Mirror: http://tinyurl.com/og6ksat
Indus Script Corpora and archaeological excavations of 'fir-altars' provide evidence for continuity of Vedic religion of fire-worship in many sites of Sarasvati-Sindhu civilization.
The metalwork catalogues of deciphered Indus Script Corpora are consistent with the fire-altars found in almost every single site of the civilization consistent with the documentation of yajna, fire-worship, in ancient texts of the Veda. The continuity of Vedic religion, veneration of Ruda-Siva among Bronze Age Bhāratam Janam, 'metalcaster folk' is firmly anchored.
kole.l signified 'smithy'. The same word kole.l also signified ' temple' (Kota)
In Hindu civilization tradition, yupa associated with smelter/furnace operations in fire-altars as evidenced in Bijnor, Kalibangan, Lothal and in many yupa pillars of Rajasthan of the historical periods, assume the aniconic form of linga venerated as Jyotirlinga, fierly pillars of light.
 A 10th-century four-headed stone lingam (Mukhalinga) from Nepal. The 'mukha' or face on the linga is a hieroglyph read rebus muh 'ingot'. Hieroglyph: mũh 'face' (Hindi) rebus: mũhe 'ingot' (Santali) mũhã̄ = the quantity of iron produced at one time in a native smelting furnace of the Kolhes; iron produced by the Kolhes and formed like a four-cornered piece a little pointed at each end; mūhā mẽṛhẽt = iron smelted by the Kolhes and formed into an equilateral lump a little pointed at each of four ends; kolhe tehen mẽṛhẽt ko mūhā akata = the Kolhes have to-day produced pig iron (Santali) muhA 'the quantity of iron produced at one time in a native smelting furnace' (Santali. Campbell)
A 10th-century four-headed stone lingam (Mukhalinga) from Nepal. The 'mukha' or face on the linga is a hieroglyph read rebus muh 'ingot'. Hieroglyph: mũh 'face' (Hindi) rebus: mũhe 'ingot' (Santali) mũhã̄ = the quantity of iron produced at one time in a native smelting furnace of the Kolhes; iron produced by the Kolhes and formed like a four-cornered piece a little pointed at each end; mūhā mẽṛhẽt = iron smelted by the Kolhes and formed into an equilateral lump a little pointed at each of four ends; kolhe tehen mẽṛhẽt ko mūhā akata = the Kolhes have to-day produced pig iron (Santali) muhA 'the quantity of iron produced at one time in a native smelting furnace' (Santali. Campbell)"The worship of the lingam originated from the famous hymn in the Atharva-Veda Samhitâ sung in praise of the Yupa-Skambha, the sacrificial post. In that hymn, a description is found of the beginningless and endless Stambha or Skambha, and it is shown that the said Skambha is put in place of the eternal Brahman. Just as the Yajna (sacrificial) fire, its smoke, ashes, and flames, the Soma , and the ox that used to carry on its back the wood for the Vedic sacrifice gave place to the conceptions of the brightness of Shiva's body, his tawny matted hair, his blue throat, and the riding on the bull of the Shiva, the Yupa-Skambha gave place in time to the Shiva-Linga. In the text Linga Purana, the same hymn is expanded in the shape of stories, meant to establish the glory of the great Stambha and the superiority of Shiva as Mahadeva. Jyotirlinga means "The Radiant sign of The Almighty". The Jyotirlingas are mentioned in the Shiva Purana." https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shiva
Sources: Harding, Elizabeth U. (1998). "God, the Father". Kali: The Black Goddess of Dakshineswar. Motilal Banarsidass. pp. 156–157
Vivekananda, Swami. "The Paris Congress of the History of Religions" The Complete Works of Swami Vivekananda 4.
Chaturvedi, B. K. (2006), Shiv Purana (First ed.), New Delhi: Diamond Pocket Books (P) Ltd,
Pl. XXII B. Terracotta cake with incised figures on obverse and reverse, Harappan. On one side is a human figure wearing a head-dress having two horns and a plant in the centre; on the other side is an animal-headed human figure with another animal figure, the latter being dragged by the former.
Decipherment of hieroglyphs on the Kalibangan terracotta cake:
bhaTa 'warrior' rebus: bhaTa 'furnace'
kolmo 'rice plant' rebus: kolimi 'smithy, forge'
koD 'horn' rebus: koD 'workshop'
kola 'tiger' rebus: kolle 'blacksmith', kolhe 'smelter' kol 'working in iron'
Thus, the terracotta cake inscription signifies a iron workshop smelter/furnace and smithy.
The recording of an inscription on a terracotta cake used in a fire-altar continues as a tradition with inscriptions recorded on Yupa, 'pillars' of Rajasthan indicating the type of yajna's performed using those Yupa.
Binjor seal with Indus Script deciphered. Binjor attests Vedic River Sarasvati as a Himalayan navigable channel en route to Persian Gulf
![]()
The fire altar, with a yasti made of an octagonal brick. Photo:Subhash Chandel, ASIBinjor seal
Binjor (4MSR) seal.Binjor Seal Text.Fish + scales, aya ã̄s (amśu) ‘metallic stalks of stone ore’. Vikalpa: badhoṛ ‘a species of fish with many bones’ (Santali) Rebus: baḍhoe ‘a carpenter, worker in wood’; badhoria ‘expert in working in wood’(Santali)
gaNDa 'four' Rebus: khaNDa 'metal implements' Together with cognate ancu 'iron' the message is: native metal implements.
Thus, the hieroglyph multiplex reads: aya ancu khaNDa 'metallic iron alloy implements'.
koḍi ‘flag’ (Ta.)(DEDR 2049). Rebus 1: koḍ ‘workshop’ (Kuwi) Rebus 2: khŏḍ m. ‘pit’, khö̆ḍü f. ‘small pit’ (Kashmiri. CDIAL 3947)
The bird hieroglyph: karaḍa
करण्ड m. a sort of duck L. కారండవము (p. 0274) [ kāraṇḍavamu ] kāraṇḍavamu. [Skt.] n. A sort of duck. (Telugu) karaṭa1 m. ʻ crow ʼ BhP., °aka -- m. lex. [Cf. karaṭu -- , karkaṭu -- m. ʻ Numidian crane ʼ, karēṭu -- , °ēṭavya -- , °ēḍuka -- m. lex., karaṇḍa2 -- m. ʻ duck ʼ lex: see kāraṇḍava -- ]Pk. karaḍa -- m. ʻ crow ʼ, °ḍā -- f. ʻ a partic. kind of bird ʼ; S. karaṛa -- ḍhī˜gu m. ʻ a very large aquatic bird ʼ; L. karṛā m., °ṛī f. ʻ the common teal ʼ.(CDIAL 2787) Rebus: karaḍā 'hard alloy'
Thus, the text of Indus Script inscription on the Binjor Seal reads: 'metallic iron alloy implements, hard alloy workshop' PLUSthe hieroglyphs of one-horned young bull PLUS standard device in front read rebus:
kõda 'young bull, bull-calf' rebus: kõdā 'to turn in a lathe'; kōnda 'engraver, lapidary'; kundār 'turner'.
Hieroglyph: sãghāṛɔ 'lathe'.(Gujarati) Rebus: sangara 'proclamation.Together, the message of the Binjor Seal with inscribed text is a proclamation, a metalwork catalogue (of) 'metallic iron alloy implements, hard alloy workshop'
करण्ड m. a sort of duck L. కారండవము (p. 0274) [ kāraṇḍavamu ] kāraṇḍavamu. [Skt.] n. A sort of duck. (Telugu) karaṭa
Naga worshippers of fiery pillar, Amaravati stup Smithy is the temple of Bronze Age: stambha, thãbharā fiery pillar of light, Sivalinga. Rebus-metonymy layered Indus script cipher signifies: tamba, tã̄bṛā, tambira 'copper'


http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2015/05/smithy-is-temple-of-bronze-age-stambha_14.html

Yupa. Yupa from 4th century. Kutai Kingdom. Inscription in Samskritam.
Badwa Yupa. "It is one of the four places in Rajasthan where such inscribed stone pillars were erected during the third century CE. which signifies the revival of the Vedic religion. The Badva stone pillar inscription informs that the Maukharis performed a triratra sacrifice in CE. 239. It is probable that these Maukharis owed allegiance to the Malava Republic. Four pillars have been shifted to the State Archaeology Museum at Kota and only one remains at the site." http://asijaipurcircle.com/badva_baran.php#
"

![[prasati%2520mulawarman%255B3%255D.jpg]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-L7CZvk8_Iys/ToIb1RXc2QI/AAAAAAAAAR0/aPzxQNQq0Tg/s1600/prasati%252520mulawarman%25255B3%25255D.jpg) praśasti प्रशस्तिYūpa यूप Indonesia:
praśasti प्रशस्तिYūpa यूप Indonesia:kuṇḍuṅgasya mahātmanaḥ;
putro śvavarmmo vikhyātah;
vaṅśakarttā yathāṅśumān;
tasya putrā mahātmānaḥ;
trayas traya ivāgnayaḥ;
teṣān trayāṇām pravaraḥ;
tapo-bala-damānvitaḥ;
śrī mūlavarmmā rājendro;
yaṣṭvā bahusuvarṇnakam;
tasya yajñasya yūpo ‘yam;
dvijendrais samprakalpitaḥ.
Yupa Inscriptions The Kutei Stone
.jpg)

.jpg)


YUPA PILLARS IN BICHPURIA TEMPLE
"The inscribed stone is a sacrificial pillar, commemorating revival of the rituals during third century A.D. by the Malava Republic. The inscription records the erection of the pillar by Ahisarman, son of Dharaka who was Agnihotri. Ahisarman seems to be a Malava chief.."
“…Malavas, Yaudheyas, Arjunayanas, Rajanyas etc...seem to have been patrons of Vedic sacrifices and rituals. Rajasthan witnessed the revival of Vedic religion under these people in the early centuries of the Common era and thus it was natural to get the largest number of inscribed yupa pillars (sacrificial posts) in various parts of Rajasthan. Dr. Satya Prakash discovered as early as in 1952, a yupa pillar inscribed in Brahmi script and dated Krita (Vikram) Samvat 321 (CD 264) from the village Bichpuria near Nagar (district Tonk) which records the performance of some sacrifice (name not specified) by Dharaka, who is styled as agnihotri. He brought to light this important epigraph and edited the same (Maru Bharti, Pilani, Vol. I, No. 2, February 1953). Rajasthan has provided the largest number of yupa pillars in the country of SaSthi-rAtra sacrifice, two pillars (now in Amber Museum) from Barnala (Jaipur) dated v.s. 284 (CE 227) recording the installation of seven yupa pillars by Vardhana and the second dated v.s. 335 (CE 278) referring to the TrirAtra sacrifice, four yupa pillars from Badva (now in Kotah Museum) three of them of the Maukhari dynasty ruling the area. The three inscribed yupa pillars record the performance of TrirAtr yajnas by Balavardhana, Somadeva and Bala Singh, the three sons of the commander-in-chief of the Maukhari kings. Each of them gave one hundred cows in gift on the occasion and installed sacrificial posts. The undated pillar belongs to DhanutrAta of the same dynasty who is credited with the performance of the AstoyAma yajna and putting up a yupa pillar in commemoration thereof. Sri ViSNuvardhana, son of the celebrated Yas'ovarman, performed puNdarIka yajna in the Malava era 428 (CE 371) and installed a yupa pillar at Vijaigarh (Bayana in Bharatpur region). Dr. Prakash studied in detail these incontrovertible evidences in his interesting paper 'Yupa pillars of Rajasthan' (JRIHR, Vol. IV, No. 2, April-June 1968) and evaluated their contribution in Rajasthan Through the Ages (Vol. 1, Chapter IV, 1966).” (Sharma, RG, 'History and Culture' in: Vijai Shankar Srivastava, ed., Abhinav Publications, 1981, Cultural Contours of India: Dr Satya Prakash Felicitation Volume, pp.81-82).
“The new light that the excavations at Kalibangan have shed on the religious aspects are discovery of the 'fire-places' and the terracotta cakes...The oval fire pits were observed as early as 1960-61, but these could not be then properly understood. Their importance was realised in the subsequent field-seasons. The occurrence of oval, round or rectangular 'fire-altars' has been observed on all the three mounds at Kalibangan in the Harappan context. On the western mound (KLB-1) over a platform was found a rectangular 'fire-altar' of baked bricks. It contained the 'bones of a bovine and antlers, representing perhaps a sacrifice'. Atop another platform were unearthed a row of seven rectangular mud enclosures with varying sizes approximately 50x45 cm, with walls about 10 cm high from the ground surface. These lay by the side of a well. In the centre of each enclosure was placed a cylindrical terracotta phallus-like object. 'The remains of th fire are indicated by ash. The walls of these enclosures are also burnt. All these 'fire-altars' were situated in a room. In the 'city mound' (KLB-2) a room almost in every house contained such fire-altars and they continued to occur in successive levels (Pl. XX, A in Ind. Arch. 1963-64—A review). A shallow pit, oval or rectangular in shape was first excavated. In this pit fire was made and in the centre a cylindrical sun-dried or pre-fired rectangular block or baked brick was fixed. The presene of charcoal lumps suggest that the fire was 'put out in situ'. The occurrence of the triangular or circular terracotta cakes, in these 'fire-altars', suggests that these were used as offerings, baked or unbaked. About the 'fire-altars' found in the citadel-complex it has been suggested that these may have been used for ongregational rituals, whereas in the 'city mound' these were for the individuals. The low mound (KLB-3) towards the eas of the 'city mound', has laid bare very significant data about the religion. This mound is not a habitation site. Here the remains of a huge mud-brick structure, possibly enclosing a smaller one, have come to light. Within this inner structure are several 'fire-altars' containing terracotta cakes, ash and the cylindrical objects. The circumstantial and environmental evidences added together suggest that this low mound is exclusively of religious significance where a temporal edifice existed, which, however, stratigraphically has been equated with the Harappan habitational phase at the site. The cylindrical columns are rectangular, round or fluted. The complete specimens on average are 20-25 cm. High. The terracotta cakes of several forms have been found at the site. But as pointed out earlier only the triangular or discular types have been found in the 'fire-altars'. It may not be out of place to mention that both at Bara and Chandigarh, phallus-shaped rectangular but slightly tapering terracotta objects have been recovered. These, of course, have no association with 'fire-altars' or terracotta cakes. In the light of evidence from Kalibangan and Lothal, it may be surmised that they are aniconic representations of S'iva, as we have today. This tends to be a mutually corroborative phenomenon at these sites which are more or less contemporary. The triangular terracotta cakes had been reported from Mohenjodaro and Harappa. Their proper significance was evaded, for want of a convincing explanation, by a passing remark that these may have some ritualistic use. This glib remark has, of late, come true. On one side is a human figure wearing a head-dress having two horns and a plant in the centre; on the other side is an animal-headed human figure with another animal figure, the latter being dragged by the former. The horned head-gear reminds of the horned deity on the Mohenjodaro seal and the other motif seems to have little significance without the religious affiliation...The cylindrical objects in the 'fire-altars' found at Kalibangan may have been aniconic representation of S'iva. Their association with fire may suggest the earlier manifestation of Jyotirlinga. Agarwala has pointed out that Rudra himself is the Fire-God. He has further elucidated that water and fire are the two parents of the universe – water being the female and fire the male form respectively. It is very interesting to note that in such 'fire-altars' lumps of charcoal have been discovered which are the outcome of the putting out in situ of the blazing embers. It is difficult to deny that these burning pieces of charcoal were extinguished with the use of water as a part of the ritual. If this is true, then we have at Kalibangan the elements of Purusha and Prakriti. As shown by Agarwala, with which the present writer concurs, the cylindrical objects and fire represent the male element (what in later days is reognised as Jyotirlinga) and water represents the female element. This also explains the absense of the terracotta female figurines representing the earth or mother-goddess at Kalibangan, Banawali (Haryana) and Lothal (Gujarat). At both Kalibangan and Lothal, the 'fire-altrs' with their contents described above have been found. Broadly speaking the religious beliefs of the Harappans through both time and space do not differ much as revealed by their homogeneous remains. But local variations did exist as discussed above. Certain new features have also come to light regarding the funerary customs both at Kalibangan and Lothal, which differ from those at other sites. It seems the strong strains of local elements could not be subduded and were rather adopted by the Harappans.” (JS Nigam, 'The religion of the Harapans in Rajasthan' in: Vijai Shankar Srivastava, ed., Abhinav Publications, 1981, Cultural Contours of India: Dr Satya Prakash Felicitation Volume, p.33-34).
Kalibangan. Fire-altar with stele 'linga' and terracotta cakes. Plate XXA. "Within one of the rooms of amost each house was found the curious 'fire-altar', sometimes also in successive levels, indicating their recurrent function." (p.31)
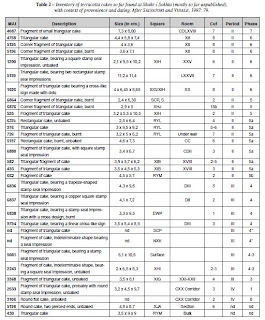
Shahr-i Sokhta, terracotta cakes, Periods II and III, I, MAI 1026 (front and rear); 2. MAI 376 (front and rear); 3. MAI 9794 (3a, photograph of front and read; 3b, drawing -- After Fig. 12 in E. Cortesi et al. 2008)
 Number nd percentages of terracotta cakes found t Shahr-i Sokhta, total 31. (After Table 2 in E. Cortesi et al. 2008).
Number nd percentages of terracotta cakes found t Shahr-i Sokhta, total 31. (After Table 2 in E. Cortesi et al. 2008)."Terracotta cakes. Variously called 'terracotta tablets', 'triangular plaques' or 'triangular terracotta cakes' these artifacts (fig. 12, tables 2 and 3), made of coarse chaff-tempered clay, are a very common find in several protohistoric sites of the Subcontinent from the late Regionalization Era (2800-2600 BCE) to the Localization Er (1900-1700 BCE). In this latter time0-span they frequently assume irregular round shapes, to finally retain the form of a lump of clay squeezed in the hand. Despite abudant and often unnecessary speculation, archaeological evidence demonstrates tht they were used in pyrotechnological activities, both in domestic and industrial contexts. The most likely hypothesis is tht these objets, in the common kitchen areas, were heated to boil water, and used as kiln setters in other contexts. Shahr-i Sokhta is the only site in the eastern Iranian plateau where such terracotta cakes, triangular or more rarely rectangular, are found in great quantity. Their use, perhaps by families or individuals having special ties with the Indus region, might have been part of simple domestic activities, but this conclusion is questioned by the fact that several terracotta cakes, at Shahr-i Sokhta, bear stamp seal impressions or other graphic signs (in more than 30% of the total cases). In many cases the actual impressions are poorly preserved, and require detailed study. Perhaps these objects used in some form of administrative practice. Although many specimens are fired or burnt, a small percentge of the 'cakes' found at Shahr-i Sokhta is unfired (table 2). On the other hand, their modification in the frame of one or more unknown semantic contexts is not unknown in the Indus valley. At Kalibangan (Haryana, India), for example, two terracotta cake fragments respectively bear a cluster of signs of the Indus writing system and a possible scene of animal sacrifice in front of a possible divinity. While a terracotta cake found at Chanhu-Daro (Sindh, Pakistan) bears a star-like design, anothr has three central depressions. The most important group of incised terracotta cakes comes from Lothal, where the record includes specimens with vertical strokes, central depressions, a V-shaped sign, a triangle, and a cross-like sign identical to those found at Shahr-i Sokhta. Tables 2 and 3 shows a complete inventory of these objects (most so far unpublished), their provenience and proposed dating, and finally summarize their frequencies across the Shahr-i Sokhta sequence. The data suggest that terracotta cakes are absent from Period I. This might be due to the very small amount of excavated deposits in the earliest settlement layers, but the almost total absence of terracotta cakes in layers dtable to phases 8-7, exposed in some extension both in the Eastern Residential Area and in the Centrl Quarter, is remarkable. The majority of the finds belong to Period II, phases 6 and 5 (mount together to about 60% of the cases). As the amount of sediments investigated for Period III in the settlement areas, for various reasons, is much less than what was done for Period II, the percentage of about 40% obtained for Period III (which, we believe, dates to the second hald of the 3rd millennium BCE) actually demonstrates that the use of terracotta cakes at Shahr-i Sokht continued to increase." (E. Cortesi, M. Tosi, A. Lazzari and M. Vidale, 2008, Cultural relationships beyond the Iranian plateau: the Helmand Civilization, Baluchistan and the Indus Valley in the 3rd millennium, pp. 17-18)
 Indus terracotta nodules. Source: "Terra cotta nodules and cakes of different shapes are common at most Indus sites. These objects appear to have been used in many different ways depending on their shape and size. The flat triangular and circular shaped cakes may have been heated and used for baking small triangular or circular shaped flat bread. The round and irregular shaped nodules have been found in cooking hearths and at the mouth of pottery kilns where they served as heat baffles. Broken and crushed nodule fragments were used instead of gravel for making a level foundation underneath brick walls."
Indus terracotta nodules. Source: "Terra cotta nodules and cakes of different shapes are common at most Indus sites. These objects appear to have been used in many different ways depending on their shape and size. The flat triangular and circular shaped cakes may have been heated and used for baking small triangular or circular shaped flat bread. The round and irregular shaped nodules have been found in cooking hearths and at the mouth of pottery kilns where they served as heat baffles. Broken and crushed nodule fragments were used instead of gravel for making a level foundation underneath brick walls." Terracotta cake. Mohenjo-daro Excavation Number: VS3646. Location of find: 1, I, 37 (near NE corner of the room)."People have many different ideas about how these triangular blocks of clay were used. One idea is that they were placed inside kilns to keep in the heat while objects were fired. Another idea is that they were heated in a fire or oven, then placed in pots to boil liquids." Source: http://www.ancientindia.co.uk/indus/explore/nvs_tcake.html
Terracotta cake. Mohenjo-daro Excavation Number: VS3646. Location of find: 1, I, 37 (near NE corner of the room)."People have many different ideas about how these triangular blocks of clay were used. One idea is that they were placed inside kilns to keep in the heat while objects were fired. Another idea is that they were heated in a fire or oven, then placed in pots to boil liquids." Source: http://www.ancientindia.co.uk/indus/explore/nvs_tcake.htmlThese terracotta cakes are like Ancient Near East tokens used for accounting, as elaborated by Denise Schmandt-Besserat in her pioneering researches.
The context in which an incised terracotta cake was found at Kalibangan is instructive. I suggest that terracotta cakes were tokens to count the ingots produced in a 'fire-altar' and crucibles, by metallurgists of Sarasvati civilization. This system of incising is found in scores of miniature incised tablets of Harappa, incised with Indus writing. Some of these tablets are shaped like bun ingots, some are triangular and some are shaped like fish. Each shape should have had some semantic significance, e.g., fish may have connoted ayo 'fish' as a glyph; read rebus: ayas 'metal (alloy)'. A horned person on the Kalibangan terracotta cake described herein might have connoted: kōṭu 'horn'; rebus: खोट khōṭa 'A mass of metal (unwrought or of old metal melted down); an ingot or wedge. Hence 2 A lump or solid bit'; खोटसाळ khōṭasāḷa 'Alloyed--a metal'(Marathi) A stake associated with the fire-altar was ढांगर [ ḍhāṅgara ] n 'A stout stake or stick as a prop to a Vine or scandent shrub]' (Marathi); rebus:ḍhaṅgar 'smith' (Maithili. Hindi)
At Kalibangan, fire Vedic altars have been discovered, similar to those found at Lothal which S.R. Rao thinks could have served no other purpose than a ritualistic one.[18] These altars suggest fire worship or worship of Agni, the Hindu god of fire. It is the only Indus Valley Civilization site where there is no evidence to suggest the worship of the "mother goddess".
Within the fortified citadel complex, the southern half contained many (five or six) raised platforms of mud bricks, mutually separated by corridors. Stairs were attached to these platforms. Vandalism of these platforms by brick robbers makes it difficult to reconstruct the original shape of structures above them but unmistakable remnants of rectangular or oval kuṇḍas or fire-pits of burnt bricks for Vedi (altar)s have been found, with a yūpa or sacrificial post (cylindrical or with rectangular cross-section, sometimes bricks were laid upon each other to construct such a post) in the middle of each kuṇḍa and sacrificial terracotta cakes (piṇḍa) in all these fire-pits. Houses in the lower town also contain similar altars. Burnt charcoals have been found in these fire-pits. The structure of these fire-altars is reminiscent of (Vedic) fire-altars, but the analogy may be coincidental, and these altars are perhaps intended for some specific (perhaps religious) purpose by the community as a whole. In some fire-altars remnants of animals have been found, which suggest a possibility of animal-sacrifice." Source: Elements of Indian Archaeology (Bharatiya Puratatva,in Hindi) by Shri Krishna Ojha, published by Research Publications in Social Sciences, 2/44 Ansari Riad, Daryaganj, New Delhi-2, pp.119-120. (The fifth chapter summarizes the excavation report of Kalibangan in 11 pages).
Tu. kandůka, kandaka ditch, trench. Te. kandakamu id. Konḍa kanda trench made as a fireplace during weddings. Pe. kanda fire trench. Kui kanda small trench for fireplace. Malt. kandri a pit. (DEDR 1214)
Ka. kunda a pillar of bricks, etc. Tu. kunda pillar, post. Te. kunda id. Malt.
kunda block, log. ? Cf. Ta. kantu pillar, post. (DEDR 1723)
kándu f. ʻ iron pot ʼ Suśr., °uka -- m. ʻ saucepan ʼ.Pk. kaṁdu -- , kaṁḍu -- m.f. ʻ cooking pot ʼ; K. kō̃da f. ʻ potter's kiln, lime or brick kiln ʼ; -- ext. with -- ḍa -- : K. kã̄dur m. ʻ oven ʼ. -- Deriv. Pk.kaṁḍua -- ʻ sweetseller ʼ (< *kānduka -- ?); H. kã̄dū m. ʻ a caste that makes sweetmeats ʼ. (CDIAL 2726) *kandukara ʻ worker with pans ʼ. [kándu -- , kará -- 1]
K. kã̄dar, kã̄duru dat. °daris m. ʻ baker ʼ.(CDIAL 2728)
Rebus: khāṇḍā 'tools, pots and pans,metal-
S. Kalyanaraman
Sarasvati Research Center
December 15, 2015