmun, made of soft stone, classified as the 3rd largest seal in Failaka Island, decorated with human and zoomorphic figures. 0.16 X 4.8 cm. Site: the Ruler's Palace. 2nd millennium BCE, Dilmun civilization [NOTE: Many such seals of Failaka and Dilmun have been read rebus as Indus writing.]
Inventory No. 8480. A seal from Dilmun, A seal from Dilmun, made of soft stone, classified as the 3rd largest seal in Failaka Island, decorated with human and zoomorphic figures. 0.16 X 4.8 cm. Site: the Ruler's Palace. 2nd millennium BCE, Dilmun civilization [NOTE: Many such seals of Failaka and Dilmun have been read rebus as Indus writing.]Hieroglyphs on this Dilmun seal are: star, tabernae montana flower, cock, two divided squares, two bulls, antelope, sprout (paddy plant), drinking (straw), stool, twig or tree branch. A person with upraised arm in front of the antelope. All these hieroglyphs are read rebus using lexemes (Meluhha, Mleccha) of Indiansprachbund.
meḍha ‘polar star’ (Marathi). Rebus: meḍ ‘iron’ (Ho.Mu.)
ṭagara (tagara) fragrant wood (Pkt.Skt.).tagara 'antelope'. Rebus 1: tagara 'tin' (ore) tagromi 'tin, metal alloy' (Kuwi) Rebus 2: damgar 'merchant'
kuṭi (-pp-, -tt-) to drink, inhale. Rebus: kuṭhi ‘smelting furnace’ (Santali)
ḍangar ‘bull’; rebus: ḍangar ‘blacksmith’ (Hindi) dula 'pair' (Kashmiri). Rebus: dul 'cast metal' (Santali) Thus, a pair of bulls connote 'cast metal blacksmith'.
khaṇḍ ‘field, division’ (Skt.) Rebus 1: Ga. (Oll.) kanḍ, (S.) kanḍu (pl. kanḍkil) stone (ore). Rebus 2: kaṇḍ 'fire-altar' (Santali) Thus, the two divided squares connote furnace for stone (ore).
kolmo ‘paddy plant’ (Santali) Rebus: kolami ‘furnace, smithy’ (Telugu)
Kur. kaṇḍō a stool. Rebus: kaṇḍ 'fire-altar' (Santali)
Tu. aḍaru twig. Rebus: aduru 'native (unsmelted) metal' (Kannada) Alternative reading: కండె [kaṇḍe] kaṇḍe. [Tel.] n. A head or ear of millet or maize. Rebus 1: kaṇḍ 'fire-altar' (Santali) Rebus 2: khānḍa ‘tools, pots and pans, metal-ware’.
eraka ‘upraised arm’ (Te.); eraka ‘copper’ (Te.)
Thus, the Dilmun seal is a metalware catalog of damgar 'merchant' dealing with copper and tin.
The two divided squares attached to the straws of two vases in the following seal can also be read as hieroglyphs:
khaṇḍ ‘field, division’ (Skt.) Rebus 1: Ga. (Oll.) kanḍ, (S.) kanḍu (pl. kanḍkil) stone (ore). Rebus 2: kaṇḍ 'fire-altar' (Santali) Thus, the two divided squares connote furnace for stone (ore).
kuṭi (-pp-, -tt-) to drink, inhale. Rebus: kuṭhi ‘smelting furnace’ (Santali)
ḍangā = small country boat, dug-out canoe (Or.); ḍõgā trough, canoe, ladle (H.)(CDIAL 5568). Rebus: ḍānro term of contempt for a blacksmith (N.); ḍangar (H.) (CDIAL 5524)
Thus, a smelting furnace for stone (ore) is connoted by the seal of a blacksmith, ḍangar
Ta. kara-tāḷam palmyra palm. Ka. kara-tāḷa fan-palm, Corypha umbraculifera Lin. Tu. karatāḷa cadjan. Te. (B.) kara-tāḷamu the small-leaved palm tree.(DEDR 1270). karukku teeth of a saw or sickle, jagged edge of palmyra leaf-stalk, sharpness (Ta.) Ka. garasu. / Cf. Skt. karaṭa- a low, unruly, difficult person; karkara- hard, firm; karkaśa- rough, harsh, hard; krakaca-, karapattra- saw; khara- hard, harsh, rough, sharp-edged; kharu- harsh, cruel; Pali kakaca- saw; khara- rough; saw; Pkt.karakaya- saw; Apabhraṃśa (Jasaharacariu) karaḍa- hard. Cf. esp. Turner, CDIAL, no. 2819. Cf. also Skt. karavāla- sword (for second element, cf. 5376 Ta. vāḷ). (DEDR 1265) Allograph: Ta. karaṭi, karuṭi, keruṭi fencing, school or gymnasium where wrestling and fencing are taught. Ka. garaḍi, garuḍi fencing school. Tu.garaḍi, garoḍi id. Te. gariḍi, gariḍī id., fencing.(DEDR 1262)
Allograph: eagle: garuḍá m. ʻ a mythical bird ʼ Mn. Pa. garuḷa -- m., Pk. garuḍa -- , °ula -- m.; P. garaṛ m. ʻ the bird Ardea argala ʼ; N. garul ʻ eagle ʼ, Bhoj. gaṛur; OAw. garura ʻ blue jay ʼ; H. garuṛ m. ʻ hornbill ʼ, garul ʻ a large vulture ʼ; Si. guruḷā ʻ bird ʼ (kurullā infl. by Tam.?). -- Kal. rumb. gōrvḗlik ʻ kite ʼ?? (CDIAL 4041). gāruḍa ʻ relating to Garuḍa ʼ MBh., n. ʻ spell against poison ʼ lex. 2. ʻ emerald (used as an antidote) ʼ Kālid. [garuḍá -- ]1. Pk. gāruḍa -- , °ula -- ʻ good as antidote to snakepoison ʼ, m. ʻ charm against snake -- poison ʼ, n. ʻ science of using such charms ʼ; H. gāṛrū, gārṛū m. ʻ charm against snake -- poison ʼ; M. gāruḍ n. ʻ juggling ʼ. 2. M. gāroḷā ʻ cat -- eyed, of the colour of cat's eyes ʼ.(CDIAL 4138). கருடக்கல் karuṭa-k-kal, n. < garuḍa. (Tamil) Rebus: karaDa 'hard alloy' (Marathi)
Hieroglyphs: kandə ʻpineʼ, ‘ear of maize’. Rebus: kaṇḍa ‘tools, pots and pans of metal’. Rebus: kāḍ ‘stone’. Ga. (Oll.) kanḍ, (S.) kanḍu (pl. kanḍkil) stone (DEDR 1298).

A fish's head can be seen on the Apkallu's head, and its skin hangs down over the back of his body. Neo-Assyrian era, 865-860 BCE.

Bas-relief from Nimrud. Bird-apkallu raise mulillu cones.

God Ea at far lef, wears horned headdress, with water coursing from his shoulders. Two fish-apkallu.

Apkallu portrayed as fish-men.


Fish-man known as Kulullu. Terracotta figurine (8th-7th BCE). Louvre collection, Nr. 3337.

Sowie Museum 9-1796 sun-dried clay figurine of a suhurmashshu, probably from Assur. Previously published HF Lutz, Univ. of California Publications in Semitic Philology 9/7 (1930), Rittig.97.

Fish-Apkallu statuettes of the type that were buried in the foundations of buildings. The so-called paRadu-fish apkallu were the seven antedeluvian sages of Sumeria.

Two kusarikku or 'bull men' holding a sacred palm tree surmounted by the eight pointed star of Ishtar. From Eshnunna (Tell Asmar near Baghdad, Iraq). Early 2nd millennium BCE. Louvre AO 12446
http://therealsamizdat.com/
tamar 'date palm' (Aramaic, Ethiopic, and Hebrew) tamr, 'fruit of the date-palm' (Arabic) http://www.jewishencyclopedia.com/articles/11873-palm Rebus: tam(b)ra 'copper' (Pali) arka 'sun' Rebus: araka, eraka 'copper, moltencast' (Kannada.Tulu).
See the peg shown on the crown of Nihal Mishmar cire perdue alloy hoard of artifacts:
kūṭa 'a peg, etc.'; kūṭi 'a hat turban peg or stand' (Kannada) khut.i Nag. (Or. khut.i_) diminutive of khun.t.a, a peg driven into the ground, as for tying a goat (Mundari) khun.t.i = pillar (Santali) Rebus: kuThi 'smelter'.
Cognate hieroglyph: Ta. kuṭai umbrella, parasol, canopy. Ma.
kuṭa umbrella. Ko. koṛ umbrella made of leaves (only in a proverb);
keṛ umbrella. To. kwaṛ id. Ka. koḍe id., parasol. Koḍ. koḍe umbrella.
Tu. koḍè id. Te. goḍugu id., parasol. Kuwi (F.) gūṛgū, (S.) gudugu, (Su. P.) guṛgu umbrella (< Te.). / Cf. Skt. (lex.) utkūṭa- umbrella, parasol. (DER 1663) उत्-कूट [p= 176,2] m. an umbrella or parasol L. (Monier-Williams) utkūṭḥ उत्कूटः [उन्नतं कूटमस्य] A parasol or umbrella.(Pali)
The Sheorajpur anthropomorph (348 on Plate A) has a 'fish' hieroglyph incised on the chest
Hieroglyphs: tagara ‘ram’ (Kannada) Rebus: damgar ‘merchant’ (Akk.) Rebus: tagara ‘tin’ (Kannada)
Ta. takar sheep, ram, goat, male of certain other animals (yāḷi, elephant, shark). பொருநகர் தாக்கற்குப் பேருந் தகைத்து (குறள், 486).Ma. takaran huge, powerful as a man, bear, etc. Ka. tagar, ṭagaru, ṭagara, ṭegaru ram. Tu. tagaru, ṭagarů id. Te. tagaramu, tagaru id. / Cf. Mar. tagar id. (DEDR 3000). Rebus 1:tagromi 'tin, metal alloy' (Kuwi) takaram tin, white lead, metal sheet, coated with tin (Ta.); tin, tinned iron plate (Ma.); tagarm tin (Ko.); tagara, tamara, tavara id. (Ka.) tamaru, tamara, tavara id. (Ta.): tagaramu, tamaramu, tavaramu id. (Te.); ṭagromi tin metal, alloy (Kuwi); tamara id. (Skt.)(DEDR 3001). trapu tin (AV.); tipu (Pali); tau, taua lead (Pkt.); tū̃ tin (P.); ṭau zinc, pewter (Or.); tarūaum lead (OG.);tarvũ (G.); tumba lead (Si.)(CDIAL 5992). Rebus 2: damgar ‘merchant’.
Hieroglyphs, allographs: ram, tabernae montana coronaria flower: तगर [ tagara ] f A flowering shrub, Tabernæ montana coronaria. 2 n C The flower of it. 3 m P A ram. (Marathi)
*tagga ʻ mud ʼ. [Cf. Bur. t*lg*l ỵ ʻ mud ʼ] Kho. (Lor.) toq ʻ mud, quagmire ʼ; Sh. tăgāˊ ʻ mud ʼ; K. tagöri m. ʻ a man who makes mud or plaster ʼ; Ku. tāgaṛ ʻ mortar ʼ; B. tāgāṛ ʻ mortar, pit in which it is prepared ʼ.(CDIAL 5626). (Note: making of mud or plaster is a key step in dhokra kamar's work of cire perdue (lost-wax) casting.)
Hieroglyphs, allographs: ram, tabernae montana coronaria flower: तगर [ tagara ] f A flowering shrub, Tabernæ montana coronaria. 2 n C The flower of it. 3 m P A ram. (Marathi)
*tagga ʻ mud ʼ. [Cf. Bur. t
krəm backʼ(Kho.) karmāra ‘smith, artisan’ (Skt.) kamar ‘smith’ (Santali)
Meluhha 'fish' hieroglyphs
Meluhha 'fish' hieroglyphs
Mohenjo-daro Seals m1118 and Kalibangan 032, glyphs used are: Zebu (bos taurus indicus), fish, four-strokes (allograph: arrow).ayo ‘fish’ (Mu.) + kaṇḍa ‘arrow’ (Skt.) ayaskāṇḍa ‘a quantity of iron, excellent iron’ (Pāṇ.gaṇ) aya = iron (G.); ayah, ayas = metal (Skt.) gaṆḌa, ‘four’ (Santali); Rebus: kaṇḍ ‘fire-altar’, ‘furnace’), arrow read rebus in mleccha (Meluhhan) as a reference to a guild of artisans working with ayaskāṇḍa ‘excellent quantity of iron’ (Pāṇini) is consistent with the primacy of economic activities which resulted in the invention of a writing system, now referred to as Indus Writing.
khũṭro = entire bull; khũṭ= bra_hman.i bull (G.) khuṇṭiyo = an uncastrated bull (Kathiawad. G.lex.) khũ_ṭaḍum a bullock (used in Jhālwāḍ)(G.) kuṇṭai = bull (Ta.lex.) cf. khũ_dhi hump on the back; khuĩ_dhũ hump-backed (G.)(CDIAL 3902). Rebus: kūṭa a house, dwelling (Skt.lex.) khũṭ = a community, sect, society, division, clique, schism, stock; khũṭren peṛa kanako = they belong to the same stock (Santali)
Allograph: काण्डः kāṇḍḥ ण्डम् ṇḍam The portion of a plant from one knot to another. काण्डात्काण्ड- त्प्ररोहन्ती Mahānār.4.3. A stem, stock, branch; लीलोत्खातमृणालकाण्डकवलच्छेदे U.3.16; Amaru.95; Ms. 1.46,48, Māl.3.34.
కాండము [ kāṇḍamu ] kānḍamu. [Skt.] n. Water. నీళ్లు (Telugu) kaṇṭhá -- : (b) ʻ water -- channel ʼ: Paš. kaṭāˊ ʻ irrigation channel ʼ, Shum. xãṭṭä. (CDIAL 14349).
lokhãḍ ‘overflowing pot’ Rebus: ʻtools, iron, ironwareʼ (Gujarati)
काण्ड an arrow MBh. xiii , 265 Hit. (Monier-Williams, p. 269) Rebus: काण्ड abundance; a multitude , heap , quantity (ifc.) Pa1n2. 4-2 , 51 Ka1s3.
Kalibangan 37, 34
Two Kalibangan seals show an antelope and fish glyphs as the inscription. Mẽḍha ‘antelope’; rebus: ‘iron’ (Ho.) ayo ‘fish’; rebs: ayo ‘metal’ (G.) [These are examples which clearly demonstrate that Indus script is a glyptic writing system and hence, all glyphs and glyptic elements have to be decoded.] miṇḍālmarkhor (Tor.wali) meḍho a ram, a sheep (G.)(CDIAL 10120) iron (Ho.) meṛed-bica = iron stone ore, in contrast to bali-bica, iron sand ore (Munda) meḍ ‘iron’.
Meluhha 'crocodile' hieroglyph in Ancient Near East and India
A cylinder seal showing hieroglyphs of crocodile, elephant and rhinoceros was found in Tell Asmar (Eshnunna), Iraq. This is an example of Meluhha writing using hieroglyphs to denote the competence of kāru ‘artisan’ -- kāru 'crocodile' (Telugu) Rebus: khar ‘blacksmith’ (Kashmiri); kāru ‘artisan’ (Marathi) He was also ibbo 'merchant' (Hieroglyph: ibha 'elephant' Rebus: ib 'iron') and maker of metal artifacts: kāṇḍā ‘metalware, tools, pots and pans’ (kāṇḍā mṛga 'rhinoceros' (Tamil).
One side (m1431B) of a four-sided tablet shows a procession of a tiger, an elephant and a rhinoceros (with fishes (or perhaps, crocodile) on top?).
![]()
![]()
![Enki]()
![]()
![]() Shell inlay: skirt-clad figure carrying fish, Early Dynastic III, ca. 2600-2350 BCE, Mesopotamia, Nippur, Sumerian.metmuseum.org
Shell inlay: skirt-clad figure carrying fish, Early Dynastic III, ca. 2600-2350 BCE, Mesopotamia, Nippur, Sumerian.metmuseum.org![SUMER SCULPTURE 5TH-2ND MILL.BCE Fish-man or water-sprite. Terracotta figurine (8th-7th BCE) Length 12 cm Nr. 3337 Iraq Museum, Baghdad, Iraq]() SUMER SCULPTURE 5TH-2ND MILL.BCE Fish-man or water-sprite. Terracotta figurine (8th-7th BCE) Length 12 cm Nr. 3337 Iraq Museum, Baghdad, Iraq
SUMER SCULPTURE 5TH-2ND MILL.BCE Fish-man or water-sprite. Terracotta figurine (8th-7th BCE) Length 12 cm Nr. 3337 Iraq Museum, Baghdad, Iraq![]()
![]()
![]() Gudea. Overflowing pot. Sumer.
Gudea. Overflowing pot. Sumer.
![Medallion 01]() Medallion. Makara, fishes. kara 'crocodile' rebus: khara 'blacksmith' ibha 'elephant' rebus: ib 'iron'; ayo 'fish' rebus: aya 'metal alloy'.
Medallion. Makara, fishes. kara 'crocodile' rebus: khara 'blacksmith' ibha 'elephant' rebus: ib 'iron'; ayo 'fish' rebus: aya 'metal alloy'.
Meluhha 'crocodile' hieroglyph in Ancient Near East and India
A cylinder seal showing hieroglyphs of crocodile, elephant and rhinoceros was found in Tell Asmar (Eshnunna), Iraq. This is an example of Meluhha writing using hieroglyphs to denote the competence of kāru ‘artisan’ -- kāru 'crocodile' (Telugu) Rebus: khar ‘blacksmith’ (Kashmiri); kāru ‘artisan’ (Marathi) He was also ibbo 'merchant' (Hieroglyph: ibha 'elephant' Rebus: ib 'iron') and maker of metal artifacts: kāṇḍā ‘metalware, tools, pots and pans’ (kāṇḍā mṛga 'rhinoceros' (Tamil).
Glazed steatite . Cylinder seal. 3.4cm high; imported from Indus valley. Rhinoceros, elephant, crocodile (lizard? ).Tell Asmar (Eshnunna), Iraq. IM 14674; Frankfort, 1955, No. 642; Collon, 1987, Fig. 610. ibha‘elephant’ Rebus: ibbo ‘merchant’, ib ‘iron’காண்டாமிருகம் kāṇṭā-mirukam , n. [M. kāṇṭāmṛgam.] Rhinoceros; கல்யானை. Rebus: kāṇḍā ‘metalware, tools, pots and pans’.kāru ‘crocodile’ Rebus: kāru ‘artisan’. Alternative: araṇe ‘lizard’ Rebus: airaṇ ‘anvil’.
Crocodile hieroglyph in combination with other animal hieroglphs also appears on a Mohenjo-daro seal m0489 in the context of an erotic Meluhha hieroglyph: a tergo copulation hieroglyph
m0489a,b,c Mohenjo-daro prism tablet
A standing human couple mating (a tergo); one side of a prism tablet from Mohenjo-daro (m489b). Other motifs on the inscribed object are: two goats eating leaves on a platform; a cock or hen (?) and a three-headed animal (perhaps antelope, one-horned bull and a short-horned bull). The leaf pictorial connotes on the goat composition connotes loa; hence, the reading is of this pictorial component is: lohar kamar = a blacksmith, worker in iron, superior to the ordinary kamar (Santali.)]
kāruvu ‘crocodile’ Rebus: ‘artisan, blacksmith’. pasaramu, pasalamu = an animal, a beast, a brute, quadruped (Telugu) Thus, the depiction of animals in epigraphs is related to, rebus: pasra = smithy (Santali)
pisera_ a small deer brown above and black below (H.)(CDIAL 8365).
ḍān:gra = wooden trough or manger sufficient to feed one animal (Mundari). iṭan:kārri = a capacity measure (Ma.) Rebus: ḍhan:gar ‘blacksmith’ (Bi.)
ḍān:gra = wooden trough or manger sufficient to feed one animal (Mundari). iṭan:kārri = a capacity measure (Ma.) Rebus: ḍhan:gar ‘blacksmith’ (Bi.)
pattar ‘goldsmiths’ (Ta.) patra ‘leaf’ (Skt.)
r-an:ku, ran:ku = fornication, adultery (Telugu); rebus: ranku ‘tin’ (Santali)
Rebus readings of Meluhha hieroglyphs:
Hieroglhyphs: elephant (ibha), boar/rhinoceros[kāṇḍā mṛga 'rhinoceros' (Tamil)], tiger (kol), tiger face turned (krammara), young bull calf (khōṇḍa) [खोंड m A young bull, a bullcalf. (Marathi)], antelope, ḍangur ʻbullockʼ, melh ‘goat’ (Brahui)
Rebus mleccha glosses: Ib 'iron' ibbo 'merchant'; kāṇḍā, 'tools, pots and pans, metalware'; kol 'worker in iron, smithy'; krammara, kamar 'smith, artisan', kõdā 'lathe-turner' [B. kõdā ‘to turn in a lathe’; Or. kū̆nda ‘lathe’, kũdibā, kū̃d ‘to turn’ (→ Drav. Kur. kū̃d ‘lathe’) (CDIAL 3295)], khũṭ ‘guild, community’, ḍāṅro ’blacksmith’ (Nepalese) milakkhu ‘copper’ (Pali) [Meluhha!]
Iron (ib), carpenter (badhi), smithy (kol ‘pancaloha’), alloy-smith (kol kamar)
tam(b)ra copper, milakkhu copper, bali (iron sand ore), native metal (aduru), ḍhangar ‘smith’.
Smithy with an armourer
http://www.harappa.com/indus/32.html Seal. Mohenjo-daro. Terracotta sealing from Mohenjo-daro depicting a collection of animals and some script symbols. In the centre is a horned crocodile (gharial) surrounded by other animals including a monkey.
In these seals of Mohenjo-daro ‘horned crocodile’ hieroglyph is the center-piece surrounded by hieroglyphs of a pair of bullocks, elephant, rhinoceros, tiger looking back and a monkey-like creature.
It is also possible that the centre-piece is an orthographic variation to depict the fin of a large fish.
Ta. kōṭaram monkey. Ir. kōḍa (small) monkey; kūḍag monkey. Ko. ko·ṛṇ small monkey. To. kwṛṇ monkey. Ka. kōḍaga monkey, ape. Koḍ. ko·ḍë monkey. Tu. koḍañji, koḍañja, koḍaṅgů baboon. (DEDR 2196). kuṭhāru = a monkey (Sanskrit) Rebus: kuṭhāru ‘armourer or weapons maker’(metal-worker), also an inscriber or writer.
Pa. kōḍ (pl. kōḍul) horn; Ka. kōḍu horn, tusk, branch of a tree; kōr horn Tu. kōḍů, kōḍu horn Ko. kṛ (obl. kṭ-)( (DEDR 2200) Paš. kōṇḍā ‘bald’, Kal. rumb. kōṇḍa ‘hornless’.(CDIAL 3508). Kal. rumb. khōṇḍ a ‘half’ (CDIAL 3792).
Rebus: koḍ 'workshop' (Gujarati) Thus, a horned crocodile is read rebus: koḍ khar 'blacksmith workshop'. khar ‘blacksmith’ (Kashmiri) kāruvu ‘crocodile’ Rebus: ‘artisan, blacksmith’.
Hieroglyph: Joined animals (tigers): sangaḍi = joined animals (M.) Rebus: sãgaṛh m. ʻ line of entrenchments, stone walls for defence ʼ (Lahnda)(CDIAL 12845) sang संग् m. a stone (Kashmiri) sanghāḍo (G.) = cutting stone, gilding; sangatarāśū = stone cutter; sangatarāśi = stone-cutting; sangsāru karan.u = to stone (S.), cankatam = to scrape (Ta.), sankaḍa (Tu.), sankaṭam = to scrape (Skt.) kol 'tiger' Rebus: kol 'working in iron'. Thus, the multi-headed tiger is read rebus: kol sangaḍi 'fortified place for metal (& ore stone) workers'.
Rebus readings of Hieroglyphs on two Meluhha tablets: Crocodile, tiger looking back, spy on tree
h1973B h1974B Harappa Two tablets. One side shows a person seated on a tree branch, a tiger looking up, a crocodile on the top register and other animals in procession in the bottom register. Obverse side (comparable to h1970, h1971 and h1972) shows an elephant, a person strangling two tigers (jackals or foxes) and a six-spoked wheel.
The glyphic which is common to both set 1 (h1970B, h1971B and h1972B) and set 2: (h1973B and h1974B) is: crocodile on the top register.
karā ‘crocodile’ (Telugu). Rebus: khara ‘blacksmith’ (Kashmiri)
Set 1: crocodile + person with foot on head of animal + spearing + bison + horned (with twig) seated person in penance
h1971B Harappa. Three tablets with identical glyphic compositions on both sides: h1970, h1971 and h1972. Seated figure or deity with reed house or shrine at one side. Left: H95-2524; Right: H95-2487.
Harappa. Planoconvex molded tablet found on Mound ET. A. Reverse. a female deity battling two tigers and standing above an elephant and below a six-spoked wheel; b. Obverse. A person spearing with a barbed spear a buffalo in front of a seated horned deity wearing bangles and with a plumed headdress. The person presses his foot down the buffalo’s head. An alligator with a narrow snout is on the top register. “We have found two other broken tablets at Harappa that appear to have been made from the same mold that was used to create the scene of a deity battling two tigers and standing above an elephant. One was found in a room located on the southern slope of Mount ET in 1996 and another example comes from excavations on Mound F in the 1930s. However, the flat obverse of both of these broken tablets does not show the spearing of a buffalo, rather it depicts the more well-known scene showing a tiger looking back over its shoulder at a person sitting on the branch of a tree. Several other flat or twisted rectangular terracotta tablets found at Harappa combine these two narrative scenes of a figure strangling two tigers on one side of a tablet, and the tiger looking back over its shoulder at a figure in a tree on the other side.” (JM Kenoyer, 1998, Ancient cities of the Indus Valley, Oxford University Press, p. 115.)
Set 2: crocodile + person seated on branch of tree + tiger looking back and up + rhinoceros + tiger in procession.
The following glyphics of m1431 prism tablet show the association between the tiger + person on tree glyphic set and crocile + 3 animal glyphic set.
Mohenjo-daro m1431 four-sided tablet. Row of animals in file (a one-horned bull, an elephant and a rhinoceros from right); a gharial with a fish held in its jaw above the animals; a bird (?) at right. Pict-116: From R.—a person holding a vessel; a woman with a platter (?); a kneeling person with a staff in his hands facing the woman; a goat with its forelegs on a platform under a tree. [Or, two antelopes flanking a tree on a platform, with one antelope looking backwards?]
One side (m1431B) of a four-sided tablet shows a procession of a tiger, an elephant and a rhinoceros (with fishes (or perhaps, crocodile) on top?).
koḍe ‘young bull’ (Telugu) खोंड [ khōṇḍa ] m A young bull, a bullcalf. Rebus: kõdā ‘to turn in a lathe’ (B.)कोंद kōnda ‘engraver, lapidary setting or infixing gems’ (Marathi) कोंडण [kōṇḍaṇa] f A fold or pen. (Marathi) ayakāra ‘ironsmith’ (Pali)[fish = aya (G.); crocodile = kāru (Te.)] baṭṭai quail (N.Santali) Rebus: bhaṭa = an oven, kiln, furnace (Santali)
ayo 'fish' Rebus: ayas 'metal'. kaṇḍa 'arrow' Rebus: khāṇḍa ‘tools, pots and pans, and metal-ware’. ayaskāṇḍa is a compounde word attested in Panini. The compound or glyphs of fish + arrow may denote metalware tools, pots and pans.kola 'tiger' Rebus: kol 'working in iron, alloy of 5 metals - pancaloha'. ibha 'elephant' Rebus ibbo 'merchant'; ib ‘iron'. Alternative: కరటి [ karaṭi ] karaṭi. [Skt.] n. An elephant. ఏనుగు (Telugu) Rebus: kharādī ‘ turner’ (Gujarati) kāṇḍa 'rhimpceros' Rebus:khāṇḍa ‘tools, pots and pans, and metal-ware’. The text on m0489 tablet: loa 'ficus religiosa' Rebus: loh 'copper'. kolmo 'rice plant' Rebus: kolami 'smithy, forge'. dula 'pair' Rebus: dul 'cast metal'. Thus the display of the metalware catalog includes the technological competence to work with minerals, metals and alloys and produce tools, pots and pans. The persons involved are krammara 'turn back' Rebus: kamar 'smiths, artisans'. kola 'tiger' Rebus: kol 'working in iron, working in pancaloha alloys'. పంచలోహము pancha-lōnamu. n. A mixed metal, composed of five ingredients, viz., copper, zinc, tin, lead, and iron (Telugu). Thus, when five svastika hieroglyphs are depicted, the depiction is of satthiya 'svastika' Rebus: satthiya 'zinc' and the totality of 5 alloying metals of copper, zinc, tin, lead and iron.
Glyph: Animals in procession: खांडा [khāṇḍā] A flock (of sheep or goats) (Marathi) கண்டி¹ kaṇṭi Flock, herd (Tamil) Rebus: khāṇḍā ‘tools, pots and pans, and metal-ware’.
m0489A One side of a prism tablet shows: crocodile + fish glyphic on the top register. Glyphs: crocodile + fish Rebus: ayakāra ‘blacksmith’ (Pali)
Glyph: Animals in procession: खांडा [khāṇḍā] A flock (of sheep or goats) (Marathi) கண்டி¹ kaṇṭi Flock, herd (Tamil) Rebus: khāṇḍā ‘tools, pots and pans, and metal-ware’.
It is possible that the broken portions of set 2 (h1973B and h1974B) showed three animals in procession: tiger looking back and up + rhinoceros + tiger.
Reverse side glyphs:
eraka ‘nave of wheel’. Rebus: era ‘copper’.
Animal glyph: elephant ‘ibha’. Rebus ibbo, ‘merchant’ (Gujarati).
Composition of glyphics: Woman with six locks of hair + one eye + thwarting + two pouncing tigers (jackals)+ nave with six spokes. Rebus: kola ‘woman’ + kaṇga ‘eye’ (Pego.), bhaṭa ‘six’+ dul‘casting (metal)’ + kũdā kol (tiger jumping) or lo ‘fox’ (WPah.) rebus: lōha ʻmetalʼ (Pali) + era āra (nave of wheel, six spokes), ibha (elephant). Rebus: era ‘copper’; kũdār dul kol ‘turner, casting, working in iron’;kan ‘brazier, bell-metal worker’; ibbo ‘merchant’.
The glyphic composition read rebus: copper, iron merchant with taṭu kanḍ kol bhaṭa ‘iron stone (ore) mineral ‘furnace’.
lōpāka m. ʻa kind of jackalʼ Suśr., lōpākikā -- f. lex. 1. H. lowā m. ʻfoxʼ.2. Ash. ẓōki, žōkī ʻfoxʼ, Kt. ŕwēki, Bashg. wrikī, Kal.rumb. lawák: < *raupākya -- NTS ii 228; -- Dm. rɔ̈̄pak ← Ir.? lōpāśá m. ʻfox, jackalʼ RV., lōpāśikā -- f. lex. [Cf. lōpāka -- . -- *lōpi -- ] Wg. liwášä, laúša ʻfoxʼ, Paš.kch. lowóċ, ar. lṓeč ʻjackalʼ (→ Shum. lṓeč NTS xiii 269), kuṛ. lwāinč; K. lośu, lōh, lohu, lôhu ʻporcupine, foxʼ.1. Kho. lōw ʻfoxʼ, Sh.gil. lótilde;i f., pales. lṓi f., lṓo m., WPah.bhal. lōī f., lo m.2. Pr. ẓūwī ʻfoxʼ.(CDIAL 11140-2).Rebus:lōhá ʻred, copper -- colouredʼ ŚrS., ʻmade of copperʼ ŚBr., m.n. ʻcopperʼ VS., ʻironʼ MBh. [*rudh -- ] Pa. lōha -- m. ʻmetal, esp. copper or bronzeʼ; Pk. lōha -- m. ʻironʼ, Gy. pal. li°, lihi, obl. elhás, as. loa JGLS new ser. ii 258; Wg. (Lumsden) "loa"ʻsteelʼ; Kho. loh ʻcopperʼ; S. lohu m. ʻironʼ, L. lohā m., awāṇ. lōˋā, P. lohā m. (→ K.rām. ḍoḍ. lohā), WPah.bhad. lɔ̃u n., bhal. lòtilde; n., pāḍ. jaun. lōh, paṅ. luhā, cur. cam. lohā, Ku. luwā, N. lohu, °hā, A. lo, B. lo, no, Or. lohā, luhā, Mth. loh, Bhoj. lohā, Aw.lakh. lōh, H. loh, lohā m., G. M. loh n.; Si. loho, lō ʻ metal, ore, iron ʼ; Md. ratu -- lō ʻ copper lōhá -- : WPah.kṭg. (kc.) lóɔ ʻironʼ, J. lohā m., Garh. loho; Md. lō ʻmetalʼ. (CDIAL 11158).
Glyph: ‘woman’: kola ‘woman’ (Nahali). Rebus kol ‘working in iron’ (Tamil)
Glyph: ‘impeding, hindering’: taṭu (Ta.) Rebus: dhatu ‘mineral’ (Santali) Ta. taṭu (-pp-, -tt) to hinder, stop, obstruct, forbid, prohibit, resist, dam, block up, partition off, curb, check, restrain, control, ward off, avert; n. hindering, checking, resisting; taṭuppu hindering, obstructing, resisting, restraint; Kur. ṭaṇḍnā to prevent, hinder, impede. Br. taḍ power to resist. (DEDR 3031)
Allograph: ‘notch’: Marathi: खांडा [ khāṇḍā ] m A jag, notch, or indentation (as upon the edge of a tool or weapon).
Glyph: ‘full stretch of one’s arms’: kāḍ 2 काड् । पौरुषम् m. a man's length, the stature of a man (as a measure of length) (Rām. 632, zangan kaḍun kāḍ, to stretch oneself the whole length of one's body. So K. 119). Rebus: kāḍ ‘stone’. Ga. (Oll.) kanḍ, (S.) kanḍu (pl. kanḍkil) stone (DEDR 1298). mayponḍi kanḍ whetstone; (Ga.)(DEDR 4628). (खडा) Pebbles or small stones: also stones broken up (as for a road), metal. खडा [ khaḍā ] m A small stone, a pebble. 2 A nodule (of lime &c.): a lump or bit (as of gum, assafœtida, catechu, sugar-candy): the gem or stone of a ring or trinket: a lump of hardened fæces or scybala: a nodule or lump gen. CDIAL 3018 kāṭha m. ʻ rock ʼ lex. [Cf. kānta -- 2 m. ʻ stone ʼ lex.] Bshk. kōr ʻ large stone ʼ AO xviii 239. கண்டு³ kaṇṭu , n. < gaṇḍa. 1. Clod, lump; கட்டி. (தைலவ. தைல.99.) 2. Wen; கழலைக்கட்டி. 3. Bead or something like a pendant in an ornament for the neck; ஓர் ஆபரணவுரு. புல்லிகைக்கண்ட நாண் ஒன்றிற் கட்டின கண்டு ஒன்றும் (S.I.I. ii, 429). (CDIAL 3023) kāṇḍa cluster, heap ʼ (in tr̥ṇa -- kāṇḍa -- Pāṇ. Kāś.). [Poss. connexion with gaṇḍa -- 2 makes prob. non -- Aryan origin (not with P. Tedesco Language 22, 190 < kr̥ntáti). Pa. kaṇḍa -- m.n. joint of stalk, lump. काठः A rock, stone. kāṭha m. ʻ rock ʼ lex. [Cf. kānta -- 2 m. ʻ stone ʼ lex.]Bshk. kōr ʻ large stone ʼ AO xviii 239.(CDIAL 3018). অয়সঠন [ aẏaskaṭhina ] as hard as iron; extremely hard (Bengali)
Glyph: ‘one-eyed’: काण a. [कण् निमीलने कर्तरि घञ् Tv.] 1 One-eyed; अक्ष्णा काणः Sk; काणेन चक्षुषा किं वा H. Pr.12; Ms.3.155. -2 Perforated, broken (as a cowrie) <kaNa>(Z) {ADJ} ``^one-^eyed, ^blind''. Ju<kaNa>(DP),,<kana>(K) {ADJ} ``^blind, blind in one eye''. (Munda) Go. (Ma.) kanḍ reppa eyebrow (Voc. 3047(a))(DEDR 5169). Ka. kāṇ (kaṇḍ-) to see; Ko. kaṇ-/ka·ṇ- (kaḍ-) to see; Koḍ. ka·ṇ- (ka·mb-, kaṇḍ-) to see; Ta. kāṇ (kāṇp-, kaṇṭ-) to see; Kol.kanḍt, kanḍakt seen, visible. (DEDR 1443). Ta. kaṇ eye, aperture, orifice, star of a peacock's tail. (DEDR 1159a) Rebus ‘brazier, bell-metal worker’: கன்னான் kaṉṉāṉ , n. < கன்¹. [M. kannān.] Brazier, bell-metal worker, one of the divisions of the Kammāḷa caste; செம்புகொட்டி. (திவா.) Ta. kaṉ copper work, copper, workmanship; kaṉṉāṉ brazier. Ma. kannān id. (DEDR 1402). கன்¹ kaṉ , n. perh. கன்மம். 1. Workmanship; வேலைப்பாடு. கன்னார் மதில்சூழ் குடந்தை (திவ். திருவாய். 5, 8, 3). 2. Copper work; கன்னார் தொழில். (W.) 3. Copper; செம்பு. (ஈடு, 5, 8, 3.) 4. See கன்னத்தட்டு. (நன். 217, விருத்.) கன்² kaṉ , n. < கல். 1. Stone; கல். (சூடா.) 2. Firmness; உறுதிப்பாடு. (ஈடு, 5, 8, 3.)
kã̄ḍ 2 काँड् m. a section, part in general; a cluster, bundle, multitude (Śiv. 32). kã̄ḍ 1 काँड् । काण्डः m. the stalk or stem of a reed, grass, or the like, straw. In the compound with dan 5 (p. 221a, l. 13) the word is spelt kāḍ.
kō̃da कोँद । कुलालादिकन्दुः f. a kiln; a potter's kiln (Rām. 1446; H. xi, 11); a brick-kiln (Śiv. 133); a lime-kiln. -bal -बल् । कुलालादिकन्दुस्थानम् m. the place where a kiln is erected, a brick or potter's kiln (Gr.Gr. 165). -- । कुलालादिकन्दुयथावद्भावः f.inf. a kiln to arise; met. to become like such a kiln (which contains no imperfectly baked articles, but only well-made perfectly baked ones), hence, a collection of good ('pucka') articles or qualities to exist.
kāru ‘crocodile’ (Telugu). Rebus: artisan (Marathi) Rebus: khar ‘blacksmith’ (Kashmiri) kola ‘tiger’ Rebus: kol ‘working in iron’. Heraka ‘spy’ Rebus: eraka ‘copper’. khōṇḍa ‘leafless tree’ (Marathi). Rebus: kõdār’turner’ (Bengali)
Looking back: krammara ‘look back’ Rebus: kamar ‘smith, artisan’.

One side of a triangular terracotta tablet (Md 013); surface find at Mohenjo-daro in 1936. Dept. of Eastern Art, Ashmolean Museum, Oxford.
Hieroglyph: kamaḍha 'penance' (Prakrit) kamaḍha, kamaṭha, kamaḍhaka, kamaḍhaga, kamaḍhaya = a type of penance (Prakrit)
Rebus: kamaṭamu, kammaṭamu = a portable furnace for melting precious metals; kammaṭīḍu = a goldsmith, a silversmith (Telugu) kãpṛauṭ jeweller's crucible made of rags and clay (Bi.); kampaṭṭam coinage, coin, mint (Tamil)
kamaṭhāyo = a learned carpenter or mason, working on scientific principles; kamaṭhāṇa [cf. karma, kām, business + sthāna, thāṇam, a place fr. Skt. sthā to stand] arrangement of one’s business; putting into order or managing one’s business (Gujarati)
The composition of two hieroglyphs: kāru 'crocodile' (Telugu) + kamaḍha 'a person seated in penance' (Prakrit) denote rebus: khar ‘blacksmith’ (Kashmiri); kāru ‘artisan’ (Marathi) + kamaṭa 'portable furnace'; kampaṭṭam 'coinage, coin, mint'. Thus, what the tablet conveys is the mint of a blacksmith. A copulating crocodile hieroglyph -- kāru 'crocodile' (Telugu) + kamḍa, khamḍa 'copulation' (Santali) -- conveys the same message: mint of a blacksmith kāru kampaṭṭa 'mint artisan'.
m1429B and two other tablets showing the typical composite hieroglyph of fish + crocodile. Glyphs: crocodile + fish ayakāra ‘blacksmith’ (Pali) kāru a wild crocodile or alligator (Telugu) aya 'fish' (Munda) The method of ligaturing enables creation of compound messages through Indus writing inscriptions. kāru a wild crocodile or alligator (Telugu) Rebus: khar ‘blacksmith’ (Kashmiri); kāru ‘artisan’ (Marathi).
Kashmiri glosses:
Pali: ayakāra ‘iron-smith’. ] Both ayaskāma and ayaskāra are attested in Panini (Pan. viii.3.46; ii.4.10). WPah. bhal. kamīṇ m.f. labourer (man or woman) ; MB. kāmiṇā labourer (CDIAL 2902) N. kāmi blacksmith (CDIAL 2900).
Kashmiri glosses:
khār 1 खार् । लोहकारः m. (sg. abl. khāra 1 खार ; the pl. dat. of this word is khāran 1 खारन् , which is to be distinguished from khāran 2, q.v., s.v.), a blacksmith, an iron worker (cf. bandūka-khār, p. 111b, l. 46; K.Pr. 46; H. xi, 17); a farrier (El.). This word is often a part of a name, and in such case comes at the end (W. 118) as in Wahab khār, Wahab the smith (H. ii, 12; vi, 17). khāra-basta khāra-basta खार-बस््त । चर्मप्रसेविका f. the skin bellows of a blacksmith. -büṭhü -ब&above;ठू&below; । लोहकारभित्तिः f. the wall of a blacksmith's furnace or hearth. -bāy -बाय् । लोहकारपत्नी f. a blacksmith's wife (Gr.Gr. 34). -dŏkuru लोहकारायोघनः m. a blacksmith's hammer, a sledge-hammer. -gȧji or -güjü - लोहकारचुल्लिः f. a blacksmith's furnace or hearth. -hāl -हाल् । लोहकारकन्दुः f. (sg. dat. -höjü -हा&above;जू&below; ), a blacksmith's smelting furnace; cf. hāl 5. -kūrü लोहकारकन्या f. a blacksmith's daughter. -koṭu - लोहकारपुत्रः m. the son of a blacksmith, esp. a skilful son, who can work at the same profession. -küṭü लोहकारकन्या f. a blacksmith's daughter, esp. one who has the virtues and qualities properly belonging to her father's profession or caste. -më˘ʦü 1 - लोहकारमृत्तिका f. (for 2, see [khāra 3] ), 'blacksmith's earth,' i.e. iron-ore. -nĕcyuwu लोहकारात्मजः m. a blacksmith's son. -nay -नय् । लोहकारनालिका f. (for khāranay 2, see [khārun] ), the trough into which the blacksmith allows melted iron to flow after smelting. -ʦañĕ । लोहकारशान्ताङ्गाराः f.pl. charcoal used by blacksmiths in their furnaces. -wānवान् । लोहकारापणः m. a blacksmith's shop, a forge, smithy (K.Pr. 3). -waṭh -वठ् । आघाताधारशिला m. (sg. dat. -waṭas -वटि ), the large stone used by a blacksmith as an anvil.
Thus, kharvaṭ may refer to an anvil. Meluhha kāru may refer to a crocodile; this rebus reading of the hieroglyph is.consistent with ayakāra ‘ironsmith’ (Pali) [fish = aya (G.); crocodile = kāru (Telugu)]
Lothal seal. L048 ibex
Fish sign incised on copper anthropomorph, Sheorajpur, upper Ganges valley, ca. 2nd millennium BCE, 4 kg; 47.7 X 39 X 2.1 cm. State Museum, Lucknow (O.37) Typical find of Gangetic Copper Hoards. miṇḍāl markhor (Tor.wali) meḍho a ram, a sheep (G.)(CDIAL 10120) Rebus: meḍh ‘helper of merchant’ (Gujarati) meḍ iron (Ho.) meṛed-bica = iron stone ore, in contrast to bali-bica, iron sand ore (Munda) ayo ‘fish’ Rebus: ayo, ayas ‘metal. Thus, together read rebus: ayo meḍh ‘iron stone ore, metal merchant.’
ayo ‘fish’ (Mu.); rebus: ayo ‘metal’ (Gujarati); ayas ‘alloy’ (Sanskrit) ayo kanka ‘fish+ rim-of-jar’ rebus: metal (alloy) account (kaṇakku) scribe.
Glyph of a crocodile and a lying-in woman
This glyph is part of one side of h180 Harappa tablet. A sequence of signs is repeated on both sides of the tablet.
h705B, h172B Harappa tablets show variants of crocodile hieroglyph.
The object between the outspread legs of the woman lying upside down is comparable orthography of a crocodile holding fiish in its jaws shown on tablets h705B and h172B. The snout of the crocodile is shown in copulation with the lying-in woman (as seen from the enlarged portion of h180 Harappa tablet).
Hieroglyph: r-an:ku, ran:ku = fornication, adultery (Telugu) Rebus: ranku ‘tin’ (Santali)
Hieroglyph: kamḍa, khamḍa 'copulation' (Santali) Rebus: kammaṭi a coiner (Ka.); kampaṭṭam coinage, coin, mint (Ta.) kammaṭa = mint, gold furnace (Te.) kamaṭa = portable furnace for melting precious metals (Telugu); kampaṭṭam = mint (Tamil)
Glyph: kuṭhi = pubes. Hieroglyph: kuṭhi pubes (lower down than paṇḍe) (Santali), pudendum muliebre (Munda, Santali) Cognates: koṭṭha (m. nt.) [Sk. koṣṭha abdomen, any cavity for holding food, cp. kuṣṭa groin, and also Gr.ku/tos cavity, ku/sdos pudendum muliebre, ku/stis bladder = E. cyst, chest; Lat. cunnus pudendum. kuṭhi = the womb, the female sexual organ; sorrege kuṭhi menaktaea, tale tale gidrakoa lit. her womb is near, she gets children continually (H. koṭhī, the womb) (Santali.Bodding) kōṣṭha = anyone of the large viscera (MBh.); koṭṭha = stomach (Pali.Pkt.); kuṭṭha (Pkt.); koṭhī heart, breast (L.); koṭṭhā, koṭhābelly (P.); koṭho (G.); koṭhā (M.)(CDIAL 3545). kottha pertaining to the belly (Pkt.); kothā corpulent (Or.)(CDIAL 3510). koṭho [Skt. koṣṭha inner part] the stomach, the belly (Gujarat) kūti = pudendum muliebre (Ta.); posteriors, membrum muliebre (Ma.); ku.0y anus, region of buttocks in general (To.); kūdi = anus, posteriors, membrum muliebre (Tu.)(DEDR 188). kūṭu = hip (Tu.); kuṭa = thigh (Pe.); kuṭe id. (Mand.); kūṭi hip (Kui)(DEDR 1885). gūde prolapsus of the anus (Ka.Tu.); gūda, gudda id. (Te.)(DEDR 1891).
Rebus: kuṭhi ‘smelter furnace’ (Santali) kuṛī f. ‘fireplace’ (H.); krvṛi f. ‘granary (WPah.); kuṛī, kuṛo house, building’(Ku.)(CDIAL 3232) kuṭi ‘hut made of boughs’ (Skt.) guḍi temple (Telugu)
Rebus: kuṭhi ‘a furnace for smelting iron ore to smelt iron’; kolheko kuṭhieda koles smelt iron (Santali) kuṭhi, kuṭi (Or.; Sad. koṭhi) (1) the smelting furnace of the blacksmith; kuṭire bica duljad.ko talkena, they were feeding the furnace with ore; (2) the name of ēkuṭi has been given to the fire which, in lac factories, warms the water bath for softening the lac so that it can be spread into sheets; to make a smelting furnace; kuṭhi-o of a smelting furnace, to be made; the smelting furnace of the blacksmith is made of mud, cone-shaped, 2’ 6” dia. At the base and 1’ 6” at the top. The hole in the centre, into which the mixture of charcoal and iron ore is poured, is about 6” to 7” in dia. At the base it has two holes, a smaller one into which the nozzle of the bellow is inserted, as seen in fig. 1, and a larger one on the opposite side through which the molten iron flows out into a cavity (Mundari) kuṭhi = a factory; lil kuṭhi = an indigo factory (koṭhi - Hindi) (Santali.Bodding) kuṭhi = an earthen furnace for smelting iron; make do., smelt iron; kolheko do kuṭhi benaokate baliko dhukana, the Kolhes build an earthen furnace and smelt iron-ore, blowing the bellows; tehen:ko kuṭhi yet kana, they are working (or building) the furnace to-day (H. koṭhī ) (Santali. Bodding) kuṭṭhita = hot, sweltering; molten (of tamba, cp. uttatta)(Pali.lex.) uttatta (ut + tapta) = heated, of metals: molten, refined; shining, splendid, pure (Pali.lex.) kuṭṭakam, kuṭṭukam = cauldron (Ma.); kuṭṭuva = big copper pot for heating water (Kod.)(DEDR 1668). gudgā to blaze; gud.va flame (Man.d); gudva, gūdūvwa, guduwa id. (Kuwi)(DEDR 1715). dāntar-kuṭha = fireplace (Sv.); kōti wooden vessel for mixing yeast (Sh.); kōlhā house with mud roof and walls, granary (P.); kuṭhī factory (A.); koṭhābrick-built house (B.); kuṭhī bank, granary (B.); koṭho jar in which indigo is stored, warehouse (G.); koṭhīlare earthen jar, factory (G.); kuṭhī granary, factory (M.)(CDIAL 3546). koṭho = a warehouse; a revenue office, in which dues are paid and collected; koṭhī a store-room; a factory (Gujarat) koḍ = the place where artisans work (Gujarati)
The overflowing pot held by the divinity on the left is a hieroglyph: lokhanDa 'pot overflowing water' Rebus: lokhaNDA 'metal pots and pans, metalware, weapons'. The overflowing pots are imageries on a cuneiform seals (unprovenanced).
lokhãḍ ‘overflowing pot’ Rebus: ʻtools, iron, ironwareʼ (Gujarati)
Source: http://eden-saga.com/en/sumer-mythology-anunnaki-oannes-nommo-viracocha-serpent-people-enki.html
lokhãḍ ‘overflowing pot’ Rebus: ʻtools, iron, ironwareʼ (Gujarati)lokhãḍ ‘overflowing pot’ Rebus: ʻtools, iron, ironwareʼ (Gujarati)
Overflowing water kaNDa. Dang 'mountain' Rebus: dhangar 'blacksmith'. ayo 'fish' rebus: aya 'metal alloy'
lokhãḍ ‘overflowing pot’ Rebus: ʻtools, iron, ironwareʼ (Gujarati)
lokhãḍ ‘overflowing pot’ Rebus: ʻtools, iron, ironwareʼ (Gujarati)
 Shell inlay: skirt-clad figure carrying fish, Early Dynastic III, ca. 2600-2350 BCE, Mesopotamia, Nippur, Sumerian.metmuseum.org
Shell inlay: skirt-clad figure carrying fish, Early Dynastic III, ca. 2600-2350 BCE, Mesopotamia, Nippur, Sumerian.metmuseum.org SUMER SCULPTURE 5TH-2ND MILL.BCE Fish-man or water-sprite. Terracotta figurine (8th-7th BCE) Length 12 cm Nr. 3337 Iraq Museum, Baghdad, Iraq
SUMER SCULPTURE 5TH-2ND MILL.BCE Fish-man or water-sprite. Terracotta figurine (8th-7th BCE) Length 12 cm Nr. 3337 Iraq Museum, Baghdad, Iraq
A map showing the principal canals of Lower Mesopotamia (p. 34. Map 2. "Map of Sumer, showing the course of ancient rivers and canals.
Overflowing pot. A cylinder seal of Enki (Ea) holding a pot with two streams of freshwater seated in his Abzu/Apsu shrine guarded by two naked men (Lakhmu?) holding stylized gate posts (?). Before him is his two-faced sukkal or vizier Izimud (cf. p. 98. "Ea." Piotr Bienkowski & Alan Millard. Dictionary of the Ancient Near East. Philadelphia. University of Pennsylvania Press. 2000).
lokhãḍ ‘overflowing pot’ Rebus: ʻtools, iron, ironwareʼ (Gujarati)
 Gudea. Overflowing pot. Sumer.
Gudea. Overflowing pot. Sumer.lokhãḍ ‘overflowing pot’ Rebus: ʻtools, iron, ironwareʼ (Gujarati)
(picture cf. p. 15. figure 7. "Fish Gods at the Tree pf Life; Assyria, c. 700 BC." Joseph Campbell. The Masks of God: Creative Mythology. New York. Viking Penguin. 1968. Reprinted 1976)
 Medallion. Makara, fishes. kara 'crocodile' rebus: khara 'blacksmith' ibha 'elephant' rebus: ib 'iron'; ayo 'fish' rebus: aya 'metal alloy'.
Medallion. Makara, fishes. kara 'crocodile' rebus: khara 'blacksmith' ibha 'elephant' rebus: ib 'iron'; ayo 'fish' rebus: aya 'metal alloy'.Hieroglyph multiplex: अयस् ayas 'alloymetal' + भरती bharatī (fish + quail, partridge) as 'metal + copper, pewter, tin alloy'
Mirror: http://tinyurl.com/ofmxt4j
In Indus Script Corpora which is catalogus catalogorum of metalwork of Meluhha artisans, a hieroglyph is displayed on 26+ objects shaped like fish (all found at Harappa) and with a high frequency of 1241 as a 'sign' in Mahadevan corpus of about 2000 inscriptions. Variants of fish hieroglyhph occur within this set:
अयस् áyas n. ʻ metal, iron ʼ RV.Pa. ayō nom. sg. n. and m., aya -- n. ʻ iron ʼ, Pk. aya -- n., Si. ya.ayaścūrṇa -- , ayaskāṇḍa -- , *ayaskūṭa -- .Addenda: áyas -- : Md. da ʻ iron ʼ, dafat ʻ piece of iron ʼ. (CDIAL 590) Ayo & Aya (nt.) [Sk. ayaḥ nt. iron & ore, Idg. *ajes -- , cp. Av. ayah, Lat. aes, Goth. aiz, Ohg. ēr (= Ger. Erz.), Ags. ār (= E. ore).] iron. The nom.ayo found only in set of 5 metals forming an alloy of gold (jātarūpa), viz. ayo, loha (copper), tipu (tin), sīsa (lead), sajjha (silver) A iii. 16 = Sv. 92; of obl. cases only the instr. ayasā occurs Dh 240 (= ayato DhA iii. 344); Pv i. 1013 (paṭikujjita, of Niraya). -- Iron is the material usedkat)e)coxh/n in the outfit & construction of Purgatory or Niraya (see niraya & Avīci & cp. Vism 56 sq.). -- In compn. both ayo˚ & aya˚ occur as bases. I. ayo˚: -- kapāla an iron pot A iv. 70 (v. l. ˚guhala); Nd2 304 iii. d 2v. 444; M iii. 183 = Nd2 304 iii. c v. 283; Dh 308; It 43 = 90; Th 2, 489; DA i. 84. -- ghana an iron club Ud 93; VvA 20. -- ghara an iron house J iv. 492. -- paṭala an iron roof or ceiling (of Niraya) PvA 52. -- pākāra an iron fence Pv i. 1013 = Nd2 304 iii. d 1iv. 492 (nāvā); Pv i. 1014 (bhūmi of N.); PvA 43, 52. -- muggara an iron club PvA 55. -- sanku an iron spike S iv. 168; Sn 667. II. aya˚: -- kapāla = ayo˚ DhA i. 148 (v. l. ayo˚). -kāra a worker in iron Miln 331. -- kūṭa = ayo˚ J i. 108; DhA ii. 69 (v. l.). -- nangala an iron plough DhA i. 223; iii. 67. -- paṭṭaka an iron plate or sheet (cp. loha˚) J v. 359. -- paṭhavi an iron floor (of Avīci) DhA i. 148. -- sanghāṭaka an iron (door) post DhA iv. 104. -- sūla an iron stake Sn 667; DhA i. 148. (Pali)
Fish 381
Fish + four gills (short strokes) 279
Fish + inverted 'V' superscript 216
Fish + oblique cross line 188
Fish + circumgraph of 4 notches 29
Fish shaped objects 26
Fish + notch (See hieroglyph multiplex on Harappa h-73 seal)
I agree with CJ Gadd that parenthesis ( ) hieroglyph component can be seen as split oval or lozenge. This split oval or lozenge is an ingot. Using ( ) as parenthesis, the circumscripted bird (quail, partridge) + fish hieroglyph multiplex can be seen as a descriptive pictorial motif of types of metal ingots: aya 'iron' + bharatI 'alloy of copper, pewter, tin'. Thus, the hieroglyph multiplex of parenthesis + fish + bird may signify the plain text: ingot of iron, alloy of copper, pewter, tin. This makes the portion of the text a descriptive metalwork catalogue of the metals turner (alloy mixer) from sangaR 'fortification'.
![]() m495G
m495G
![]() m1278
m1278
![]() m107
m107![]() m1169
m1169![]() m82
m82![]() m446
m446![]() m10
m10
It is submitted that it is consistent to read the bird hierolyph as bharatI 'quail, partridge' Rebus: bharat 'alloy of copper, pewter, tin'. Together with aya 'fish' Rebus: ayas 'metal alloy', the descriptive nature of the metalwork catalogue compiled on Indus inscription becomes a precise delineation of the artisan's competence in metallurgy.
Rebus-metonymy cipher of hieroglyph-multiplexes with 'fish' hierolyph component:
![Image result for indus script sign bird fish parenthesis]()
Text. Reading of glyphs on m0314 Seal impression. A notable featue of the sequencing of glyphs is the use of three variants of 'fish' glyphs on line 1 of the inscription. Each variant 'fish' glyph has been distinctively decoded as working with ore, metalwork (forging, turning) and casting.
Rebus decoding of glyphs on the seal impression:
Three lines of the inscription with glyphs can be read rebus from right to left -- listing the metallurgical competence of the artisans' guild:
Line 1: Turner workshop; forge, stone ore, ingot; excellent cast metal
Line 2: Metal workshop, ingot furnace, casting, riveting smithy,forge; Furnace scribe
Line 3: Smithy, lump of silver (forging metal); Mint, gold furnace; Smithy/forge; Turner small workshop
In Indus Script Corpora which is catalogus catalogorum of metalwork of Meluhha artisans, a hieroglyph is displayed on 26+ objects shaped like fish (all found at Harappa) and with a high frequency of 1241 as a 'sign' in Mahadevan corpus of about 2000 inscriptions. Variants of fish hieroglyhph occur within this set:
अयस् áyas n. ʻ metal, iron ʼ RV.Pa. ayō nom. sg. n. and m., aya -- n. ʻ iron ʼ, Pk. aya -- n., Si. ya.
Fish 381
Fish + four gills (short strokes) 279
Fish + inverted 'V' superscript 216
Fish + oblique cross line 188
Fish + circumgraph of 4 notches 29
Fish shaped objects 26
Fish + notch (See hieroglyph multiplex on Harappa h-73 seal)
I agree with CJ Gadd that parenthesis ( ) hieroglyph component can be seen as split oval or lozenge. This split oval or lozenge is an ingot. Using ( ) as parenthesis, the circumscripted bird (quail, partridge) + fish hieroglyph multiplex can be seen as a descriptive pictorial motif of types of metal ingots: aya 'iron' + bharatI 'alloy of copper, pewter, tin'. Thus, the hieroglyph multiplex of parenthesis + fish + bird may signify the plain text: ingot of iron, alloy of copper, pewter, tin. This makes the portion of the text a descriptive metalwork catalogue of the metals turner (alloy mixer) from sangaR 'fortification'.
 m495G
m495G m1278
m1278 m107
m107 m1169
m1169 m82
m82 m446
m446 m10
m10It is submitted that it is consistent to read the bird hierolyph as bharatI 'quail, partridge' Rebus: bharat 'alloy of copper, pewter, tin'. Together with aya 'fish' Rebus: ayas 'metal alloy', the descriptive nature of the metalwork catalogue compiled on Indus inscription becomes a precise delineation of the artisan's competence in metallurgy.
Rebus-metonymy cipher of hieroglyph-multiplexes with 'fish' hierolyph component:
Fish + scales, aya ã̄s (amśu) ‘metallic stalks of stone ore’. Vikalpa: badhoṛ ‘a species of fish with many bones’ (Santali) Rebus: baḍhoe ‘a carpenter, worker in wood’; badhoria ‘expert in working in wood’(Santali)khambhaṛā ʻfinʼ rebus: kammaṭṭam, kammiṭṭam coinage, mint.
Fish + splinter, aya aduru ‘smelted native metal’
Fish + sloping stroke, aya ḍhāḷ ‘metal ingot’
This may explain the occurrence of three fish hieroglyph multiplexes in sequence in a hypertext, as metalwork descriptive determinants on Mohenjodro 0304 seal impression:
Text. Reading of glyphs on m0314 Seal impression. A notable featue of the sequencing of glyphs is the use of three variants of 'fish' glyphs on line 1 of the inscription. Each variant 'fish' glyph has been distinctively decoded as working with ore, metalwork (forging, turning) and casting.
Rebus decoding of glyphs on the seal impression:
Three lines of the inscription with glyphs can be read rebus from right to left -- listing the metallurgical competence of the artisans' guild:
Line 1: Turner workshop; forge, stone ore, ingot; excellent cast metal
Line 2: Metal workshop, ingot furnace, casting, riveting smithy,forge; Furnace scribe
Line 3: Smithy, lump of silver (forging metal); Mint, gold furnace; Smithy/forge; Turner small workshop
The bharatI bird (quail, partridge) within parenthesis denotes: ingot of bharat 'alloy of copper, pewter, tin'
Decoding the identical inscription on Prism tablets m0494 and m0495
Line 1 Turner, mint, brass-work, furnace scribe, smelter, gridiron smithy, smithy/forge
Line 2 Mineral (ore), furnace/altar, furnace scribe workshop; metal (a kind of iron), casting furnace; cast metal ingot; casting workshop
Line 3 Furnace scribe workshop; cast bronze; kiln; gridiron; casting workshop; smithy (with) furnace; cast bronze; native metal; metal turner; furnace scribe.
http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2011/11/decoding-longest-inscription-of-indus.html
![]() Ayo ‘fish’; kaṇḍa ‘arrow’ See: अयस्कांत [ ayaskānta ] m S (The iron gem.) The loadstone. (Molesworth. Marathi)
Ayo ‘fish’; kaṇḍa ‘arrow’ See: अयस्कांत [ ayaskānta ] m S (The iron gem.) The loadstone. (Molesworth. Marathi)
Mohenjo-daro Seals m1118 and Kalibangan 032, glyphs used are: Zebu (bos taurus indicus), fish, four-strokes (allograph: arrow).ayo ‘fish’ (Mu.) + kaṇḍa ‘arrow’ (Skt.) ayaskāṇḍa ‘a quantity of iron, excellent iron’ (Pāṇ.gaṇ) aya = iron (G.); ayah, ayas = metal (Skt.) gaṆḌa, ‘four’ (Santali); Rebus: kaṇḍ ‘fire-altar’, ‘furnace’), arrow read rebus in mleccha (Meluhhan) as a reference to a guild of artisans working with ayaskāṇḍa ‘excellent quantity of iron’ (Pāṇini) is consistent with the primacy of economic activities which resulted in the invention of a writing system, now referred to as Indus Writing. poLa 'zebu' Rebus: poLa 'magnetite'.
![]() Harappa seal (H-73)[Note: the hieroglyph ‘water carrier’ pictorial of Ur Seal Impression becomes a hieroglyph sign] Hieroglyph: fish + notch: aya 'fish' + khāṇḍā m A jag, notch Rebus: aya 'metal'+ khāṇḍā ‘tools, pots and pans, metal-ware’. kuṭi 'water-carrier' Rebus: kuṭhi 'smelter'. खोंड (p. 216) [khōṇḍa] m A young bull, a bullcalf; खोंडा [ khōṇḍā ] m A
Harappa seal (H-73)[Note: the hieroglyph ‘water carrier’ pictorial of Ur Seal Impression becomes a hieroglyph sign] Hieroglyph: fish + notch: aya 'fish' + khāṇḍā m A jag, notch Rebus: aya 'metal'+ khāṇḍā ‘tools, pots and pans, metal-ware’. kuṭi 'water-carrier' Rebus: kuṭhi 'smelter'. खोंड (p. 216) [khōṇḍa] m A young bull, a bullcalf; खोंडा [ khōṇḍā ] m A कांबळा of which one end is formed into a cowl or hood. खोंडरूं [ khōṇḍarūṃ ] n A contemptuous form of खोंडा in the sense of कांबळा -cowl (Marathi); kōḍe dūḍa bull calf (Telugu); kōṛe 'young bullock' (Konda) rebus: kõdā ‘to turn in a lathe’ (Bengali) [The characteristic pannier which is ligatured to the young bull pictorial hieroglyph is a synonym खोंडा 'cowl' or 'pannier').खोंडी [ khōṇḍī ] f An outspread shovelform sack (as formed temporarily out of a कांबळा , to hold or fend off grain, chaff &c.) ] खोंड (p. 216) [ khōṇḍa ] m A young bull, a bullcalf.(Marathi) खोंडरूं [ khōṇḍarūṃ ] n A contemptuous form of खोंडा in the sense of कांबळा -cowl.खोंडा [ khōṇḍā ] m A कांबळा of which one end is formed into a cowl or hood. खोंडी [ khōṇḍī ] f An outspread shovelform sack (as formed temporarily out of a कांबळा , to hold or fend off grain, chaff &c.)
खोदणें Dug. 2 Engraved, carved, sculptured. http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2015/04/excavations-at-dholavifra-1989-2005-rs.html
The intimations of a metals turner as a scribe are also gleaned from the gloss: खोडाखोड or डी [ khōḍākhōḍa or ḍī ] f (खोडणें ) Erasing, altering, interlining &c. in numerous places: also the scratched, scrawled, and disfigured state of the paper so operated upon; खोडींव [ khōḍīṃva ] p of खोडणें v c Erased or crossed out.Marathi). खोडपत्र [ khōḍapatra ] n Commonly खोटपत्र .खोटपत्र [ khōṭapatra ] n In law or in caste-adjudication. A written acknowledgment taken from an offender of his falseness or guilt: also, in disputations, from the person confuted. (Marathi) Thus, khond 'turner' is also an engraver, scribe.
That a metals turner is engaged in metal alloying is evident from the gloss: खोट [ khōṭa ] f A mass of metal (unwrought or of old metal melted down); an ingot or wedge. Hence 2 A lump or solid bit (as of phlegm, gore, curds, inspissated milk); any concretion or clot.खोटीचा Composed or made of खोट , as खोटीचें भांडें .
In addition, hierolyph multiplexes include 'fish': fish + bird within parenthesis; bird + fish within parenthesis. In the context of the water-carrier hieroglyph PLUS stars enclosed within parenthesis, CJ Gadd had rightly noted that these are determinatives that the writing system was hieroglyphic.
By ligaturing hieroglyph components and by creating hieroglyph multiplexes such as fish + bird, the messaging system seeks to convey semantics of the technical specifications of metalwork catalogues.
![]() With curved horns, the ’anthropomorph’ is a ligature of a mountain goat or markhor (makara) and a fish incised between the horns. Typical find of Gangetic Copper Hoards. At Sheorajpur, three anthropomorphs in metal were found. (Sheorajpur, Dt. Kanpur. Three anthropomorphic figures of copper. AI, 7, 1951, pp. 20, 29).
With curved horns, the ’anthropomorph’ is a ligature of a mountain goat or markhor (makara) and a fish incised between the horns. Typical find of Gangetic Copper Hoards. At Sheorajpur, three anthropomorphs in metal were found. (Sheorajpur, Dt. Kanpur. Three anthropomorphic figures of copper. AI, 7, 1951, pp. 20, 29).
![]() Seal National Museum, Delhi. barad, barat 'ox' Rebus: bharat 'alloy of copper, pewter, tin'(Marathbaruth
Seal National Museum, Delhi. barad, barat 'ox' Rebus: bharat 'alloy of copper, pewter, tin'(Marathbaruth बरुथ् । संसृष्टद्रावितधातुमयः m. (sg. dat. baratas बरतस् ), a dish or other vessel made of an alloy of several metals melted together. (Kashmiri) L. bhāraṇ ʻ to spread or bring out from a kiln ʼ; G. bhārvũ ʻ to keep live coals buried in ashes ʼ(CDIAL 9463)
Matsya avatara in Hindu tradition, Fish hieroglyph ligatured to a man from Nimrud, Khorsabad artefacts and a Babylonian seal
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Source for images: http://alternatewars.com/Mythology/Reliquary/Reliquary_Mermaid_Symbolism.htm
m1429C
![]()
![]() A fragment of a relief 'The spinner' made of bitumen mastic of Neo-Elamite period (8th cent. BCE-mid 6th cent. BCE) was found in Susa. This fragment displayed a well-coiffured woman being fanned by an attendant while the woman wearing bangles on both arms -- seated on a stool with feline legs -- held what may be a spinning device before a table with feline legs with a bowl containing a whole fish with six blobs assembled on top of the fish.
A fragment of a relief 'The spinner' made of bitumen mastic of Neo-Elamite period (8th cent. BCE-mid 6th cent. BCE) was found in Susa. This fragment displayed a well-coiffured woman being fanned by an attendant while the woman wearing bangles on both arms -- seated on a stool with feline legs -- held what may be a spinning device before a table with feline legs with a bowl containing a whole fish with six blobs assembled on top of the fish.
Hieroroglyph: aya 'fish' Rebus: aya 'iron' (Gujarati) ayas 'metal' (Rigveda)
kola 'tiger' Rebus: kolle 'blacksmith' kol 'working in iron'; kolhe 'smelter' kole.l 'smithy, temple'; kolimi 'smithy, forge' Hieroglyph: bhaTa 'six' Rebus: baTa 'furnace'. kAtI 'spinner' Rebus: kAtI 'wheelwright'
![]()
![]() aya 'fish' Rebus: aya, ayas 'iron, metal'
aya 'fish' Rebus: aya, ayas 'iron, metal'![]() aya dhAL, 'fish+slanted stroke' Rebus: aya DhALako 'iron/metal ingot'
aya dhAL, 'fish+slanted stroke' Rebus: aya DhALako 'iron/metal ingot'![]() aya aDaren,'fish+superscript lid' Rebus: aya aduru 'iron/metal native unsmelted metal'
aya aDaren,'fish+superscript lid' Rebus: aya aduru 'iron/metal native unsmelted metal'![]() aya khANDa, 'fish+notch' Rebus: aya khaNDa 'iron/metal implements'
aya khANDa, 'fish+notch' Rebus: aya khaNDa 'iron/metal implements'![]() aya kolom 'fish+ numeral 3' Rebus:aya kolimi 'iron/metal smithy/forge'
aya kolom 'fish+ numeral 3' Rebus:aya kolimi 'iron/metal smithy/forge'![]() aya baTa 'fish+numeral 6' Rebus: aya bhaTa 'iron/metal furnace'
aya baTa 'fish+numeral 6' Rebus: aya bhaTa 'iron/metal furnace'![]() aya gaNDa kolom'fish+numeral4+numeral3' Rebus: aya khaNDa kolimi 'metal/iron implements smithy/forge'
aya gaNDa kolom'fish+numeral4+numeral3' Rebus: aya khaNDa kolimi 'metal/iron implements smithy/forge'![]() aya dula 'fish+two' Rebus: aya dul 'metal/iron cast metal or metalcasting'
aya dula 'fish+two' Rebus: aya dul 'metal/iron cast metal or metalcasting'![]() aya tridhAtu 'fish+three strands of rope' Rebus: aya kolom dhatu 'metal/iron , three mineral ores'
aya tridhAtu 'fish+three strands of rope' Rebus: aya kolom dhatu 'metal/iron , three mineral ores'![]() Ayo ‘fish’; kaṇḍa ‘arrow’ See: अयस्कांत [ ayaskānta ] m S (The iron gem.) The loadstone. (Molesworth. Marathi) Fish + circumgraph of 4 (gaNDa) notches: ayaskāṇḍa ‘a quantity of iron, excellent iron’ (Pāṇ.gaṇ) The gloss kāṇḍa may also signify 'metal implements'. A cognate compound in Santali has: me~r.he~t khaNDa 'iron implements'.
Ayo ‘fish’; kaṇḍa ‘arrow’ See: अयस्कांत [ ayaskānta ] m S (The iron gem.) The loadstone. (Molesworth. Marathi) Fish + circumgraph of 4 (gaNDa) notches: ayaskāṇḍa ‘a quantity of iron, excellent iron’ (Pāṇ.gaṇ) The gloss kāṇḍa may also signify 'metal implements'. A cognate compound in Santali has: me~r.he~t khaNDa 'iron implements'.
Mohenjo-daro Seals m1118 and Kalibangan 032, glyphs used are: Zebu (bos taurus indicus), fish, four-strokes (allograph: arrow).ayo ‘fish’ (Mu.) + kaṇḍa ‘arrow’ (Skt.) ayaskāṇḍa ‘a quantity of iron, excellent iron’ (Pāṇ.gaṇ) aya = iron (G.); ayah, ayas = metal (Skt.) gaṆḌa, ‘four’ (Santali); Rebus: kaṇḍ ‘fire-altar’, ‘furnace’), arrow read rebus in mleccha (Meluhhan) as a reference to a guild of artisans working with ayaskāṇḍa ‘excellent quantity of iron’ (Pāṇini) is consistent with the primacy of economic activities which resulted in the invention of a writing system, now referred to as Indus Writing. poLa 'zebu' Rebus: poLa 'magnetite'.![]() Harappa seal (H-73)[Note: the hieroglyph ‘water carrier’ pictorial of Ur Seal Impression becomes a hieroglyph sign] Hieroglyph: fish + notch: aya 'fish' + khāṇḍā m A jag, notch Rebus: aya 'metal'+ khāṇḍā ‘tools, pots and pans, metal-ware’. kuṭi 'water-carrier' Rebus: kuṭhi 'smelter'. खोंड (p. 216) [khōṇḍa] m A young bull, a bullcalf; खोंडा [ khōṇḍā ] m A
Harappa seal (H-73)[Note: the hieroglyph ‘water carrier’ pictorial of Ur Seal Impression becomes a hieroglyph sign] Hieroglyph: fish + notch: aya 'fish' + khāṇḍā m A jag, notch Rebus: aya 'metal'+ khāṇḍā ‘tools, pots and pans, metal-ware’. kuṭi 'water-carrier' Rebus: kuṭhi 'smelter'. खोंड (p. 216) [khōṇḍa] m A young bull, a bullcalf; खोंडा [ khōṇḍā ] m A कांबळा of which one end is formed into a cowl or hood. खोंडरूं [ khōṇḍarūṃ ] n A contemptuous form of खोंडा in the sense of कांबळा -cowl (Marathi); kōḍe dūḍa bull calf (Telugu); kōṛe 'young bullock' (Konda) rebus: kõdā ‘to turn in a lathe’ (Bengali) [The characteristic pannier which is ligatured to the young bull pictorial hieroglyph is a synonym खोंडा 'cowl' or 'pannier').खोंडी [ khōṇḍī ] f An outspread shovelform sack (as formed temporarily out of a कांबळा , to hold or fend off grain, chaff &c.) ] खोंड (p. 216) [ khōṇḍa ] m A young bull, a bullcalf.(Marathi) खोंडरूं [ khōṇḍarūṃ ] n A contemptuous form of खोंडा in the sense of कांबळा -cowl.खोंडा [ khōṇḍā ] m A कांबळा of which one end is formed into a cowl or hood. खोंडी [ khōṇḍī ] f An outspread shovelform sack (as formed temporarily out of a कांबळा , to hold or fend off grain, chaff &c.)
खोदणें Dug. 2 Engraved, carved, sculptured. http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2015/04/excavations-at-dholavifra-1989-2005-rs.html
The intimations of a metals turner as a scribe are also gleaned from the gloss: खोडाखोड or डी [ khōḍākhōḍa or ḍī ] f (खोडणें ) Erasing, altering, interlining &c. in numerous places: also the scratched, scrawled, and disfigured state of the paper so operated upon; खोडींव [ khōḍīṃva ] p of खोडणें v c Erased or crossed out.Marathi). खोडपत्र [ khōḍapatra ] n Commonly खोटपत्र .खोटपत्र [ khōṭapatra ] n In law or in caste-adjudication. A written acknowledgment taken from an offender of his falseness or guilt: also, in disputations, from the person confuted. (Marathi) Thus, khond 'turner' is also an engraver, scribe.
That a metals turner is engaged in metal alloying is evident from the gloss: खोट [ khōṭa ] f A mass of metal (unwrought or of old metal melted down); an ingot or wedge. Hence 2 A lump or solid bit (as of phlegm, gore, curds, inspissated milk); any concretion or clot.खोटीचा Composed or made of खोट , as खोटीचें भांडें .
![]() A Susa ritual basin dated to ca. 12th or 13th century BCE depicts goat and fish ligatured into a 'fabulous' or 'composite' animal representation, clearly intended to connote the underlying hieroglyphic meaning. Susa ritual basin dates from 13th or 12th cent. BCE. The hieroglyph-multiplex flanks reedposts, spathes, molluscs. http://www.louvre.fr/en/oeuvre-notices/ritual-basin-decorated-goatfish-figures aya 'fish' Rebus: aya 'iron' (Gujarati) ayas 'metal' (Rigveda) meḷh ‘goat’ (Br. mr̤eka (Te.); mēṭam (Ta.); meṣam (Samskritam) Te. mr̤eka (DEDR 5087) (DEDR 5087) Rebus: meluh.h.a (Akkadian) mleccha (Samskritam) milakkhu 'copper' (Pali) An alternative reading for the composite animal: goat PLUS fish-fin. mr̤eka 'copper' rebus: milakkhu 'copper' PLUS khamba 'wing' fish-fin 'khambhaṛā' (Lahnda) rebus: kammaTa 'mint' (Kannada) eruvai 'reed' rebus: eruvai 'copper' sippi 'mollusc' rebus: sippi 'artificer, sculptor'. Thus, the hieroglyph-multiplex (hypertext) signifies a copper metalwork sculptor. The basin is for purification by Potr. 'purifier' who is also dhā̆vaḍ 'smelter', derived from dhāˊtu n. ʻ substance ʼ RV; dhāu -- m. ʻ metal, red chalk ʼ (Prakrtam)
A Susa ritual basin dated to ca. 12th or 13th century BCE depicts goat and fish ligatured into a 'fabulous' or 'composite' animal representation, clearly intended to connote the underlying hieroglyphic meaning. Susa ritual basin dates from 13th or 12th cent. BCE. The hieroglyph-multiplex flanks reedposts, spathes, molluscs. http://www.louvre.fr/en/oeuvre-notices/ritual-basin-decorated-goatfish-figures aya 'fish' Rebus: aya 'iron' (Gujarati) ayas 'metal' (Rigveda) meḷh ‘goat’ (Br. mr̤eka (Te.); mēṭam (Ta.); meṣam (Samskritam) Te. mr̤eka (DEDR 5087) (DEDR 5087) Rebus: meluh.h.a (Akkadian) mleccha (Samskritam) milakkhu 'copper' (Pali) An alternative reading for the composite animal: goat PLUS fish-fin. mr̤eka 'copper' rebus: milakkhu 'copper' PLUS khamba 'wing' fish-fin 'khambhaṛā' (Lahnda) rebus: kammaTa 'mint' (Kannada) eruvai 'reed' rebus: eruvai 'copper' sippi 'mollusc' rebus: sippi 'artificer, sculptor'. Thus, the hieroglyph-multiplex (hypertext) signifies a copper metalwork sculptor. The basin is for purification by Potr. 'purifier' who is also dhā̆vaḍ 'smelter', derived from dhāˊtu n. ʻ substance ʼ RV; dhāu -- m. ʻ metal, red chalk ʼ (Prakrtam)
![]()
![]() Ligatures to fish: parentheses + snout dul kuṭila ayas 'cast bronze ayas alloy with tuttha, copper sulphate'
Ligatures to fish: parentheses + snout dul kuṭila ayas 'cast bronze ayas alloy with tuttha, copper sulphate'
![]() With curved horns, the ’anthropomorph’ is a ligature of a mountain goat or markhor (makara) and a fish incised between the horns. Typical find of Gangetic Copper Hoards. At Sheorajpur, three anthropomorphs in metal were found. (Sheorajpur, Dt. Kanpur. Three anthropomorphic figures of copper. AI, 7, 1951, pp. 20, 29).
With curved horns, the ’anthropomorph’ is a ligature of a mountain goat or markhor (makara) and a fish incised between the horns. Typical find of Gangetic Copper Hoards. At Sheorajpur, three anthropomorphs in metal were found. (Sheorajpur, Dt. Kanpur. Three anthropomorphic figures of copper. AI, 7, 1951, pp. 20, 29).
Text: aya khaNDa kolimi 'metal/iron implements smithy/forge'
Pictorial motifs or hieroglyph-multiplexes: sangaDa 'lathe, portable furnace' Rebus: sangar 'fortification' sanghAta 'adamantine glue' (Varahamihira) samghAta 'collection of articles (i.e. cargo)' PLUS khōṇḍa m A young bull, a bullcalf (Marathi) kōḍe dūḍa bull calf (Telugu); kōṛe 'young bullock' (Konda)Rebus: kõdā 'to turn in a lathe' (Bengali)
![]() mū̃h ‘ingot’ (Santali) PLUS (infixed) kolom 'sprout, rice plant' Rebus: kolimi 'smithy, forge' Thus, ingot smithy
mū̃h ‘ingot’ (Santali) PLUS (infixed) kolom 'sprout, rice plant' Rebus: kolimi 'smithy, forge' Thus, ingot smithy ![]() kolom 'rice-plant, sprout' Rebus: kolimi 'smithy, forge' (Alternative: kuTi 'tree' Rebus: kuThi 'smelter')
kolom 'rice-plant, sprout' Rebus: kolimi 'smithy, forge' (Alternative: kuTi 'tree' Rebus: kuThi 'smelter')
kaṇḍa kanka ‘rim of jar’ Rebus: karṇīka ‘account (scribe)’karṇī‘supercargo’.
kaṇḍa ‘fire-altar’.
लोह --कार [p= 908,3]
kamaṭh a crab (Skt.) kamāṭhiyo=archer;kāmaṭhum =a bow; kāmaḍī ,kāmaḍum=a chip of bamboo (G.) kāmaṭhiyo bowman; an archer(Skt.lex.) kamaṛkom= fig leaf (Santali.lex.)kamarmaṛā(Has.), kamaṛkom(Nag.); the petiole or stalk of a leaf (Mundari.lex.)kamaṭha= fig leaf, religiosa(Skt.) dula‘tw' Rebus: dul 'cast metal ’Thus, cast loh ‘copper casting’ infurnace:baṭa= wide-mouthed pot; baṭa= kiln (Te.) kammaṭa=portable furnace(Te.) kampaṭṭam 'coiner,mint' (Tamil) kammaṭa (Malayalam) The hieroglyph-multiplex (Sign 124 Parpola conconcordance), thus orthographically signifies two ficus leaves ligatured to the top edge of a wide rimless pot and a pincers/tongs hieroglyph is inscripted. In this hieroglyph-multiplex three hieroglyph components are signified: 1. rimless pot, 2. two ficus leaves, 3. pincers. baTa 'rimless pot' Rebus: bhaTa 'furnace'; loa 'ficus' Rebus: loha 'copper, iron'; kAru 'pincers' Rebus: khAra 'blacksmith'
![]() Santali glosses. Lexis.
Santali glosses. Lexis.
This indication of the occurrence, together, of two or more 'fish' hieroglyphs with modifiers is an assurance that the modifiers ar semantic indicators of how aya 'metal' is worked on by the artisans.
ayakāṇḍa ‘’large quantity of stone (ore) metal’ or aya kaṇḍa, ‘metal fire-altar’. ayo, hako 'fish'; ãs = scales of fish (Santali); rebus: aya ‘metal, iron’ (G.); ayah, ayas = metal (Skt.) Santali lexeme, hako ‘fish’ is concordant with a proto-Indic form which can be identified as ayo in many glosses, Munda, Sora glosses in particular, of the Indian linguistic area.
 Ayo ‘fish’; kaṇḍa ‘arrow’ See: अयस्कांत [ ayaskānta ] m S (The iron gem.) The loadstone. (Molesworth. Marathi)
Ayo ‘fish’; kaṇḍa ‘arrow’ See: अयस्कांत [ ayaskānta ] m S (The iron gem.) The loadstone. (Molesworth. Marathi)Fish + circumgraph of 4 (gaNDa) notches: ayaskāṇḍa ‘a quantity of iron, excellent iron’ (Pāṇ.gaṇ) The gloss kāṇḍa may also signify 'metal implements'. A cognate compound in Santali has: me~r.he~t khaNDa 'iron implements'.
Mohenjo-daro Seals m1118 and Kalibangan 032, glyphs used are: Zebu (bos taurus indicus), fish, four-strokes (allograph: arrow).ayo ‘fish’ (Mu.) + kaṇḍa ‘arrow’ (Skt.) ayaskāṇḍa ‘a quantity of iron, excellent iron’ (Pāṇ.gaṇ) aya = iron (G.); ayah, ayas = metal (Skt.) gaṆḌa, ‘four’ (Santali); Rebus: kaṇḍ ‘fire-altar’, ‘furnace’), arrow read rebus in mleccha (Meluhhan) as a reference to a guild of artisans working with ayaskāṇḍa ‘excellent quantity of iron’ (Pāṇini) is consistent with the primacy of economic activities which resulted in the invention of a writing system, now referred to as Indus Writing. poLa 'zebu' Rebus: poLa 'magnetite'.
‘Dotted circle’ is a sacred glyph. It is a hieroglyph.
Text 5477 Dotted circles + circumscribed fish + 'comb' motif. aya ‘fish’ (Mu.); rebus: aya ‘metal’ (Skt.)
gaṇḍa set of four (Santali) kaṇḍa ‘fire-altar’ khareḍo = a currycomb (G.) Rebus: kharādī ‘ turner’ (G.)Fish + notch: Sign 15 occurs togethe with a notch-in-fixed fish hieroglyph on Harappa 73 seal:
 Harappa seal (H-73)[Note: the hieroglyph ‘water carrier’ pictorial of Ur Seal Impression becomes a hieroglyph sign] Hieroglyph: fish + notch: aya 'fish' + khāṇḍā m A jag, notch Rebus: aya 'metal'+ khāṇḍā ‘tools, pots and pans, metal-ware’. kuṭi 'water-carrier' Rebus: kuṭhi 'smelter'. खोंड (p. 216) [khōṇḍa] m A young bull, a bullcalf; खोंडा [ khōṇḍā ] m A
Harappa seal (H-73)[Note: the hieroglyph ‘water carrier’ pictorial of Ur Seal Impression becomes a hieroglyph sign] Hieroglyph: fish + notch: aya 'fish' + khāṇḍā m A jag, notch Rebus: aya 'metal'+ khāṇḍā ‘tools, pots and pans, metal-ware’. kuṭi 'water-carrier' Rebus: kuṭhi 'smelter'. खोंड (p. 216) [khōṇḍa] m A young bull, a bullcalf; खोंडा [ khōṇḍā ] m A Hieroglyph: kōḍ 'horn' Rebus: kōḍ 'place where artisans work, workshop' কুঁদন, কোঁদন [ kun̐dana, kōn̐dana ] n act of turning (a thing) on a lathe; act of carving (Bengali) कातारी or कांतारी (p. 154) [ kātārī or kāntārī ] m (कातणें ) A turner.(Marathi)
Rebus: खोदकाम [ khōdakāma ] n Sculpture; carved work or work for the carver.
खोदगिरी [ khōdagirī ] f Sculpture, carving, engraving: also sculptured or carved work.खोदणें [ khōdaṇēṃ ] v c & i (The intimations of a metals turner as a scribe are also gleaned from the gloss: खोडाखोड or डी [ khōḍākhōḍa or ḍī ] f (
That a metals turner is engaged in metal alloying is evident from the gloss: खोट [ khōṭa ] f A mass of metal (unwrought or of old metal melted down); an ingot or wedge. Hence 2 A lump or solid bit (as of phlegm, gore, curds, inspissated milk); any concretion or clot.
In addition, hierolyph multiplexes include 'fish': fish + bird within parenthesis; bird + fish within parenthesis. In the context of the water-carrier hieroglyph PLUS stars enclosed within parenthesis, CJ Gadd had rightly noted that these are determinatives that the writing system was hieroglyphic.
By ligaturing hieroglyph components and by creating hieroglyph multiplexes such as fish + bird, the messaging system seeks to convey semantics of the technical specifications of metalwork catalogues.
 With curved horns, the ’anthropomorph’ is a ligature of a mountain goat or markhor (makara) and a fish incised between the horns. Typical find of Gangetic Copper Hoards. At Sheorajpur, three anthropomorphs in metal were found. (Sheorajpur, Dt. Kanpur. Three anthropomorphic figures of copper. AI, 7, 1951, pp. 20, 29).
With curved horns, the ’anthropomorph’ is a ligature of a mountain goat or markhor (makara) and a fish incised between the horns. Typical find of Gangetic Copper Hoards. At Sheorajpur, three anthropomorphs in metal were found. (Sheorajpur, Dt. Kanpur. Three anthropomorphic figures of copper. AI, 7, 1951, pp. 20, 29).One anthropomorph had fish hieroglyph incised on the chest of the copper object, Sheorajpur, upper Ganges valley, ca. 2nd millennium BCE, 4 kg; 47.7 X 39 X 2.1 cm. State Museum, Lucknow (O.37) Typical find of Gangetic Copper Hoards. miṇḍāl markhor (Tor.wali) meḍho a ram, a sheep (G.)(CDIAL 10120) Rebus: meḍh ‘helper of merchant’ (Gujarati) meḍ iron (Ho.) meṛed-bica = iron stone ore, in contrast to bali-bica, iron sand ore (Munda) ayo ‘fish’ Rebus: ayo, ayas ‘metal. Thus, together read rebus: ayo meḍh ‘iron stone ore, metal merchant.’
See: http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2015/05/composite-copper-alloy-anthropomorphic.htmlmiṇḍāl markhor (Tor.wali) meḍho a ram, a sheep (G.)(CDIAL 10120) Rebus: meḍh ‘helper of merchant’ (Gujarati) meḍ iron (Ho.) meṛed-bica = iron stone ore, in contrast to bali-bica, iron sand ore (Munda) ayo ‘fish’ Rebus: ayo, ayas ‘metal. Thus, together read rebus: ayo meḍh ‘iron stone ore, metal merchant.’
ayo ‘fish’ (Mu.); rebus: ayo ‘metal’ (Gujarati); ayas ‘alloy’ (Sanskrit) ayo kanka ‘fish+ rim-of-jar’ rebus: metal (alloy) account (kaṇakku) scribe. karNaka 'rim of jar' karava 'narrow neck jar' Rebus: karNI 'supercargo' karNIka 'scribe' karba 'iron' kharva 'nidhi, wealth'. kāruvu 'artisan' (Telugu) khār 'blacksmith' (Kashmiri)
 Seal National Museum, Delhi. barad, barat 'ox' Rebus: bharat 'alloy of copper, pewter, tin'(Marathbaruth
Seal National Museum, Delhi. barad, barat 'ox' Rebus: bharat 'alloy of copper, pewter, tin'(Marathbaruth On a Mohenjo-daro seal, ayo 'fish' read rebus ayas 'metal'; ḍangar 'bull' read rebus ḍhangar 'blacksmith'; koṭ 'horn; red rebus: khoṭ 'alloy'; khoṇḍ 'young bull-calf' read rebus khuṇḍ '(metal) turner'. The ayo 'fish' hieroglyph thus adequately categorizes the metalware contents of a pot discovered in Susa.
Kalibangan 37, 34
Two Kalibangan seals show an antelope and fish glyphs as the inscription. Mẽḍha ‘antelope’; rebus: ‘iron’ (Ho.) ayo ‘fish’; rebs: ayo ‘metal’ (G.) [These are examples which clearly demonstrate that Indus script is a glyptic writing system and hence, all glyphs and glyptic elements have to be decoded.] miṇḍālmarkhor (Tor.wali) meḍho a ram, a sheep (G.)(CDIAL 10120) iron (Ho.) meṛed-bica = iron stone ore, in contrast to bali-bica, iron sand ore (Munda) meḍ ‘iron’.
Matsya avatara in Hindu tradition, Fish hieroglyph ligatured to a man from Nimrud, Khorsabad artefacts and a Babylonian seal




Source for images: http://alternatewars.com/Mythology/Reliquary/Reliquary_Mermaid_Symbolism.htm
m1429C
ayo ‘fish’ (Mu.); rebus: aya ‘(alloyed) metal’ (G.) kāru a wild crocodile or alligator (Te.) Rebus: khār a blacksmith, an iron worker (cf. bandūka-khār) (Kashmiri) ayakāra ‘blacksmith’ (Pali)

One side of a triangular terracotta tablet (Md 013); surface find at Mohenjo-daro in 1936. Dept. of Eastern Art, Ashmolean Museum, Oxford.
Hieroglyph: kamaḍha 'penance' (Prakrit) kamaḍha, kamaṭha, kamaḍhaka, kamaḍhaga, kamaḍhaya = a type of penance (Prakrit)
Rebus: kamaṭamu, kammaṭamu = a portable furnace for melting precious metals; kammaṭīḍu = a goldsmith, a silversmith (Telugu) kãpṛauṭ jeweller's crucible made of rags and clay (Bi.); kampaṭṭam coinage, coin, mint (Tamil)
kamaṭhāyo = a learned carpenter or mason, working on scientific principles; kamaṭhāṇa [cf. karma, kām, business + sthāna, thāṇam, a place fr. Skt. sthā to stand] arrangement of one’s business; putting into order or managing one’s business (Gujarati)
The composition of two hieroglyphs: kāru 'crocodile' (Telugu) + kamaḍha 'a person seated in penance' (Prakrit) denote rebus: khar ‘blacksmith’ (Kashmiri); kāru ‘artisan’ (Marathi) + kamaṭa 'portable furnace'; kampaṭṭam 'coinage, coin, mint'. Thus, what the tablet conveys is the mint of a blacksmith. A copulating crocodile hieroglyph -- kāru 'crocodile' (Telugu) + kamḍa, khamḍa 'copulation' (Santali) -- conveys the same message: mint of a blacksmith kāru kampaṭṭa 'mint artisan'.
m1429B and two other tablets showing the typical composite hieroglyph of fish + crocodile. Glyphs: crocodile + fish ayakāra ‘blacksmith’ (Pali) kāru a wild crocodile or alligator (Telugu) aya 'fish' (Munda) The method of ligaturing enables creation of compound messages through Indus writing inscriptions. kārua wild crocodile or alligator (Telugu) Rebus: khar ‘blacksmith’ (Kashmiri); kāru ‘artisan’ (Marathi).
Kashmiri glosses:
Pali: ayakāra ‘iron-smith’. ] Both ayaskāma and ayaskāra are attested in Panini (Pan. viii.3.46; ii.4.10). WPah. bhal. kamīṇ m.f. labourer (man or woman) ; MB. kāmiṇā labourer (CDIAL 2902) N. kāmi blacksmith (CDIAL 2900).
Kashmiri glosses:
khār 1 खार् । लोहकारः m. (sg. abl. khāra 1 खार ; the pl. dat. of this word is khāran 1 खारन् , which is to be distinguished from khāran 2, q.v., s.v.), a blacksmith, an iron worker (cf. bandūka-khār, p. 111b, l. 46; K.Pr. 46; H. xi, 17); a farrier (El.). This word is often a part of a name, and in such case comes at the end (W. 118) as in Wahab khār, Wahab the smith (H. ii, 12; vi, 17). khāra-basta khāra-basta खार-बस््त । चर्मप्रसेविका f. the skin bellows of a blacksmith. -büṭhü -ब&above;ठू&below; । लोहकारभित्तिः f. the wall of a blacksmith's furnace or hearth. -bāy -बाय् । लोहकारपत्नी f. a blacksmith's wife (Gr.Gr. 34). -dŏkuru लोहकारायोघनः m. a blacksmith's hammer, a sledge-hammer. -gȧji or -güjü - लोहकारचुल्लिः f. a blacksmith's furnace or hearth. -hāl -हाल् । लोहकारकन्दुः f. (sg. dat. -höjü -हा&above;जू&below; ), a blacksmith's smelting furnace; cf. hāl 5. -kūrü लोहकारकन्या f. a blacksmith's daughter. -koṭu - लोहकारपुत्रः m. the son of a blacksmith, esp. a skilful son, who can work at the same profession. -küṭü लोहकारकन्या f. a blacksmith's daughter, esp. one who has the virtues and qualities properly belonging to her father's profession or caste. -më˘ʦü 1 - लोहकारमृत्तिका f. (for 2, see [khāra 3] ), 'blacksmith's earth,' i.e. iron-ore. -nĕcyuwu लोहकारात्मजः m. a blacksmith's son. -nay -नय् । लोहकारनालिका f. (for khāranay 2, see [khārun] ), the trough into which the blacksmith allows melted iron to flow after smelting. -ʦañĕ । लोहकारशान्ताङ्गाराः f.pl. charcoal used by blacksmiths in their furnaces. -wānवान् । लोहकारापणः m. a blacksmith's shop, a forge, smithy (K.Pr. 3). -waṭh -वठ् । आघाताधारशिला m. (sg. dat. -waṭas -वटि ), the large stone used by a blacksmith as an anvil.
Thus, kharvaṭ may refer to an anvil. Meluhha kāru may refer to a crocodile; this rebus reading of the hieroglyph is.consistent with ayakāra ‘ironsmith’ (Pali) [fish = aya (G.); crocodile = kāru (Telugu)]
Lothal seal. L048 ibex
 A fragment of a relief 'The spinner' made of bitumen mastic of Neo-Elamite period (8th cent. BCE-mid 6th cent. BCE) was found in Susa. This fragment displayed a well-coiffured woman being fanned by an attendant while the woman wearing bangles on both arms -- seated on a stool with feline legs -- held what may be a spinning device before a table with feline legs with a bowl containing a whole fish with six blobs assembled on top of the fish.
A fragment of a relief 'The spinner' made of bitumen mastic of Neo-Elamite period (8th cent. BCE-mid 6th cent. BCE) was found in Susa. This fragment displayed a well-coiffured woman being fanned by an attendant while the woman wearing bangles on both arms -- seated on a stool with feline legs -- held what may be a spinning device before a table with feline legs with a bowl containing a whole fish with six blobs assembled on top of the fish.Hieroroglyph: aya 'fish' Rebus: aya 'iron' (Gujarati) ayas 'metal' (Rigveda)
kola 'tiger' Rebus: kolle 'blacksmith' kol 'working in iron'; kolhe 'smelter' kole.l 'smithy, temple'; kolimi 'smithy, forge' Hieroglyph: bhaTa 'six' Rebus: baTa 'furnace'. kAtI 'spinner' Rebus: kAtI 'wheelwright'

Jasper cylinder seal with kneeling nude heroes, ca. 2220–2159 b.c.; Akkadian Mesopotamia Red jasper H. 1 1/8 in. (2.8 cm), Diam. 5/8 in. (1.6 cm) Metropolitan Museum of Art - USA
Four flag-posts(reeds) with rings on top held by the kneeling persons define the four components of the iron smithy/forge. This is an announcement of four shops, पेढी (Gujarati. Marathi). पेंढें 'rings' Rebus: पेढी 'shop'.āra 'serpent' Rebus; āra 'brass'. karaḍa 'double-drum' Rebus: karaḍa 'hard alloy'.
Specific materials offered for sale/exchange in the shop are: hard alloy brass metal (ayo, fish); lokhaṇḍ (overflowing pot) 'metal tools, pots and pans, metalware'; arka/erka 'copper'; kammaṭa (a portable furnace for melting precious metals) 'coiner, mint' Thus, the four shops are: 1. brass alloys, 2. metalware, 3. copper and 4. mint (services).
erãguḍu bowing, salutation (Telugu) iṟai (-v-, -nt-) to bow before (as in salutation), worship (Tamil)(DEDR 516). Rebus: eraka, eṟaka any metal infusion (Kannada.Tulu) eruvai 'copper' (Tamil); ere dark red (Kannada)(DEDR 446).
puṭa Anything folded or doubled so as to form a cup or concavity; crucible. Alternative: ḍhālako = a large metal ingot (G.) ḍhālakī = a metal heated and poured into a mould; a solid piece of metal; an ingot (Gujarati)
Allograph: ढाल [ ḍhāla ] f (S through H) The grand flag of an army directing its march and encampments: also the standard or banner of a chieftain: also a flag flying on forts &c. ढालकाठी [ ḍhālakāṭhī ] f ढालखांब m A flagstaff; esp.the pole for a grand flag or standard. 2 fig. The leading and sustaining member of a household or other commonwealth. 5583 ḍhāla n. ʻ shield ʼ lex. 2. *ḍhāllā -- . 1. Tir. (Leech) "dàl"ʻ shield ʼ, Bshk. ḍāl, Ku. ḍhāl, gng. ḍhāw, N. A. B. ḍhāl, Or. ḍhāḷa, Mth. H. ḍhāl m.2. Sh. ḍal (pl. °le̯) f., K. ḍāl f., S. ḍhāla, L. ḍhāl (pl. °lã) f., P. ḍhāl f., G. M. ḍhāl f. WPah.kṭg. (kc.) ḍhāˋl f. (obl. -- a) ʻ shield ʼ (a word used in salutation), J. ḍhāl f. (CDIAL 5583).
They are four Glyphs: paṭākā 'flag' Rebus: pāṭaka, four quarters of the village.
kã̄ḍ reed Rebus: kāṇḍa 'tools, pots and pans, metal-ware'.
1. Pk. kamaḍha -- , °aya -- m. ʻ bamboo ʼ; Bhoj. kōro ʻ bamboo poles ʼ. 2. N. kāmro ʻ bamboo, lath, piece of wood ʼ, OAw. kāṁvari ʻ bamboo pole with slings at each end for carrying things ʼ, H. kã̄waṛ, °ar, kāwaṛ, °ar f., G. kāvaṛf., M. kāvaḍ f.; -- deriv. Pk. kāvaḍia -- , kavvāḍia -- m. ʻ one who carries a yoke ʼ, H. kã̄waṛī, °ṛiyā m., G. kāvaṛiyɔ m. 3. S. kāvāṭhī f. ʻ carrying pole ʼ, kāvāṭhyo m. ʻ the man who carries it ʼ. 4. Or. kāmaṛā, °muṛā ʻ rafters of a thatched house ʼ; G. kāmṛũ n., °ṛī f. ʻ chip of bamboo ʼ, kāmaṛ -- koṭiyũ n. ʻ bamboo hut ʼ. 5. B. kāmṭhā ʻ bow ʼ, G. kāmṭhũ n., °ṭhī f. ʻ bow ʼ; M. kamṭhā, °ṭā m. ʻ bow of bamboo or horn ʼ; -- deriv. G. kāmṭhiyɔ m. ʻ archer ʼ. 6. A. kabāri ʻ flat piece of bamboo used in smoothing an earthen image ʼ. 7. kã̄bīṭ, °baṭ, °bṭī, kāmīṭ, °maṭ, °mṭī, kāmṭhī, kāmāṭhī f. ʻ split piece of bamboo &c., lath ʼ.(CDIAL 2760). kambi f. ʻ branch or shoot of bamboo ʼ lex. Pk. kaṁbi -- , °bī -- , °bā -- f. ʻ stick, twig ʼ, OG. kāṁba; M. kã̄b f. ʻ longitudinal division of a bamboo &c., bar of iron or other metal ʼ. (CDIAL 2774). कंबडी [ kambaḍī ] f A slip or split piece (of a bamboo &c.)(Marathi)
The rings atop the reed standard: पेंढें [ pēṇḍhēṃ ] पेंडकें [ pēṇḍakēṃ ] n Weaver's term. A cord-loop or metal ring (as attached to the गुलडा of the बैली and to certain other fixtures). पेंडें [ pēṇḍēṃ ] n (पेड) A necklace composed of strings of pearls. 2 A loop or ring. Rebus: पेढी (Gujaráthí word.) A shop (Marathi) Alternative: koṭiyum [koṭ, koṭī neck] a wooden circle put round the neck of an animal (Gujarati) Rebus: ācāri koṭṭya = forge, kammārasāle (Tulu)
The four hieroglyphs define the four quarters of the village smithy/forge: alloy, metalware, turner's lathe-work, cruble (or, ingot).
ayo 'fish' Rebus: ayo 'metal, alloy'
కాండము [ kāṇḍamu ] kānḍamu. [Skt.] n. Water. నీళ్లు (Telugu) kaṇṭhá -- : (b) ʻ water -- channel ʼ: Paš. kaṭāˊ ʻ irrigation channel ʼ, Shum. xãṭṭä. (CDIAL 14349).
lokhãḍ 'overflowing pot' Rebus: ʻtools, iron, ironwareʼ (Gujarati)
arká1 m. ʻ flash, ray, sun ʼ RV. [√arc] Pa. Pk. akka -- m. ʻ sun ʼ, Mth. āk; Si. aka ʻ lightning ʼ, inscr. vid -- äki ʻ lightning flash ʼ.(CDIAL 624) அருக்கன் arukkaṉ, n. < arka. Sun; சூரி யன். அருக்க னணிநிறமுங் கண்டேன் (திவ். இயற். 3, 1).(Tamil) agasāle 'goldsmithy' (Kannada) అగసాలి [ agasāli ] or అగసాలెవాడు agasāli. n. A goldsmith. కంసాలివాడు. (Telugu) erka = ekke (Tbh. of arka) aka (Tbh. of arka) copper (metal); crystal (Kannada) cf. eruvai = copper (Tamil) eraka, er-aka = any metal infusion (Ka.Tu.); erako molten cast (Tulu) Rebus: eraka = copper (Ka.) eruvai = copper (Ta.); ere - a dark-red colour (Ka.)(DEDR 817). eraka, era, er-a = syn. erka, copper, weapons (Ka.) erka = ekke (Tbh. of arka) aka (Tbh. of arka) copper (metal); crystal (Kannada) akka, aka (Tadbhava of arka) metal; akka metal (Te.) arka = copper (Skt.) erako molten cast (Tulu)
Alternative: kunda 'jasmine flower' Rebus: kunda ʻa turner's latheʼ. kundaṇa pure gold.
The image could denote a crucible or a portable furnace: kammaṭa 'coiner, mint, a portable furnace for melting precious metals (Telugu) On some cylinder seals, this image is shown held aloft on a stick, comparable to the bottom register of the 'standard device' normally shown in front of a one-horned young bull. Alternatives: puṭa Anything folded or doubled so as to form a cup or concavity; crucible. Ta. kuvai, kukai crucible. Ma. kuva id. Ka. kōve id. Tu. kōvè id., mould. (DEDR 1816). Alternative: Shape of ingot: దళము [daḷamu] daḷamu. [Skt.] n. A leaf. ఆకు. A petal. A part, భాగము. dala n. ʻ leaf, petal ʼ MBh. Pa. Pk. dala -- n. ʻ leaf, petal ʼ, G. M. daḷ n.(CDIAL 6214). <DaLO>(MP) {N} ``^branch, ^twig''. *Kh.<DaoRa>(D) `dry leaves when fallen', ~<daura>, ~<dauRa> `twig', Sa.<DAr>, Mu.<Dar>, ~<Dara> `big branch of a tree', ~<DauRa> `a twig or small branch with fresh leaves on it', So.<kOn-da:ra:-n> `branch', H.<DalA>, B.<DalO>, O.<DaLO>, Pk.<DAlA>. %7811. #7741.(Munda etyma) Rebus: ḍhālako = a large metal ingot (G.) ḍhālakī = a metal heated and poured into a mould; a solid piece of metal; an ingot (Gujarati).
Mirror: http://tinyurl.com/ptqa8tz
The imperative of decipherment of Indus Script Corpora is not merely to fill out a cross-word puzzle but to understand the roots of Indian civilization, the language the people spoke and the messages documented with extraordinary fidelity in the Corpora.
While breaking away from polemical excursus, it is essential to underscore that these documents constitute structured literary evidence of the civilization.
Indus Script decipherment is, in effect, an imperative for scholars engaged in civilization studies, an essential contribution to the Itihāsa of Bhāratam Janam, an expression used by Rishi Visvamitra in Rigveda (RV 3.53.12).
It is unfortunate that the scholarly contributions have tended to become faith-based polemical exercises.
Witzel's claim was that Indus Script was not based on language and that Harappans were illiterate. To the best of my knowledge, no arguments have been advanced by Witzel to justify his incidental remark (obiter dictum) in response to the following reasoned critiques which rebut the 'illiteracy' arument and claim that Indus Script is a proto-writing system.
Instead, only a polemical exchange with postings occurred in 2011 on an e-group (see "Appendix on Indus Script polemics " for the thread of postings).
Asko Parpola's point-by-point rebuttal of Farmer, Sproat, and Witzel:
o Parpola A (2008) Is the Indus script indeed not a writing system? in Airavati: Felicitation volume in honor of Iravatham Mahadevan(Varalaaru.com publishers, Chennai , India
Massimo Vidale's "The collapse melts down: a reply to Farmer, Sproat and Witzel":
Iravatham Mahadevan's "The Indus non-script is a non-issue":
I suggest that Indus Script was a writing system based on Proto-Prakritam (called Meluhha/mleccha) to create Indus Script Corpora of about 7000 inscriptions as catalogus catalogorum of metalwork.
That a catalogue is a writing system should be obvious in the context of the story of evolution of writing during the Bronze Age in various cultures.
Here are some catalogue entries with hieroglyph-multiplexes as hypertexts.
 aya 'fish' Rebus: aya, ayas 'iron, metal'
aya 'fish' Rebus: aya, ayas 'iron, metal' aya dhAL, 'fish+slanted stroke' Rebus: aya DhALako 'iron/metal ingot'
aya dhAL, 'fish+slanted stroke' Rebus: aya DhALako 'iron/metal ingot' aya aDaren,'fish+superscript lid' Rebus: aya aduru 'iron/metal native unsmelted metal'
aya aDaren,'fish+superscript lid' Rebus: aya aduru 'iron/metal native unsmelted metal' aya khANDa, 'fish+notch' Rebus: aya khaNDa 'iron/metal implements'
aya khANDa, 'fish+notch' Rebus: aya khaNDa 'iron/metal implements' aya kolom 'fish+ numeral 3' Rebus:aya kolimi 'iron/metal smithy/forge'
aya kolom 'fish+ numeral 3' Rebus:aya kolimi 'iron/metal smithy/forge' aya baTa 'fish+numeral 6' Rebus: aya bhaTa 'iron/metal furnace'
aya baTa 'fish+numeral 6' Rebus: aya bhaTa 'iron/metal furnace' aya gaNDa kolom'fish+numeral4+numeral3' Rebus: aya khaNDa kolimi 'metal/iron implements smithy/forge'
aya gaNDa kolom'fish+numeral4+numeral3' Rebus: aya khaNDa kolimi 'metal/iron implements smithy/forge' aya dula 'fish+two' Rebus: aya dul 'metal/iron cast metal or metalcasting'
aya dula 'fish+two' Rebus: aya dul 'metal/iron cast metal or metalcasting' aya tridhAtu 'fish+three strands of rope' Rebus: aya kolom dhatu 'metal/iron , three mineral ores'
aya tridhAtu 'fish+three strands of rope' Rebus: aya kolom dhatu 'metal/iron , three mineral ores' Ayo ‘fish’; kaṇḍa ‘arrow’ See: अयस्कांत [ ayaskānta ] m S (The iron gem.) The loadstone. (Molesworth. Marathi) Fish + circumgraph of 4 (gaNDa) notches: ayaskāṇḍa ‘a quantity of iron, excellent iron’ (Pāṇ.gaṇ) The gloss kāṇḍa may also signify 'metal implements'. A cognate compound in Santali has: me~r.he~t khaNDa 'iron implements'.
Ayo ‘fish’; kaṇḍa ‘arrow’ See: अयस्कांत [ ayaskānta ] m S (The iron gem.) The loadstone. (Molesworth. Marathi) Fish + circumgraph of 4 (gaNDa) notches: ayaskāṇḍa ‘a quantity of iron, excellent iron’ (Pāṇ.gaṇ) The gloss kāṇḍa may also signify 'metal implements'. A cognate compound in Santali has: me~r.he~t khaNDa 'iron implements'.Mohenjo-daro Seals m1118 and Kalibangan 032, glyphs used are: Zebu (bos taurus indicus), fish, four-strokes (allograph: arrow).ayo ‘fish’ (Mu.) + kaṇḍa ‘arrow’ (Skt.) ayaskāṇḍa ‘a quantity of iron, excellent iron’ (Pāṇ.gaṇ) aya = iron (G.); ayah, ayas = metal (Skt.) gaṆḌa, ‘four’ (Santali); Rebus: kaṇḍ ‘fire-altar’, ‘furnace’), arrow read rebus in mleccha (Meluhhan) as a reference to a guild of artisans working with ayaskāṇḍa ‘excellent quantity of iron’ (Pāṇini) is consistent with the primacy of economic activities which resulted in the invention of a writing system, now referred to as Indus Writing. poLa 'zebu' Rebus: poLa 'magnetite'.
 Harappa seal (H-73)[Note: the hieroglyph ‘water carrier’ pictorial of Ur Seal Impression becomes a hieroglyph sign] Hieroglyph: fish + notch: aya 'fish' + khāṇḍā m A jag, notch Rebus: aya 'metal'+ khāṇḍā ‘tools, pots and pans, metal-ware’. kuṭi 'water-carrier' Rebus: kuṭhi 'smelter'. खोंड (p. 216) [khōṇḍa] m A young bull, a bullcalf; खोंडा [ khōṇḍā ] m A
Harappa seal (H-73)[Note: the hieroglyph ‘water carrier’ pictorial of Ur Seal Impression becomes a hieroglyph sign] Hieroglyph: fish + notch: aya 'fish' + khāṇḍā m A jag, notch Rebus: aya 'metal'+ khāṇḍā ‘tools, pots and pans, metal-ware’. kuṭi 'water-carrier' Rebus: kuṭhi 'smelter'. खोंड (p. 216) [khōṇḍa] m A young bull, a bullcalf; खोंडा [ khōṇḍā ] m A Hieroglyph: kōḍ 'horn' Rebus: kōḍ 'place where artisans work, workshop' কুঁদন, কোঁদন [ kun̐dana, kōn̐dana ] n act of turning (a thing) on a lathe; act of carving (Bengali) कातारी or कांतारी (p. 154) [ kātārī or kāntārī ] m (कातणें ) A turner.(Marathi)
Rebus: खोदकाम [ khōdakāma ] n Sculpture; carved work or work for the carver.
खोदगिरी [ khōdagirī ] f Sculpture, carving, engraving: also sculptured or carved work.खोदणें [ khōdaṇēṃ ] v c & i (The intimations of a metals turner as a scribe are also gleaned from the gloss: खोडाखोड or डी [ khōḍākhōḍa or ḍī ] f (
That a metals turner is engaged in metal alloying is evident from the gloss: खोट [ khōṭa ] f A mass of metal (unwrought or of old metal melted down); an ingot or wedge. Hence 2 A lump or solid bit (as of phlegm, gore, curds, inspissated milk); any concretion or clot.
Fish, fish-fin hieroglyph-multiplexes (hypertexts) on pottery inscriptions and on seals/tablets
The Susa ritual basin decipherment demonstrates the possibility that some 'fish' hieroglyphs read as aya 'fish' rebus: aya 'iron' may also signify khambhaṛā 'fin' rebus: kammaTa 'mint'.
 A Susa ritual basin dated to ca. 12th or 13th century BCE depicts goat and fish ligatured into a 'fabulous' or 'composite' animal representation, clearly intended to connote the underlying hieroglyphic meaning. Susa ritual basin dates from 13th or 12th cent. BCE. The hieroglyph-multiplex flanks reedposts, spathes, molluscs. http://www.louvre.fr/en/oeuvre-notices/ritual-basin-decorated-goatfish-figures aya 'fish' Rebus: aya 'iron' (Gujarati) ayas 'metal' (Rigveda) meḷh ‘goat’ (Br. mr̤eka (Te.); mēṭam (Ta.); meṣam (Samskritam) Te. mr̤eka (DEDR 5087) (DEDR 5087) Rebus: meluh.h.a (Akkadian) mleccha (Samskritam) milakkhu 'copper' (Pali) An alternative reading for the composite animal: goat PLUS fish-fin. mr̤eka 'copper' rebus: milakkhu 'copper' PLUS khamba 'wing' fish-fin 'khambhaṛā' (Lahnda) rebus: kammaTa 'mint' (Kannada) eruvai 'reed' rebus: eruvai 'copper' sippi 'mollusc' rebus: sippi 'artificer, sculptor'. Thus, the hieroglyph-multiplex (hypertext) signifies a copper metalwork sculptor. The basin is for purification by Potr. 'purifier' who is also dhā̆vaḍ 'smelter', derived from dhāˊtu n. ʻ substance ʼ RV; dhāu -- m. ʻ metal, red chalk ʼ (Prakrtam)
A Susa ritual basin dated to ca. 12th or 13th century BCE depicts goat and fish ligatured into a 'fabulous' or 'composite' animal representation, clearly intended to connote the underlying hieroglyphic meaning. Susa ritual basin dates from 13th or 12th cent. BCE. The hieroglyph-multiplex flanks reedposts, spathes, molluscs. http://www.louvre.fr/en/oeuvre-notices/ritual-basin-decorated-goatfish-figures aya 'fish' Rebus: aya 'iron' (Gujarati) ayas 'metal' (Rigveda) meḷh ‘goat’ (Br. mr̤eka (Te.); mēṭam (Ta.); meṣam (Samskritam) Te. mr̤eka (DEDR 5087) (DEDR 5087) Rebus: meluh.h.a (Akkadian) mleccha (Samskritam) milakkhu 'copper' (Pali) An alternative reading for the composite animal: goat PLUS fish-fin. mr̤eka 'copper' rebus: milakkhu 'copper' PLUS khamba 'wing' fish-fin 'khambhaṛā' (Lahnda) rebus: kammaTa 'mint' (Kannada) eruvai 'reed' rebus: eruvai 'copper' sippi 'mollusc' rebus: sippi 'artificer, sculptor'. Thus, the hieroglyph-multiplex (hypertext) signifies a copper metalwork sculptor. The basin is for purification by Potr. 'purifier' who is also dhā̆vaḍ 'smelter', derived from dhāˊtu n. ʻ substance ʼ RV; dhāu -- m. ʻ metal, red chalk ʼ (Prakrtam)Harappa: Fish +fins on one side of a four-sided tablet
khambhaṛā 'fin' (Lahnda) rebus: kammaTa 'mint'
A Munda gloss for fish is 'aya'. Read rebus: aya 'iron' (Gujarati) ayas 'metal' (Vedic).
The script inscriptions indicate a set of modifiers or ligatures to the hieroglyph indicating that the metal, aya, was worked on during the early Bronze Age metallurgical processes -- to produce aya ingots, aya metalware,aya hard alloys.
Fish hieroglyph in its vivid orthographic form is shown in a Susa pot which contained metalware -- weapons and vessels.

Context for use of ‘fish’ glyph. This photograph of a fish and the ‘fish’ glyph on Susa pot are comparable to the ‘fish’ glyph on Indus inscriptions.
Read on the arguments at: http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.com/2011/11/decoding-fish-and-ligatured-fish-glyphs.html
The modifiers to the 'fish' hieroglyph which commonly occur together are: slanted stroke, notch, fins, lid-of-pot ligatured as superfix:![]() For determining the semantics of the messages conveyed by the script. Positional analysis of ‘fish’ glyphs has also been presented in: The Indus Script: A Positional-statistical Approach By Michael Korvink, 2007, Gilund Press.
For determining the semantics of the messages conveyed by the script. Positional analysis of ‘fish’ glyphs has also been presented in: The Indus Script: A Positional-statistical Approach By Michael Korvink, 2007, Gilund Press.
Table from: The Indus Script: A Positional-statistical Approach By Michael Korvink, 2007, Gilund Press. Mahadevan notes (Para 6.5 opcit.) that ‘a unique feature of the FISH signs is their tendency to form clusters, often as pairs, and rarely as triplets also. This pattern has fascinated and baffled scholars from the days of Hunter posing problems in interpretation.’ One way to resolve the problem is to interpret the glyptic elements creating ligatured fish signs and read the glyptic elements rebus to define the semantics of the message of an inscription.
karaṇḍa ‘duck’ (Sanskrit) karaṛa ‘a very large aquatic bird’ (Sindhi) Rebus: करडा [karaḍā] Hard from alloy--iron, silver &c. (Marathi) Rebus: fire-god: @B27990. #16671. Remo <karandi>E155 {N} ``^fire-^god''.(Munda) Rebus:. kharādī ‘ turner’ (Gujarati)
The 'parenthesis' modifier is a circumfix for both 'fish' and 'duck' hieroglyphs, the semantics of () two parenthetical modifiers are: kuṭilá— ‘bent, crooked’ KātyŚr., °aka— Pañcat., n. ‘a partic. plant’ [√kuṭ 1] Pa. kuṭila— ‘bent’, n. ‘bend’; Pk. kuḍila— ‘crooked’, °illa— ‘humpbacked’, °illaya— ‘bent’DEDR 2054 (a) Ta. koṭu curved, bent, crooked; koṭumai crookedness, obliquity; koṭukki hooked bar for fastening doors, clasp of an ornament. A pair of curved lines: dol ‘likeness, picture, form’ [e.g., two tigers, two bulls, sign-pair.] Kashmiri. dula दुल । युग्मम् m. a pair, a couple, esp. of two similar things (Rām. 966). Rebus: dul meṛeḍ cast iron (Mundari. Santali) dul ‘to cast metal in a mould’ (Santali) pasra meṛed, pasāra meṛed = syn. of koṭe meṛed = forged iron, in contrast to dul meṛed, cast iron (Mundari.) Thus, dul kuṭila ‘cast bronze’.
The parenthetically ligatured fish+duck hieroglyphs thus read rebus: dul kuṭila ayas karaḍā 'cast bronze ayasor cast alloy metal with ayas as component to create karaḍā ''hard alloy with ayas'.
Modifier hieroglyph: 'snout' Hieroglyph: WPah.kṭg. ṭōṭ ʻ mouth ʼ.WPah.kṭg. thótti f., thótthəṛ m. ʻ snout, mouth ʼ, A. ṭhõt(phonet. thõt) (CDIAL 5853). Semantics, Rebus:
tutthá n. (m. lex.), tutthaka -- n. ʻ blue vitriol (used as an eye ointment) ʼ Suśr., tūtaka -- lex. 2. *thōttha -- 4. 3. *tūtta -- . 4. *tōtta -- 2. [Prob. ← Drav. T. Burrow BSOAS xii 381; cf. dhūrta -- 2 n. ʻ iron filings ʼ lex.]1. N. tutho ʻ blue vitriol or sulphate of copper ʼ, B. tuth.2. K. thŏth, dat. °thas m., P. thothā m.3. S.tūtio m., A. tutiyā, B. tũte, Or. tutiā, H. tūtā, tūtiyā m., M. tutiyā m.
4. M. totā m.(CDIAL 5855) Ka. tukku rust of iron; tutta, tuttu, tutte blue vitriol. Tu. tukků rust; mair(ů)suttu, (Eng.-Tu. Dict.) mairůtuttu blue vitriol. Te. t(r)uppu rust; (SAN) trukku id., verdigris. / Cf. Skt. tuttha- blue vitriol (DEDR 3343).
Fish + corner, aya koṇḍa, ‘metal turned or forged’
Fish, aya ‘metal’
Fish + scales, aya ã̄s (amśu) ‘metallic stalks of stone ore’. Vikalpa: badhoṛ ‘a species of fish with many bones’ (Santali) Rebus: baḍhoe ‘a carpenter, worker in wood’; badhoria ‘expert in working in wood’(Santali)
Fish + splinter, aya aduru ‘smelted native metal’
Fish + sloping stroke, aya ḍhāḷ ‘metal ingot’
Fish + arrow or allograph, Fish + circumscribed four short strokes
aya 'fish' Rebus: aya, ayas 'iron, metal'
 With curved horns, the ’anthropomorph’ is a ligature of a mountain goat or markhor (makara) and a fish incised between the horns. Typical find of Gangetic Copper Hoards. At Sheorajpur, three anthropomorphs in metal were found. (Sheorajpur, Dt. Kanpur. Three anthropomorphic figures of copper. AI, 7, 1951, pp. 20, 29).
With curved horns, the ’anthropomorph’ is a ligature of a mountain goat or markhor (makara) and a fish incised between the horns. Typical find of Gangetic Copper Hoards. At Sheorajpur, three anthropomorphs in metal were found. (Sheorajpur, Dt. Kanpur. Three anthropomorphic figures of copper. AI, 7, 1951, pp. 20, 29).One anthropomorph had fish hieroglyph incised on the chest of the copper object, Sheorajpur, upper Ganges valley, ca. 2nd millennium BCE, 4 kg; 47.7 X 39 X 2.1 cm. State Museum, Lucknow (O.37) Typical find of Gangetic Copper Hoards. miṇḍāl markhor (Tor.wali) meḍho a ram, a sheep (G.)(CDIAL 10120) Rebus: meḍh ‘helper of merchant’ (Gujarati) meḍ iron (Ho.) meṛed-bica = iron stone ore, in contrast to bali-bica, iron sand ore (Munda) ayo ‘fish’ Rebus: ayo, ayas ‘metal. Thus, together read rebus: ayo meḍh ‘iron stone ore, metal merchant.’
Text: aya khaNDa kolimi 'metal/iron implements smithy/forge'
Pictorial motifs or hieroglyph-multiplexes: sangaDa 'lathe, portable furnace' Rebus: sangar 'fortification' sanghAta 'adamantine glue' (Varahamihira) samghAta 'collection of articles (i.e. cargo)' PLUS khōṇḍa m A young bull, a bullcalf (Marathi) kōḍe dūḍa bull calf (Telugu); kōṛe 'young bullock' (Konda)Rebus: kõdā 'to turn in a lathe' (Bengali)
Text: aya bhaTa 'iron/metal furnace' kaNDa 'arrow' Rebus: khaNDa 'metal implements' kuTi 'curve' Rebus: kuTila 'bronze' kanac 'corner' Rebus: kancu 'bronze'
Pictorial motif or hieroglyph-multiplex: sangaDa 'lathe, portable furnace' Rebus: sangar 'fortification' sanghAta 'adamantine glue' (Varahamihira) samghAta 'collection of articles (i.e. cargo)'
Seal.
kuTi 'curve' Rebus: kuTila 'bronze' (8 parts copper, 2 parts tin)
dATu 'cross' Rebus: dhatu 'mineral ore'
aya dul 'metal/iron cast metal or metalcasting'
aya aduru 'iron/metal native unsmelted metal' mū̃h ‘ingot’ (Santali) PLUS (infixed) kolom 'sprout, rice plant' Rebus: kolimi 'smithy, forge' Thus, ingot smithy
mū̃h ‘ingot’ (Santali) PLUS (infixed) kolom 'sprout, rice plant' Rebus: kolimi 'smithy, forge' Thus, ingot smithy kuTi 'curve' Rebus: kuTila 'bronze'
ranku 'liquid measure' Rebus: ranku 'tin' (Santali)
 kolom 'rice-plant, sprout' Rebus: kolimi 'smithy, forge' (Alternative: kuTi 'tree' Rebus: kuThi 'smelter')
kolom 'rice-plant, sprout' Rebus: kolimi 'smithy, forge' (Alternative: kuTi 'tree' Rebus: kuThi 'smelter')kaṇḍa kanka ‘rim of jar’ Rebus: karṇīka ‘account (scribe)’karṇī‘supercargo’.
kaṇḍa ‘fire-altar’.
A painted goblet. Ficus leaves. Nausharo ID. c. 2600-2550 BCE (After Samzun. Anaick, 1992, Observations on the characteristisc of the Pre-Harappan remains, pottery, and artifacts at Nausharo, Pakistan (2700-2500 BCE), pp. 245-252 in: Catherine Jarrige ed. South Asian Archaeology 1989 (Monographs in World Archaeology 14, Madison, Wisconsin, Prehistory Press: 250, fig. 29.4 no.2)
Inscribed pots. Mundigak IV, 1 (eastern Afghanistan), after Casal 1961: II, fig. 64, nos. 167, 169, 172. Courtesy: Delegation archeologique francaise en Afghanistan. Ficus leaves.
Harappa seal. Harappa excavation no. 13751. Harappa museum. Courtesy: Dept. of Archaeology and Museums, Govt. of Pakistan
rimless pot: baTa 'rimless pot' Rebus: bhaTa 'furnace'
tri-dhAtu, three minerals: tridhAtu 'three strands of rope' Rebus: dhatu 'mineral ore' (three ores)
oval ingot: DhALako 'large ingot'
Mohenjo-daro. Copper plate. obverse. Excavation no. E 214-215. Courtesy. ASI. Purana Qila, New Delhi.
rimless pot: baTa 'rimless pot' Rebus: bhaTa 'furnace'
tri-dhAtu, three minerals: tridhAtu 'three strands of rope' Rebus: dhatu 'mineral ore' (three ores)
kolmo 'three' Rebus: kolimi 'smithy, forge'.
Mohenjodaro. Tablet. Crocodile + fish DK 8037. E 2500 Purana Qila, New Delhi. ASI.
Hieroglyph-multiplex: aya 'fish' + kara 'crocodile' Rebus: ayakara 'metalsmith'
khambhaṛā ʻfinʼ rebus: kammaṭṭam, kammiṭṭam coinage, mint
aya 'fish' Rebus: aya, ayas 'iron, metal' PLUS meḍha '
Cylinder seal. Water flowing from the shoulder. Stars.
 Santali glosses. Lexis.
Santali glosses. Lexis.meḍha '
m 305 Seal. Mohenjo-daro.
Fish + scales, aya ã̄s (amśu) ‘metallic stalks of stone ore’. Vikalpa: badhoṛ ‘a species of fish with many bones’ (Santali) Rebus: baḍhoe ‘a carpenter, worker in wood’; badhoria ‘expert in working in wood’(Santali)khambhaṛā ʻfinʼ rebus: kammaṭṭam, kammiṭṭam coinage, mint.
gaNDa 'four' Rebus: khaNDa 'metal implements' Together with cognate ancu 'iron' the message is: native metal implements.
aya 'fish' Rebus: aya, ayas 'iron, metal'
Pictorial hieroglyph-multiplex: kuThi 'twig' Rebus: kuThi 'smelter' thattAr 'buffalo horn' Rebus: taTThAr 'brass worker' meḍha '
Cylinder seal. Ancient Near East.
Triangula tablet. Horned seated person. crocodile. Split ellipse (parenthesis)
Cylinder seal. Akkadian.
Seal. Mohenjo-daro
Seal. Mohenjo-daro
Copper tablet. Mohenjo-daro
Seal. Harappa.
m478A, m479 Mohenjo-daro seal.
After Fig. 2. Asko Parpola. http://www.harappa.com/script/indus-writing.pdf Texts of inscriptions from different sites, demonstrating ordering sequence of 'signs' (Parpola, Asko, 2008, Is the Indus script indeed not a writing system? in: AirAvati, Felicitation volume in honour of Iravatham Mahadevan, Chennai, Varalaru, pp.111-131
Appendix on Indus Script decipherment polemics
Those interested can follow the thread (URL cited):
The Indus script as proto-writing
Asko Parpola (July 14, 2011)
It is widely agreed that the Archaic Sumerian script or "Proto-Cuneiform" is the world's oldest writing system, used in the Late Uruk Period (Uruk strata IV and III, c. 3400-3000 BCE). It was used as an administrative tool to record on clay tablets such matters as grain distribution, land, animal and personnel management, and the processing of fruits and cereals. "The script can be 'understood' in some sense, but it cannot be fully read; although there has been some doubt concerning the language that was the basis for this written
expression, there is clear evidence that it was Sumerian" (Michalowski
1996: 33). Archaic Sumerian was logosyllabic writing because its signs stood for elements of a spoken language, words and morphemes, with initially rare phonetization. It was not from the beginning able to record everything: it took many centuries of ever increasing phonetization for this "nuclear writing" to develop into a "full writing" where all grammatical elements were written. Yet it is considered "true writing", because it was a language-based system of
visual aigns.
The Egyptian Hieroglyphic writing was certainly used in Pre-Dynastic times. The royal tomb U-j at Umm el-Qa'ab near Abydos in Upper Egypt, dated to c 3200 BCE, contained 150 inscribed bone tags originally attached to grave goods recording the places of origin of these goods, as well as pottery inscriptions and sealings. These were excavated in 1988 and published ten years later (Dreyer 1998). This earliest form of Egyptian script was already a well-formed logophonic writing system, which can be partially understood on the basis of later Egyptian writing. "By the early 1st Dynasty, almost all the uniconsonantal signs are attested, as well as the use of classifiers or determinatives, so that the writing system was in essence fully formed even though a very limited range of material was written." (Baines 1999: 882). "Many inscribed artifacts are preserved from the first two Dynasties, the most numerous categories being cylinder seals and sealings, cursive annotations on pottery, and tags originally attached to tomb equipment, especially of the 1st Dynasty kings.
Continuous language was still not recorded" (Baines 1999: 883). Thus until the beginning of the Old Kingdom starting with the 3rd Dynasty in 2686 BCE — for about 600 years equalling the duration of the Indus Civilization — the Egyptians used a language-based, phoneticized writing system, but did not write full sentences, only very short texts fully comparable to the surviving texts in the Indus script.
Early administrative documents are assumed to have existed but have not survived (cf. Baines 1999: 884).
When defining the Indus script as logosyllabic, I noted several constraints to be observed in its analysis: "the linguistic elements that are expected to correspond to the signs are morphemes rather than phonemes. Secondly, all of the morphemes pronounced in the spoken Indus language may not, and are not even likely to, have a counterpart in its written form. In the third place, all preserved Indus inscriptions are very short, appearing on objects like seals, which are not so likely to contain even normal sentences, with such basic
constituents as a verbal predicate or an object, let alone complex sentences." (Parpola 1994: 89). This was before Damerow (1999) suggested the term 'proto-writing' for the earliest, linguistically incomplete notations (cf. Houston ed. 2004: 11); on these earliest writing systems see especially Houston ed. 2004.
In my opinion Farmer, Sproat and Witzel (2004: 19 and 33) err when they suggest that "the Indus system cannot be categorized as 'script' ... capable of systematically encoding speech", and that it "cannot even be comfortably labeled as a 'proto-script', but apparently belonged to a different class of symbols." Their principal arguments, the shortness of Indus texts, their restriction to only a few text types, and the long duration (c 600 years) of this stage of script evolution, are effectively annulled by what is said above about the early Sumerian and Egyptian scripts. For their other arguments I refer
to an earlier paper of mine (Parpola 2008).
George Hart wrote yesterday (13 July 2011): "None of this proves or disproves that the fish symbol might have been pronounced [in Dravidian] mīṉ. Steve Farmer wrote in reply (13 July 2011): Probably one of the silliest claims ever made about the symbols, with no evidence whatsoever to back it. My reply: there is actually a lot of evidence to back it (see Parpola 1994: 179-272; and new evidence in Parpola 2009). Due to a complete lack of bilinguals, it is very
difficult to verify sign interpretations, but not altogether impossible. Perhaps the most important test stone is supplied by the nominal compounds actually existing in languages that are historically likely to be related to the Harappan language: these can be compared to Harappan sign sequences that can be pictorially interpreted and perhaps deciphered with the help of linguistically acceptable homophonies (used in all early scripts for phonetication: the rebus
puns). The accumulation of iconically acceptable, systematic and interconnected interpretations can eliminate chance coincidences in a process comparable to filling cross-word puzzles.
References:
Baines, John, 1999. Writing: invention and early development. Pp.882-885 in: Kathryn A. Bard (ed.), Encyclopedia of the archaeology of ancient Egypt. London and New York: Routledge.
Dreyer, Günter, 1998. Umm el-Qaab I: Das prädynastische Königsgrab U-j
und seine frühen Schriftzeugnisse. (Archäologische Veröffentlichungen 86.) Mainz: Verlag Philipp von Zabern.
Farmer, Steve, Richard Sproat and Michael Witzel, 2004. The collapse
of the Indus-scrpt thesis: The myth of a literate Harappan civilization: Electronic Journal of Vedic Studies 11 (2): 19-57.
Houston, Stephen (ed.), 2004. The first writing: Script invention as history and process. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Michalowski, Piotr, 1996. Mesopotamian cuneiform: Origins. Pp. 33-36 in: Peter T. Danies & William Bright (eds.), The world's writing systems. New York: Oxford University Press.
Parpola, Asko, 1994. Deciphering the Indus script. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Parpola, Asko, 2008. Is the Indus script indeed not a writing system? (Pp. 111-131 in: Airavati: Felicitation volume in honour of Iravatham Mahadevan, Chennai: Varalaaru.com. Downloadable from www.harappa.com
Parpola, Asko, 2009. 'Hind leg' + 'fish': Towards further understanding of the Indus script. Scripta 1: 37-76. (Downloadable at www.harappa.com)
http://list.indology.info/pipermail/indology_list.indology.info/2011-July/035749.html
http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2015/08/indus-script-fish-ficus-hieroglyph.html
Below a picture of a fisherman (?) with four fish from the the so-called "Standard of Ur "(circa 2600-2400 B.C.).
As Ur is near Eridu (12 miles north of Eridu) perhaps Adapa the fisherman looked "somewhat" like this individual?
![]()
dula 'pair' rebus: dul 'cast metal' PLUS ayo, ayu 'fish' rebus: aya 'iron' ayas 'metal' PLUS khambhaṛā ʻfinʼ rebus: kammaṭṭam, kammiṭṭam coinage, mint.
S. Kalyanaraman
Sarasvati Research Centre
May 6, 2016
 A fish-apkallu drawn by AH Layard from a stone relief, one of a pair flanking a doorway in the Temple of Ninurta at Kalhu. British Museum. Reproduced in Schlomo Izre'el, Adpa and the South Wind, Language has the power of life and death, Eisenbrauns, 2001.
A fish-apkallu drawn by AH Layard from a stone relief, one of a pair flanking a doorway in the Temple of Ninurta at Kalhu. British Museum. Reproduced in Schlomo Izre'el, Adpa and the South Wind, Language has the power of life and death, Eisenbrauns, 2001.
































 Sumerian relief. Louvre.
Sumerian relief. Louvre. 

































