Mirror: http://tinyurl.com/o2uvryz
A set of five Indus seal replicas distributed to visitors by the National Museum, Janpath, New Delhi are presented in the following photographs.
These are presented as Seals 1 to 5 and deciphered in the context of comparable seals with comparable Indus Script hieroglyph/hieroglyph-multiplexes:
Seal 1 (One-horned young bull, standard device)
Seal 2 (Two heads of young bulls, nine ficus leaves)
Seal 3 (Seated person surrounded by animals and hieroglyphs)
Seal 4 (Two tigers, woman)
Seal 5 (Zebu seal)
![]()
![]()
All Indus Script hieroglyphs on this set of seals are deciphered as metalwork catalogues.
Seal 1 (One-horned young bull, standard device)
![]()
![]()
dula 'pair' rebus: dul 'cast metal'; loa 'ficus' rebus: loh 'copper'; kamaDha 'bow' rebus: kampaTTa 'mint, coiner' meD 'body' rebus: meD 'iron, copper, metal'. gaNDa 'four' rebus; kanda 'fire-altar' PLUS dula 'pair' rebus: dul 'cast metal' (Thus, the pair of four strokes signifies 'cast metal fire-altar').
ranku 'liquid measure' rebus: ranku 'tin' (One is inlaid with a pair of three short strokes: kolmo 'three' rebus: kolimi 'smithy, forge'; the other is inlaid with three horizontal strokes. One may indicate cast tin and the other may indicate a tin smithy).
eraka 'knave of wheel' rebus: erako 'moltencast'; arka 'copper'.
Hieroglyph: धातु [p= 513,3] m. layer , stratum Ka1tyS3r. Kaus3. constituent part , ingredient (esp. [ and in RV. only] ifc. , where often = " fold " e.g. त्रि-ध्/आतु , threefold &c ; cf.त्रिविष्टि- , सप्त- , सु-) RV. TS. S3Br. &c (Monier-Williams) dhāˊtu *strand of rope ʼ (cf. tridhāˊtu -- ʻ threefold ʼ RV., ayugdhātu -- ʻ having an uneven number of strands ʼ KātyŚr.).; S. dhāī f. ʻ wisp of fibres added from time to time to a rope that is being twisted ʼ, L. dhāī˜ f.(CDIAL 6773) tántu m. ʻ thread, warp ʼ RV. [√tan ] Pa. tantu -- m. ʻ thread, cord ʼ, Pk. taṁtu -- m.; Kho. (Lor.) ton ʻ warp ʼ < *tand (whence tandeni ʻ thread between wings of spinning wheel ʼ); S. tandu f. ʻ gold or silver thread ʼ; L. tand (pl. °dũ) f. ʻ yarn, thread being spun, string of the tongue ʼ; P. tand m. ʻ thread ʼ, tanduā, °dūā m. ʻ string of the tongue, frenum of glans penis ʼ; A. tã̄t ʻ warp in the loom, cloth being woven ʼ; B. tã̄t ʻ cord ʼ; M. tã̄tū m. ʻ thread ʼ; Si. tatu, °ta ʻ string of a lute ʼ; -- with -- o, -- ā to retain orig. gender: S. tando m. ʻ cord, twine, strand of rope ʼ; N. tã̄do ʻ bowstring ʼ; H. tã̄tā m. ʻ series, line ʼ; G. tã̄tɔ m. ʻ thread ʼ; -- OG. tāṁtaṇaü m. ʻ thread ʼ < *tāṁtaḍaü, G.tã̄tṇɔ m.(CDIAL 5661)
Rebus: M. dhāū, dhāv m.f. ʻ a partic. soft red stone ʼ (whence dhā̆vaḍ m. ʻ a caste of iron -- smelters ʼ, dhāvḍī ʻ composed of or relating to iron ʼ); dhāˊtu n. ʻ substance ʼ RV., m. ʻ element ʼ MBh., ʻ metal, mineral, ore (esp. of a red colour) ʼ; Pk. dhāu -- m. ʻ metal, red chalk ʼ; N. dhāu ʻ ore (esp. of copper) ʼ; Or. ḍhāu ʻ red chalk, red ochre ʼ (whence ḍhāuā ʻ reddish ʼ; (CDIAL 6773) धातु primary element of the earth i.e. metal , mineral, ore (esp. a mineral of a red colour) Mn. MBh. &c element of words i.e. grammatical or verbal root or stem Nir. Pra1t. MBh. &c (with the southern Buddhists धातु means either the 6 elements [see above] Dharmas. xxv ; or the 18 elementary spheres [धातु-लोक] ib. lviii ; or the ashes of the body , relics L. [cf. -गर्भ]) (Monier-Williams. Samskritam).
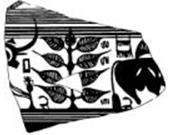
Seal 2 (Two heads of young bulls, nine ficus leaves)
m0296 Two heads of one-horned bulls with neck-rings, joined end to end (to a standard device with two rings coming out of the top part?), under a stylized pipal tree with nine leaves. Text 1387
![]() Ayo ‘fish’; kaṇḍa‘arrow’; rebus: ayaskāṇḍa. The sign sequence is ayaskāṇḍa ‘a quantity of iron,excellent iron’ (Pāṇ.gaṇ) ayo, hako 'fish'; a~s = scales of fish (Santali); rebus:aya = iron (G.); ayah, ayas = metal (Skt.) kaṇḍa‘fire-altar’ (Santali) DEDR 191 Ta. ayirai,acarai, acalai loach, sandy colour, Cobitisthermalis; ayilai a kind of fish. Ma. ayala a fish,mackerel, scomber; aila, ayila a fish; ayira a kind ofsmall fish, loach.
Ayo ‘fish’; kaṇḍa‘arrow’; rebus: ayaskāṇḍa. The sign sequence is ayaskāṇḍa ‘a quantity of iron,excellent iron’ (Pāṇ.gaṇ) ayo, hako 'fish'; a~s = scales of fish (Santali); rebus:aya = iron (G.); ayah, ayas = metal (Skt.) kaṇḍa‘fire-altar’ (Santali) DEDR 191 Ta. ayirai,acarai, acalai loach, sandy colour, Cobitisthermalis; ayilai a kind of fish. Ma. ayala a fish,mackerel, scomber; aila, ayila a fish; ayira a kind ofsmall fish, loach.![]() kole.l 'temple, smithy'(Ko.); kolme ‘smithy' (Ka.) kol ‘working in iron, blacksmith (Ta.); kollan-blacksmith (Ta.); kollan blacksmith, artificer (Ma.)(DEDR 2133) kolme =furnace (Ka.) kol = pan~calo_ha (fivemetals); kol metal (Ta.lex.) pan~caloha = a metallic alloy containing five metals: copper, brass, tin, lead and iron (Skt.); an alternative list of five metals: gold, silver, copper, tin (lead), and iron (dhātu; Nānārtharatnākara. 82; Man:garāja’s Nighaṇṭu. 498)(Ka.) kol, kolhe, ‘the koles, an aboriginal tribe if iron smelters speaking a language akin to that of Santals’ (Santali)
kole.l 'temple, smithy'(Ko.); kolme ‘smithy' (Ka.) kol ‘working in iron, blacksmith (Ta.); kollan-blacksmith (Ta.); kollan blacksmith, artificer (Ma.)(DEDR 2133) kolme =furnace (Ka.) kol = pan~calo_ha (fivemetals); kol metal (Ta.lex.) pan~caloha = a metallic alloy containing five metals: copper, brass, tin, lead and iron (Skt.); an alternative list of five metals: gold, silver, copper, tin (lead), and iron (dhātu; Nānārtharatnākara. 82; Man:garāja’s Nighaṇṭu. 498)(Ka.) kol, kolhe, ‘the koles, an aboriginal tribe if iron smelters speaking a language akin to that of Santals’ (Santali)
![]() dol = likeness, picture, form (Santali) [e.g., two tigers, two bulls, duplicated signs] me~ṛhe~t iron; ispat m. = steel; dul m. = cast iron (Santali) [Thus, the paired glyph of one-horned heifers connotes (metal) casting (dul) workshop (koḍ)]
dol = likeness, picture, form (Santali) [e.g., two tigers, two bulls, duplicated signs] me~ṛhe~t iron; ispat m. = steel; dul m. = cast iron (Santali) [Thus, the paired glyph of one-horned heifers connotes (metal) casting (dul) workshop (koḍ)]
Head gear: Hieroglyph: taTThAr 'buffalo horn' Rebus: taTTAr 'brass worker'; Hieroglyph: goṇḍe ʻ cluster ʼ (Kannada) Rebus: kuṇḍi-a = village headman; leader of a village (Prakritam)
Decoding the text of the inscriptionText 2420 on m0304
Line 2 (bottom): 'body' glyph. mēd ‘body’ (Kur.)(DEDR 5099); meḍ ‘iron’ (Ho.)
Line 1 (top):
'Body' glyph plus ligature of 'splinter' shown between the legs: mēd ‘body’ (Kur.)(DEDR 5099); meḍ ‘iron’ (Ho.) sal ‘splinter’; Rebus: sal ‘workshop’ (Santali) Thus, the ligatured glyph is read rebus as: meḍ sal 'iron (metal) workshop'.
Sign 216 (Mahadevan). ḍato ‘claws or pincers (chelae) of crabs’; ḍaṭom, ḍiṭom to seize with the claws or pincers, as crabs, scorpions; ḍaṭkop = to pinch, nip (only of crabs) (Santali) Rebus: dhatu ‘mineral’ (Santali) Vikalpa: erā ‘claws’; Rebus: era ‘copper’. Allograph: kamaṛkom = fig leaf (Santali.lex.) kamarmaṛā (Has.), kamaṛkom (Nag.); the petiole or stalk of a leaf (Mundari.lex.) kamat.ha = fig leaf, religiosa (Skt.)
Sign 229. sannī, sannhī = pincers, smith’s vice (P.) śannī f. ʻ small room in a house to keep sheep in ‘ (WPah.) Bshk. šan, Phal.šān ‘roof’ (Bshk.)(CDIAL 12326). seṇi (f.) [Class. Sk. śreṇi in meaning "guild"; Vedic= row] 1. a guild Vin iv.226; J i.267, 314; iv.43; Dāvs ii.124; their number was eighteen J vi.22, 427; VbhA 466. ˚ -- pamukha the head of a guild J ii.12 (text seni -- ). -- 2. a division of an army J vi.583; ratha -- ˚ J vi.81, 49; seṇimokkha the chief of an army J vi.371 (cp. senā and seniya). (Pali)
Sign 342. kaṇḍa kanka 'rim of jar' (Santali): karṇaka rim of jar’(Skt.) Rebus: karṇaka ‘scribe, accountant’ (Te.); gaṇaka id. (Skt.) (Santali) copper fire-altar scribe (account)(Skt.) Rebus: kaṇḍ ‘fire-altar’ (Santali) Thus, the 'rim of jar' ligatured glyph is read rebus: fire-altar (furnace) scribe (account) karNI 'supercargo' (Marathi)
Sign 344. Ligatured glyph: 'rim of jar' ligature + splinter (infixed); 'rim of jar' ligature is read rebus: kaṇḍa karṇaka 'furnace scribe (account)'.
sal stake, spike, splinter, thorn, difficulty (H.); Rebus: sal ‘workshop’ (Santali) *ஆலை³ ālai, n. < šālā. 1. Apartment, hall; சாலை. ஆலைசேர் வேள்வி (தேவா. 844. 7). 2. Elephant stable or stall; யானைக்கூடம். களிறு சேர்ந் தல்கிய வழுங்க லாலை (புறநா. 220, 3).ஆலைக்குழி ālai-k-kuḻi, n. < ஆலை¹ +. Receptacle for the juice underneath a sugar-cane press; கரும்பாலையிற் சாறேற்கும் அடிக்கலம்.*ஆலைத்தொட்டி ālai-t-toṭṭi, n. < id. +. Cauldron for boiling sugar-cane juice; கருப்பஞ் சாறு காய்ச்சும் சால்.ஆலைபாய்-தல் ālai-pāy-, v. intr. < id. +. 1. To work a sugar-cane mill; ஆலையாட்டுதல். ஆலைபாயோதை (சேதுபு. நாட்டு. 93). 2. To move, toss, as a ship; அலைவுறுதல். (R.) 3. To be undecided, vacillating; மனஞ் சுழலுதல். நெஞ்ச மாலைபாய்ந் துள்ள மழிகின்றேன் (அருட்பா,) Vikalpa: sal ‘splinter’; rebus: workshop (sal)’ ālai ‘workshop’ (Ta.) *ஆலை³ ālai, n. < šālā. 1. Apartment, hall; சாலை. ஆலைசேர் வேள்வி (தேவா. 844. 7). 2. Elephant stable or stall; யானைக்கூடம். களிறு சேர்ந் தல்கிய வழுங்க லாலை (புறநா. 220, 3).ஆலைக்குழி ālai-k-kuḻi, n. < ஆலை¹ +. Receptacle for the juice underneath a sugar-cane press; கரும்பாலையிற் சாறேற்கும் அடிக்கலம்.*ஆலைத்தொட்டி ālai-t-toṭṭi, n. < id. +. Cauldron for boiling sugar-cane juice; கருப்பஞ் சாறு காய்ச்சும் சால்.ஆலைபாய்-தல் ālai-pāy-, v. intr. < id. +. 1. To work a sugar-cane mill; ஆலையாட்டுதல். ஆலைபாயோதை (சேதுபு. நாட்டு. 93) Thus, together with the 'splinter' glyph, the entire ligature 'rim of jar + splinter/splice' is read rebus as: furnace scribe (account workshop). Sign 59. ayo, hako 'fish'; a~s = scales of fish (Santali); rebus: aya = iron (G.); ayah, ayas = metal (Skt.) Sign 342. kaṇḍa karṇaka 'rim of jar'; rebus: 'furnace scribe (account)'. Thus the inscription reads rebus: iron, iron (metal) workshop, copper (mineral) guild, fire-altar (furnace) scribe (account workshop), metal furnace scribe (account) As the decoding of m0304 seal demonstrates, the Indus hieroglyphs are the professional repertoire of an artisan (miners'/metalworkers') guild detailing the stone/mineral/metal resources/furnaces/smelters of workshops (smithy/forge/turners' shops).
Seal 4 (Two tigers, woman)
![A woman flanked by rampant tigers, a theme repeated in another seal, with identical glyphs at top.:]()
![woman flanked by tigers]()
![]() Text 2086 m0306 Person grappling with two tigers standing on either side of him and rearing on their hindlegs.
Text 2086 m0306 Person grappling with two tigers standing on either side of him and rearing on their hindlegs.
dula 'pair' rebus: dul 'cast metal' kola 'tiger' rebus; kol 'working in iron'. Thus, iron casting.
kola 'tiger', kola 'woman' rebus: kolle 'blacksmith' kolhe 'smelter' kol 'working in iron' kolimi 'smithy, forge'
kole.l 'temple' rebus; koe.l 'smithy'
karNika 'rim of jar' rebus: karNI 'supercargo' kanka, karNIka 'scribe' kanga 'brazier'
kamaDha 'crab' rebus: kampaTTa 'mint, coiner'
Oval shaped glyph: muhe 'ingot' PLUS kolmo 'rice plant' rebus: kolimi 'smithy,forge'. Thus, ingot smithy. Alternative: pair of parentheses or curves:
![]() The 'curve' hieroglyph is a splitting of the ellipse. kuṭila ‘bent’ CDIAL 3230 kuṭi— in cmpd. ‘curve’, kuṭika— ‘bent’ MBh.
The 'curve' hieroglyph is a splitting of the ellipse. kuṭila ‘bent’ CDIAL 3230 kuṭi— in cmpd. ‘curve’, kuṭika— ‘bent’ MBh.
Notch inlaid in rim of jar: karNika 'rim of jar' rebus: karNI 'supercargo' kanka, karNIka 'scribe' kanga 'brazier' PLUS kaNDa 'notch' rebus: kANDA 'tools, pots and pans, implements'.
sãghāṛɔ 'lathe'.(Gujarati) sangaDa 'lathe, portable furnace' rebus: sangara 'proclamation' sangāṭhसंगाठ् । सामग्री m. (sg. dat. sangāṭas संगाटस् ), a collection (of implements, tools, materials, for any object), apparatus, furniture, a collection of the things wanted on a journey, luggage, and so on. -- karun -- करुन् । सामग्रीसंग्रहः m.inf. to collect the ab. (L.V. 17).(Kashmiri).
Seal 5 (Zebu seal)
kanac 'corner' rebus: kancu 'bronze'.
![]() Zebu seal inscription, Hieroglyphs from r. sluice, one linear stroke, two short strokes superscript, three short strokes, rice plantHieroglyph: poLa 'zebu' Rebus: poLa 'magnetite'
Zebu seal inscription, Hieroglyphs from r. sluice, one linear stroke, two short strokes superscript, three short strokes, rice plantHieroglyph: poLa 'zebu' Rebus: poLa 'magnetite'
Hieroglyphs on text and rebus readings:
koḍa 'sluice'; Rebus: koḍ 'artisan's workshop (Kuwi). See alternative reading.
koḍa 'one' Rebus: koḍ 'artisan's workshop (Kuwi). Phonetic determinative.
sal 'splinter' Rebus: sal 'workshop' Phonetic determinative.
kolmo 'three' Rebus: kolimi 'smithy, forge' Phonetic determinative.
kolom 'rice plant' Rebus: kolimi 'smithy, forge'
![Magnetite exposed on the ground. The mineral is black and irregularly smooth. Individual chunks jut at angles characteristic of the crystal habit.]() Magnetite and pyrite from, Piedmont, Italy.
Magnetite and pyrite from, Piedmont, Italy.
![Image result for standard device indus script]() m0490At m0490Bt Tablet showing Meluhha combined standard of four standards carried in a procession, comparable to Tablet m0491.
m0490At m0490Bt Tablet showing Meluhha combined standard of four standards carried in a procession, comparable to Tablet m0491. ![]() m0491 This is a report on the transition from lapidary to bronze-age metalware in ancient Near East.
m0491 This is a report on the transition from lapidary to bronze-age metalware in ancient Near East.
eraka 'nave of wheel' Rebus: moltencast copper
dhatu 'scarf' Rebus: mineral ore dhāū, dhāv m.f. ʻa partic. soft red stoneʼ (Marathi) (whence dhā̆vaḍ m. ʻa caste of iron -- smeltersʼ, dhāvḍī ʻ composed of or relating to iron ʼ)
kōnda 'young bull' Rebus: turner
sãgaḍ 'lathe' Rebus: sangara proclamation
kanga 'portable brazier' Rebus: fireplace, furnace
Glyphic element: erako nave; era = knave of wheel. Glyphic element: āra ‘spokes’. Rebus: āra ‘brass’ as in ārakūṭa (Skt.) Rebus: Tu. eraka molten, cast (as metal); eraguni to melt (DEDR 866) erka = ekke (Tbh. of arka) aka (Tbh. of arka) copper (metal); crystal (Kannada.) cf. eruvai = copper (Ta.lex.) eraka, er-aka = any metal infusion (Ka.Tu.); erako molten cast (Tulu) The same spoked-wheel hieroglyph adorns the Dholavira Sign-board.
āra 'spokes' Rebus: āra 'bronze'. cf. erka = ekke (Tbh. of arka) aka (Tbh. of arka) copper (metal); crystal (Kannada) Glyph: eraka
![]()
![]() Other examples of 'standard device' in front of one-horned young bull. The second from r. is an example of the 'standard' as an object.
Other examples of 'standard device' in front of one-horned young bull. The second from r. is an example of the 'standard' as an object.
Note the doted circles on the bottom register of the hieroglyph-multiplex of the standard device. These signify the semantics: 'full of holes'. The signifier is the word: Pk. kāṇa -- ʻ full of holes ʼ, G. kāṇũ ʻ full of holes ʼ, n. ʻ hole ʼ (< ʻ empty eyehole ʼ?(CDIAL 3019)kaṇa (pl. kaṇul) hole; (Go.)(DEDR 1159) Pe. kaṇga (pl. -ŋ, kaṇku) eye. Rebus: kanga ' large portable brazier, fire-place' (Kashmiri). Thus, the standard device is a combination of two hieroglyh components signifying: lathe, portable brazier: sangaDa + kanga Rebus: proclamation (collected products out of)+ fireplace.
![]() 'Eye' hieroglyph shown on Kuwait gold disk signifying kanga 'portable brazier' Rebus: kanga 'fireplace, furnace'
'Eye' hieroglyph shown on Kuwait gold disk signifying kanga 'portable brazier' Rebus: kanga 'fireplace, furnace'
See: http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2015/08/indus-script-hieroglyph-multiplex.html![]() Components: top register: lathe with pointed gimlet in churning motion; bottom register: portable furnace/crucible with smoke emanating from the surface PLUS flagposthttp://www.rmrl.in/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2014/02/papers/11.pdf
Components: top register: lathe with pointed gimlet in churning motion; bottom register: portable furnace/crucible with smoke emanating from the surface PLUS flagposthttp://www.rmrl.in/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2014/02/papers/11.pdf
kõdā‘to turn in a lathe’(B.) कोंद kōnda ‘engraver, lapidary setting or infixing gems’ (Marathi) koḍ ‘artisan’s workshop’ (Kuwi) koḍ = place where artisans work (G.) ācāri koṭṭya ‘smithy’ (Tu.) कोंडण [kōṇḍaṇa] f A fold or pen. (Marathi) B. kõdā ‘to turn in a lathe’; Or.kū̆nda ‘lathe’, kũdibā, kū̃d ‘to turn’ (→ Drav. Kur. Kū̃d ’ lathe’) (CDIAL 3295) A. kundār, B. kũdār, ri, Or.Kundāru; H. kũderā m. ‘one who works a lathe, one who scrapes’, rī f., kũdernā ‘to scrape, plane, round on a lathe’; kundakara—m. ‘turner’ (Skt.)(CDIAL 3297). कोंदण [ kōndaṇa ] n (कोंदणें) Setting or infixing of gems.(Marathi) খোদকার [ khōdakāra ] n an engraver; a carver. খোদকারি n. engraving; carving; interference in other’s work. খোদাই [ khōdāi ] n engraving; carving. খোদাই করা v. to engrave; to carve. খোদানো v. & n. en graving; carving. খোদিত [ khōdita ] a engraved. (Bengali) खोदकाम [ khōdakāma ] n Sculpture; carved work or work for the carver. खोदगिरी [ khōdagirī ] f Sculpture, carving, engraving: also sculptured or carved work. खोदणावळ [ khōdaṇāvaḷa ] f (खोदणें) The price or cost of sculpture or carving. खोदणी [ khōdaṇī ] f (Verbal of खोदणें) Digging, engraving &c. 2 fig. An exacting of money by importunity. V लाव, मांड. 3 An instrument to scoop out and cut flowers and figures from paper. 4 A goldsmith’s die. खोदणें [ khōdaṇēṃ ] v c & i ( H) To dig. 2 To engrave. खोद खोदून विचारणें or –पुसणें To question minutely and searchingly, to probe. खोदाई [ khōdāī ] f (H.) Price or cost of digging or of sculpture or carving. खोदींव [ khōdīṃva ] p of खोदणें Dug. 2 Engraved, carved, sculptured. (Marathi)
Hieroglyphs: G. sãghāṛɔ m. ʻ lathe ʼ; M. sãgaḍ f. ʻ a body formed of two or more fruits or animals or men &c. linked together, part of a turner's apparatus ʼ, m.f. ʻ float made of two canoes joined together ʼ (LM 417 compares saggarai at Limurike in the Periplus, Tam.śaṅgaḍam, Tu. jaṅgala ʻ double -- canoe ʼ), sã̄gāḍā m. ʻ frame of a building ʼ, °ḍī f. ʻ lathe ʼ; Si. san̆gaḷa ʻ pair ʼ, han̆guḷa, an̆g° ʻ double canoe, raft ʼ.(CDIAL 12859) Pa. saṅghāta -- m. ʻ killing, knocking together ʼ; Pk. saṁghāya -- m. ʻ closeness, collection ʼ; Or. saṅghā, saṅgā ʻ bamboo scaffolding inside triangular thatch, crossbeam of thatched house, copulation (of animals) ʼ; -- adj. ʻ bulled (of a cow) ʼ < *saṁghātā -- or saṁhatā -- ?(CDIAL 12862)
Rebus: Sangara [fr. saŋ+gṛ1 to sing, proclaim, cp. gāyati & gīta] 1. a promise, agreement J iv. 105, 111, 473; v. 25, 479
Rebus: saṁghāṭa m. ʻ fitting and joining of timber ʼ R. [√ghaṭ ](CDIAL 12859) संगत saṅgata Assembled, collected, convened, met together.संगतिः saṅgatiḥ Company, society, association, intercourse (Samskritam. Apte) Sangata [pp. of sangacchati] 1. come together, met Sn 807, 1102 (=samāgata samohita sannipātita Nd2 621); nt. sangataŋ association Dh 207. -- 2. compact, tightly fastened or closed, well -- joined Vv 642 (=nibbivara VvA 275).Sangati (f.) [fr. sangacchati] 1. meeting, intercourse J iv. 98; v. 78, 483. In defn of yajati (=service?) at Dhtp 62 & Dhtm 79. -- 2. union, combination M i. 111; Sii. 72; iv. 32 sq., 68 sq.; Vbh 138 (=VbhA 188). <-> 3. accidental occurrence D i. 53; DA i. 161. (Pali)
Proclamation of procession on Jasper Akkadian cylinder seal
See: http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2015/08/indus-script-hieroglyph-readings-on.html
Jasper Akkadian cylinder seal ca. 2220-2159 BCE
A set of five Indus seal replicas distributed to visitors by the National Museum, Janpath, New Delhi are presented in the following photographs.
These are presented as Seals 1 to 5 and deciphered in the context of comparable seals with comparable Indus Script hieroglyph/hieroglyph-multiplexes:
Seal 1 (One-horned young bull, standard device)
Seal 2 (Two heads of young bulls, nine ficus leaves)
Seal 3 (Seated person surrounded by animals and hieroglyphs)
Seal 4 (Two tigers, woman)
Seal 5 (Zebu seal)


All Indus Script hieroglyphs on this set of seals are deciphered as metalwork catalogues.
Seal 1 (One-horned young bull, standard device)


dula 'pair' rebus: dul 'cast metal'; loa 'ficus' rebus: loh 'copper'; kamaDha 'bow' rebus: kampaTTa 'mint, coiner' meD 'body' rebus: meD 'iron, copper, metal'. gaNDa 'four' rebus; kanda 'fire-altar' PLUS dula 'pair' rebus: dul 'cast metal' (Thus, the pair of four strokes signifies 'cast metal fire-altar').
ranku 'liquid measure' rebus: ranku 'tin' (One is inlaid with a pair of three short strokes: kolmo 'three' rebus: kolimi 'smithy, forge'; the other is inlaid with three horizontal strokes. One may indicate cast tin and the other may indicate a tin smithy).
eraka 'knave of wheel' rebus: erako 'moltencast'; arka 'copper'.
Hieroglyph: धातु [p= 513,3] m. layer , stratum Ka1tyS3r. Kaus3. constituent part , ingredient (esp. [ and in RV. only] ifc. , where often = " fold " e.g. त्रि-ध्/आतु , threefold &c ; cf.त्रिविष्टि- , सप्त- , सु-) RV. TS. S3Br. &c (Monier-Williams) dhāˊtu *strand of rope ʼ (cf. tridhāˊtu -- ʻ threefold ʼ RV., ayugdhātu -- ʻ having an uneven number of strands ʼ KātyŚr.).; S. dhāī f. ʻ wisp of fibres added from time to time to a rope that is being twisted ʼ, L. dhāī˜ f.(CDIAL 6773) tántu m. ʻ thread, warp ʼ RV. [√
Rebus: M. dhāū, dhāv m.f. ʻ a partic. soft red stone ʼ (whence dhā̆vaḍ m. ʻ a caste of iron -- smelters ʼ, dhāvḍī ʻ composed of or relating to iron ʼ); dhāˊtu n. ʻ substance ʼ RV., m. ʻ element ʼ MBh., ʻ metal, mineral, ore (esp. of a red colour) ʼ; Pk. dhāu -- m. ʻ metal, red chalk ʼ; N. dhāu ʻ ore (esp. of copper) ʼ; Or. ḍhāu ʻ red chalk, red ochre ʼ (whence ḍhāuā ʻ reddish ʼ; (CDIAL 6773) धातु primary element of the earth i.e. metal , mineral, ore (esp. a mineral of a red colour) Mn. MBh. &c element of words i.e. grammatical or verbal root or stem Nir. Pra1t. MBh. &c (with the southern Buddhists धातु means either the 6 elements [see above] Dharmas. xxv ; or the 18 elementary spheres [धातु-लोक] ib. lviii ; or the ashes of the body , relics L. [cf. -गर्भ]) (Monier-Williams. Samskritam).
Seal 2 (Two heads of young bulls, nine ficus leaves)
m0296 Two heads of one-horned bulls with neck-rings, joined end to end (to a standard device with two rings coming out of the top part?), under a stylized pipal tree with nine leaves. Text 1387
Mohenjo-daro Seal impression. m0296 Two heads of one-horned bulls with neck-rings, joined end to end (to a standard device with two rings coming out of the top part?), under a stylized tree-branch with nine leaves.
खोंद [ khōnda ] n A hump (on the back): also a protuberance or an incurvation (of a wall, a hedge, a road). Rebus: खोदणें [ khōdaṇēṃ ] v c & i (
H) To dig. 2 To engrave. खोद खोदून विचारणें or -पुसणें To question minutely and searchingly, to probe.गोट [ gōṭa ] m (H) A metal wristlet. An ornament of women. 2 Encircling or investing. v घाल, दे. 3 An encampment or camp: also a division of a camp. 4 The hem or an appended border (of a garment).गोटा [ gōṭā ] m A roundish stone or pebble. 2 A marble (of stone, lac, wood &c.) 3 fig. A grain of rice in the ear. Ex. पावसानें भाताचे गोटे झडले. An overripe and rattling cocoanut: also such dry kernel detached from the shell. 5 A narrow fillet of brocade.गोटाळ [ gōṭāḷa ] a (गोटा) Abounding in pebbles--ground.गोटी [ gōṭī ] f (Dim. of गोटा) A roundish stone or pebble. 2 A marble. 3 A large lifting stone. Used in trials of strength among the Athletæ. 4 A stone in temples described at length under उचला 5 fig. A term for a round, fleshy, well-filled body.
H) To dig. 2 To engrave. खोद खोदून विचारणें or -पुसणें To question minutely and searchingly, to probe.गोट [ gōṭa ] m (H) A metal wristlet. An ornament of women. 2 Encircling or investing. v घाल, दे. 3 An encampment or camp: also a division of a camp. 4 The hem or an appended border (of a garment).गोटा [ gōṭā ] m A roundish stone or pebble. 2 A marble (of stone, lac, wood &c.) 3 fig. A grain of rice in the ear. Ex. पावसानें भाताचे गोटे झडले. An overripe and rattling cocoanut: also such dry kernel detached from the shell. 5 A narrow fillet of brocade.गोटाळ [ gōṭāḷa ] a (गोटा) Abounding in pebbles--ground.गोटी [ gōṭī ] f (Dim. of गोटा) A roundish stone or pebble. 2 A marble. 3 A large lifting stone. Used in trials of strength among the Athletæ. 4 A stone in temples described at length under उचला 5 fig. A term for a round, fleshy, well-filled body.
Rebus: गोटी [ gōṭī ] f (Dim. of गोटा) A lump of silver: as obtained by melting down lace or fringe.
Hieroglyph: lo = nine (Santali); no = nine (B.) on-patu = nine (Ta.)
[Note the count of nine fig leaves on m0296] Rebus: loa = a
species of fig tree, ficus glomerata,
the fruit of ficus glomerata (Santali.lex.)
species of fig tree, ficus glomerata,
the fruit of ficus glomerata (Santali.lex.)
corner (Santali); Rebus: kan~cu
= bronze (Te.)![]() Ligatured glyph. ara 'spoke' rebus: ara 'brass'. era, er-a = eraka =?nave; erako_lu = the iron axle of a carriage (Ka.M.); cf. irasu (Ka.lex.)[Note Sign 391 and its ligatures Signs 392 and 393 may connote a spoked-wheel,nave of the wheel through which the axle passes; cf. ara_, spoke]erka = ekke (Tbh.of arka) aka (Tbh. of arka) copper (metal);crystal (Ka.lex.) cf. eruvai = copper (Ta.lex.) eraka, er-aka = anymetal infusion (Ka.Tu.); erako molten cast (Tu.lex.) Rebus: eraka= copper (Ka.)eruvai =copper (Ta.); ere - a dark-red colour (Ka.)(DEDR 817). eraka, era, er-a= syn. erka, copper, weapons (Ka.)Vikalpa: ara, arā (RV.) = spokeof wheel ஆரம்² āram , n. < āra. 1. Spokeof a wheel.See ஆரக்கால். ஆரஞ்சூழ்ந்தவயில்வாய்
Ligatured glyph. ara 'spoke' rebus: ara 'brass'. era, er-a = eraka =?nave; erako_lu = the iron axle of a carriage (Ka.M.); cf. irasu (Ka.lex.)[Note Sign 391 and its ligatures Signs 392 and 393 may connote a spoked-wheel,nave of the wheel through which the axle passes; cf. ara_, spoke]erka = ekke (Tbh.of arka) aka (Tbh. of arka) copper (metal);crystal (Ka.lex.) cf. eruvai = copper (Ta.lex.) eraka, er-aka = anymetal infusion (Ka.Tu.); erako molten cast (Tu.lex.) Rebus: eraka= copper (Ka.)eruvai =copper (Ta.); ere - a dark-red colour (Ka.)(DEDR 817). eraka, era, er-a= syn. erka, copper, weapons (Ka.)Vikalpa: ara, arā (RV.) = spokeof wheel ஆரம்² āram , n. < āra. 1. Spokeof a wheel.See ஆரக்கால். ஆரஞ்சூழ்ந்தவயில்வாய்
= bronze (Te.)
 Ligatured glyph. ara 'spoke' rebus: ara 'brass'. era, er-a = eraka =?nave; erako_lu = the iron axle of a carriage (Ka.M.); cf. irasu (Ka.lex.)[Note Sign 391 and its ligatures Signs 392 and 393 may connote a spoked-wheel,nave of the wheel through which the axle passes; cf. ara_, spoke]erka = ekke (Tbh.of arka) aka (Tbh. of arka) copper (metal);crystal (Ka.lex.) cf. eruvai = copper (Ta.lex.) eraka, er-aka = anymetal infusion (Ka.Tu.); erako molten cast (Tu.lex.) Rebus: eraka= copper (Ka.)eruvai =copper (Ta.); ere - a dark-red colour (Ka.)(DEDR 817). eraka, era, er-a= syn. erka, copper, weapons (Ka.)Vikalpa: ara, arā (RV.) = spokeof wheel ஆரம்² āram , n. < āra. 1. Spokeof a wheel.See ஆரக்கால். ஆரஞ்சூழ்ந்தவயில்வாய்
Ligatured glyph. ara 'spoke' rebus: ara 'brass'. era, er-a = eraka =?nave; erako_lu = the iron axle of a carriage (Ka.M.); cf. irasu (Ka.lex.)[Note Sign 391 and its ligatures Signs 392 and 393 may connote a spoked-wheel,nave of the wheel through which the axle passes; cf. ara_, spoke]erka = ekke (Tbh.of arka) aka (Tbh. of arka) copper (metal);crystal (Ka.lex.) cf. eruvai = copper (Ta.lex.) eraka, er-aka = anymetal infusion (Ka.Tu.); erako molten cast (Tu.lex.) Rebus: eraka= copper (Ka.)eruvai =copper (Ta.); ere - a dark-red colour (Ka.)(DEDR 817). eraka, era, er-a= syn. erka, copper, weapons (Ka.)Vikalpa: ara, arā (RV.) = spokeof wheel ஆரம்² āram , n. < āra. 1. Spokeof a wheel.See ஆரக்கால். ஆரஞ்சூழ்ந்தவயில்வாய்நேமியொடு (சிறுபாண். 253). Rebus: ஆரம் brass; பித்தளை.(அக. நி.) pittal is cognate with 'pewter'.
‘iron smelter furnace’ (Santali) kuṭhī factory (A.)(CDIAL 3546)
 Ayo ‘fish’; kaṇḍa‘arrow’; rebus: ayaskāṇḍa. The sign sequence is ayaskāṇḍa ‘a quantity of iron,excellent iron’ (Pāṇ.gaṇ) ayo, hako 'fish'; a~s = scales of fish (Santali); rebus:aya = iron (G.); ayah, ayas = metal (Skt.) kaṇḍa‘fire-altar’ (Santali) DEDR 191 Ta. ayirai,acarai, acalai loach, sandy colour, Cobitisthermalis; ayilai a kind of fish. Ma. ayala a fish,mackerel, scomber; aila, ayila a fish; ayira a kind ofsmall fish, loach.
Ayo ‘fish’; kaṇḍa‘arrow’; rebus: ayaskāṇḍa. The sign sequence is ayaskāṇḍa ‘a quantity of iron,excellent iron’ (Pāṇ.gaṇ) ayo, hako 'fish'; a~s = scales of fish (Santali); rebus:aya = iron (G.); ayah, ayas = metal (Skt.) kaṇḍa‘fire-altar’ (Santali) DEDR 191 Ta. ayirai,acarai, acalai loach, sandy colour, Cobitisthermalis; ayilai a kind of fish. Ma. ayala a fish,mackerel, scomber; aila, ayila a fish; ayira a kind ofsmall fish, loach. kole.l 'temple, smithy'(Ko.); kolme ‘smithy' (Ka.) kol ‘working in iron, blacksmith (Ta.); kollan-blacksmith (Ta.); kollan blacksmith, artificer (Ma.)(DEDR 2133) kolme =furnace (Ka.) kol = pan~calo_ha (five
kole.l 'temple, smithy'(Ko.); kolme ‘smithy' (Ka.) kol ‘working in iron, blacksmith (Ta.); kollan-blacksmith (Ta.); kollan blacksmith, artificer (Ma.)(DEDR 2133) kolme =furnace (Ka.) kol = pan~calo_ha (fivefront of the standard device and the stylized tree of 9 leaves, are the black
buck antelopes. Black paint on red ware of Kulli style. Mehi. Second-half of
3rd millennium BCE. [After G.L. Possehl, 1986, Kulli: an exploration of an
ancient civilization in South Asia, Centers of Civilization, I, Durham, NC:
46, fig. 18 (Mehi II.4.5), based on Stein 1931: pl. 30.
buck antelopes. Black paint on red ware of Kulli style. Mehi. Second-half of
3rd millennium BCE. [After G.L. Possehl, 1986, Kulli: an exploration of an
ancient civilization in South Asia, Centers of Civilization, I, Durham, NC:
46, fig. 18 (Mehi II.4.5), based on Stein 1931: pl. 30.
poLa 'zebu' rebus; poLa 'magnetite'
ayir = iron dust, any ore (Ma.) aduru = gan.iyindategadu karagade iruva aduru = ore taken from the mine and not subjected to
melting in a furnace (Ka. Siddha_nti Subrahman.ya’ S’astri’s new interpretationof the Amarakos’a, Bangalore, Vicaradarpana Press, 1872, p. 330) DEDR 192 Ta. ayil iron. Ma. ayir,ayiram any ore. Ka. aduru native
metal. Tu. ajirdakarba very hard iron
melting in a furnace (Ka. Siddha_nti Subrahman.ya’ S’astri’s new interpretationof the Amarakos’a, Bangalore, Vicaradarpana Press, 1872, p. 330) DEDR 192 Ta. ayil iron. Ma. ayir,ayiram any ore. Ka. aduru native
metal. Tu. ajirdakarba very hard iron
loa = a species of fig tree, ficus glomerata, the fruit of ficus
glomerata (Santali.lex.) Vikalpa: kamaṛkom ‘ficus’ (Santali);
rebus: kampaṭṭam ‘mint’ (Ta.) patra ‘leaf’ (Skt.); rebus: paṭṭarai
‘workshop’ (Ta.) Rebus: lo ‘iron’ (Assamese, Bengali); loa ‘iron’ (Gypsy) lauha = made of
copper or iron (Gr.S'r.); metal, iron (Skt.); lo_haka_ra = coppersmith, ironsmith (Pali);lo_ha_ra = blacksmith (Pt.); lohal.a (Or.); lo_ha = metal, esp. copper or
bronze (Pali); copper (VS.); loho, lo_ = metal, ore, iron (Si.) loha lut.i = iron utensils and implements (Santali.lex.) koṭiyum = a wooden circle put round the neck of an animal; koṭ = neck (G.lex.) kōṭu = horns (Ta.) kōḍiya, kōḍe =
glomerata (Santali.lex.) Vikalpa: kamaṛkom ‘ficus’ (Santali);
rebus: kampaṭṭam ‘mint’ (Ta.) patra ‘leaf’ (Skt.); rebus: paṭṭarai
‘workshop’ (Ta.) Rebus: lo ‘iron’ (Assamese, Bengali); loa ‘iron’ (Gypsy) lauha = made of
copper or iron (Gr.S'r.); metal, iron (Skt.); lo_haka_ra = coppersmith, ironsmith (Pali);lo_ha_ra = blacksmith (Pt.); lohal.a (Or.); lo_ha = metal, esp. copper or
bronze (Pali); copper (VS.); loho, lo_ = metal, ore, iron (Si.) loha lut.i = iron utensils and implements (Santali.lex.) koṭiyum = a wooden circle put round the neck of an animal; koṭ = neck (G.lex.) kōṭu = horns (Ta.) kōḍiya, kōḍe =
young bull (G.) Rebus: koḍ = place where artisans work (G.lex.)
 dol = likeness, picture, form (Santali) [e.g., two tigers, two bulls, duplicated signs] me~ṛhe~t iron; ispat m. = steel; dul m. = cast iron (Santali) [Thus, the paired glyph of one-horned heifers connotes (metal) casting (dul) workshop (koḍ)]
dol = likeness, picture, form (Santali) [e.g., two tigers, two bulls, duplicated signs] me~ṛhe~t iron; ispat m. = steel; dul m. = cast iron (Santali) [Thus, the paired glyph of one-horned heifers connotes (metal) casting (dul) workshop (koḍ)]Seal 3 (Seatedd person surrounded by animals and hieroglyphs)
m0304 Mohenjo-daro seal. DK 5175, now in the National Museum of India, New Delhi. Seated person with buffalo horns.
Head gear: Hieroglyph: taTThAr 'buffalo horn' Rebus: taTTAr 'brass worker'; Hieroglyph: goṇḍe ʻ cluster ʼ (Kannada) Rebus: kuṇḍi-a = village headman; leader of a village (Prakritam)
mũh 'face'; rebus: metal ingot (Santali) mũhã̄ = the quantity of iron produced at one time in a native smelting furnace of the Kolhes; iron produced by the Kolhes and formed like a four-cornered piece a little pointed at each end; mūhā mẽṛhẽt = iron smelted by the Kolhes and formed into an equilateral lump a little pointed at each end; kolhe tehen me~ṛhe~t mūhā akata = the Kolhes have to-day produced pig iron (Santali.lex.)
Shoggy hair; tiger’s mane. sodo bodo, sodro bodro adj. adv. rough, hairy, shoggy, hirsute, uneven; sodo [Persian. sodā, dealing] trade; traffic; merchandise; marketing; a bargain; the purchase or sale of goods; buying and selling; mercantile dealings (G.lex.) sodagor = a merchant, trader; sodāgor (P.B.) (Santali.lex.) The face is depicted with bristles of hair, representing a tiger’s mane. cūḍā, cūlā, cūliyā tiger’s mane (Pkt.)(CDIAL 4883).Rebus: cūḷai 'furnace, kiln, funeral pile' (Te.)(CDIAL 4879; DEDR 2709). Thus the composite glyphic composition: 'bristled (tiger's mane) face' is read rebus as: sodagor mũh cūḷa 'furnace (of) ingot merchant'.
kamarasāla = waist-zone, waist-band, belt (Te.) karmāraśāla = workshop of blacksmith (Skt.) kamar ‘blacksmith’ (Santali)
The person on platform is seated in penance: kamaḍha 'penance' (Pkt.) Rebus: kammaṭa ‘mint, coiner’ (Malayalam)
Hieroglyph: arms with bangles: karã̄ n.pl.ʻwristlets, banglesʼ.(Gujarati)(CDIAL 2779) Rebus: khār खार् 'blacksmith' (Kashmiri)
khār खार् । लोहकारः m. (sg. abl. khāra 1 खार ; the pl. dat. of this word is khāran 1 खारन् , which is to be distinguished from khāran 2, q.v., s.v.), a blacksmith, an iron worker (cf. bandūka-khār, p. 111b,l. 46; K.Pr. 46; H. xi, 17); a farrier (El.). This word is often a part of a name, and in such case comes at the end (W. 118) as in Wahab khār, Wahab the smith (H. ii, 12; vi, 17). khāra-basta
khāra-basta खार-बस््त । चर्मप्रसेविका f. the skin bellows of a blacksmith. -büṭhü -ब&above;ठू&below; । लोहकारभित्तिः f. the wall of a blacksmith's furnace or hearth. -bāy -बाय् । लोहकारपत्नी f. a blacksmith's wife (Gr.Gr. 34). -dŏkuru -द्वकुरु&below; । लोहकारायोघनः m. a blacksmith's hammer, a sledge-hammer. -gȧji -ग&above;जि&below; or -güjü -ग&above;जू&below; । लोहकारचुल्लिः f. a blacksmith's furnace or hearth. -hāl -हाल् । लोहकारकन्दुः f. (sg. dat. -höjü -हा&above;जू&below; ), a blacksmith's smelting furnace; cf. hāl 5. -kūrü -कूरू&below; । लोहकारकन्या f. a blacksmith's daughter. -koṭu -क&above;टु&below; । लोहकारपुत्रः m. the son of a blacksmith, esp. a skilful son, who can work at the same profession. -küṭü -क&above;टू&below; । लोहकारकन्या f. a blacksmith's daughter, esp. one who has the virtues and qualities properly belonging to her father's profession or caste. -më˘ʦü 1 -म्य&above;च&dotbelow;ू&below; । लोहकारमृत्तिका f. (for 2, see [khāra 3] ), 'blacksmith's earth,' i.e. iron-ore. -nĕcyuwu -न्यचिवु&below; । लोहकारात्मजः m. a blacksmith's son. -nay -नय् । लोहकारनालिका f. (for khāranay 2, see [khārun] ), the trough into which the blacksmith allows melted iron to flow after smelting. -ʦañĕ -च्&dotbelow;ञ । लोहकारशान्ताङ्गाराः f.pl. charcoal used by blacksmiths in their furnaces. -wān वान् । लोहकारापणः m. a blacksmith's shop, a forge, smithy (K.Pr. 3). -waṭh -वठ् । आघाताधारशिला m. (sg. dat. -waṭas -वटि ), the large stone used by a blacksmith as an anvil.(Kashmiri)
Kur. kaṇḍō a stool. Malt. kanḍo stool, seat. (DEDR 1179) Rebus: kaṇḍ = a furnace, altar (Santali.lex.) kuntam 'haystack' (Te.)(DEDR 1236) Rebus: kuṇḍamu 'a pit for receiving and preserving consecrated fire' (Te.)
A pair of hayricks, a pair of antelopes: kundavum = manger, a hayrick (G.) Rebus: kundār turner (A.); kũdār, kũdāri (B.); kundāru (Or.); kundau to turn on a lathe, to carve, to chase; kundau dhiri = a hewn stone; kundau murhut = a graven image (Santali) kunda a turner's lathe (Skt.)(CDIAL 3295)
Decoding a pair: dula दुल । युग्मम् m. a pair, a couple, esp. of two similar things (Rām. 966) (Kashmiri); dol ‘likeness, picture, form’ (Santali) Rebus: dul ‘to cast metal in a mould’ (Santali) dul meṛeḍ cast iron (Mundari. Santali)
Antelope: miṇḍāl ‘markhor’ (Tōrwālī) meḍho a ram, a sheep (G.)(CDIAL 10120); rebus: mẽṛhẽt, meḍ ‘iron’ (Mu.Ho.)
Glyph: krammara ‘look back’ (Te.); Rebus: kamar ‘smith’ (Santali) Vikalpa 1: mlekh ‘antelope’(Br.); milakkhu ‘copper’ (Pali) Vikalpa 2: kala stag, buck (Ma.) Rebus: kallan mason (Ma.); kalla glass beads (Ma.); kalu stone (Kond.a); xal id., boulder (Br.)(DEDR 1298). Rebus: kallan ‘stone-bead-maker’.
Thus, together, the glyphs on the base of the platform are decoded rebus:meḍ kamar dul meṛeḍ kũdār,'iron(metal)smith, casting (and) turner'.
Animal glyphs around the seated person: buffalo, boar (rhinoceros), elephant, tiger (jumping).
ran:gā ‘buffalo’; ran:ga ‘pewter or alloy of tin (ran:ku), lead (nāga) and antimony (añjana)’(Santali)
kANDa 'rhinoceros' Rebus: khaNDa 'metal implements'
ibha ‘elephant’ (Skt.); rebus: ib ‘iron’ (Santali) karibha ‘trunk of elephant’ (Pali); rebus: karb ‘iron’ (Ka.)
kolo, koleā 'jackal' (Kon.Santali); kola kukur 'white tiger' (A.); dāṭu ‘leap’ (Te.); rebus: kol pañcaloha 'five metals'(Ta.); kol 'furnace, forge' (Kuwi) dāṭu 'jump' (Te.). Rebus: dhātu ‘mineral’ (Skt.) Vikalpa: puṭi 'to jump'; puṭa 'calcining of metals'. Thus the glyph 'jumping tiger' read rebus: 'furnace for calcining of metals'.
Line 2 (bottom): 'body' glyph. mēd ‘body’ (Kur.)(DEDR 5099); meḍ ‘iron’ (Ho.)
Line 1 (top):
'Body' glyph plus ligature of 'splinter' shown between the legs: mēd ‘body’ (Kur.)(DEDR 5099); meḍ ‘iron’ (Ho.) sal ‘splinter’; Rebus: sal ‘workshop’ (Santali) Thus, the ligatured glyph is read rebus as: meḍ sal 'iron (metal) workshop'.
Sign 216 (Mahadevan). ḍato ‘claws or pincers (chelae) of crabs’; ḍaṭom, ḍiṭom to seize with the claws or pincers, as crabs, scorpions; ḍaṭkop = to pinch, nip (only of crabs) (Santali) Rebus: dhatu ‘mineral’ (Santali) Vikalpa: erā ‘claws’; Rebus: era ‘copper’. Allograph: kamaṛkom = fig leaf (Santali.lex.) kamarmaṛā (Has.), kamaṛkom (Nag.); the petiole or stalk of a leaf (Mundari.lex.) kamat.ha = fig leaf, religiosa (Skt.)
Sign 229. sannī, sannhī = pincers, smith’s vice (P.) śannī f. ʻ small room in a house to keep sheep in ‘ (WPah.) Bshk. šan, Phal.šān ‘roof’ (Bshk.)(CDIAL 12326). seṇi (f.) [Class. Sk. śreṇi in meaning "guild"; Vedic= row] 1. a guild Vin iv.226; J i.267, 314; iv.43; Dāvs ii.124; their number was eighteen J vi.22, 427; VbhA 466. ˚ -- pamukha the head of a guild J ii.12 (text seni -- ). -- 2. a division of an army J vi.583; ratha -- ˚ J vi.81, 49; seṇimokkha the chief of an army J vi.371 (cp. senā and seniya). (Pali)
Sign 342. kaṇḍa kanka 'rim of jar' (Santali): karṇaka rim of jar’(Skt.) Rebus: karṇaka ‘scribe, accountant’ (Te.); gaṇaka id. (Skt.) (Santali) copper fire-altar scribe (account)(Skt.) Rebus: kaṇḍ ‘fire-altar’ (Santali) Thus, the 'rim of jar' ligatured glyph is read rebus: fire-altar (furnace) scribe (account) karNI 'supercargo' (Marathi)
Sign 344. Ligatured glyph: 'rim of jar' ligature + splinter (infixed); 'rim of jar' ligature is read rebus: kaṇḍa karṇaka 'furnace scribe (account)'.
sal stake, spike, splinter, thorn, difficulty (H.); Rebus: sal ‘workshop’ (Santali) *ஆலை³ ālai, n. < šālā. 1. Apartment, hall; சாலை. ஆலைசேர் வேள்வி (தேவா. 844. 7). 2. Elephant stable or stall; யானைக்கூடம். களிறு சேர்ந் தல்கிய வழுங்க லாலை (புறநா. 220, 3).ஆலைக்குழி ālai-k-kuḻi, n. < ஆலை¹ +. Receptacle for the juice underneath a sugar-cane press; கரும்பாலையிற் சாறேற்கும் அடிக்கலம்.*ஆலைத்தொட்டி ālai-t-toṭṭi, n. < id. +. Cauldron for boiling sugar-cane juice; கருப்பஞ் சாறு காய்ச்சும் சால்.ஆலைபாய்-தல் ālai-pāy-, v. intr. < id. +. 1. To work a sugar-cane mill; ஆலையாட்டுதல். ஆலைபாயோதை (சேதுபு. நாட்டு. 93). 2. To move, toss, as a ship; அலைவுறுதல். (R.) 3. To be undecided, vacillating; மனஞ் சுழலுதல். நெஞ்ச மாலைபாய்ந் துள்ள மழிகின்றேன் (அருட்பா,) Vikalpa: sal ‘splinter’; rebus: workshop (sal)’ ālai ‘workshop’ (Ta.) *ஆலை³ ālai, n. < šālā. 1. Apartment, hall; சாலை. ஆலைசேர் வேள்வி (தேவா. 844. 7). 2. Elephant stable or stall; யானைக்கூடம். களிறு சேர்ந் தல்கிய வழுங்க லாலை (புறநா. 220, 3).ஆலைக்குழி ālai-k-kuḻi, n. < ஆலை¹ +. Receptacle for the juice underneath a sugar-cane press; கரும்பாலையிற் சாறேற்கும் அடிக்கலம்.*ஆலைத்தொட்டி ālai-t-toṭṭi, n. < id. +. Cauldron for boiling sugar-cane juice; கருப்பஞ் சாறு காய்ச்சும் சால்.ஆலைபாய்-தல் ālai-pāy-, v. intr. < id. +. 1. To work a sugar-cane mill; ஆலையாட்டுதல். ஆலைபாயோதை (சேதுபு. நாட்டு. 93) Thus, together with the 'splinter' glyph, the entire ligature 'rim of jar + splinter/splice' is read rebus as: furnace scribe (account workshop). Sign 59. ayo, hako 'fish'; a~s = scales of fish (Santali); rebus: aya = iron (G.); ayah, ayas = metal (Skt.) Sign 342. kaṇḍa karṇaka 'rim of jar'; rebus: 'furnace scribe (account)'. Thus the inscription reads rebus: iron, iron (metal) workshop, copper (mineral) guild, fire-altar (furnace) scribe (account workshop), metal furnace scribe (account) As the decoding of m0304 seal demonstrates, the Indus hieroglyphs are the professional repertoire of an artisan (miners'/metalworkers') guild detailing the stone/mineral/metal resources/furnaces/smelters of workshops (smithy/forge/turners' shops).
Seal 4 (Two tigers, woman)



dula 'pair' rebus: dul 'cast metal' kola 'tiger' rebus; kol 'working in iron'. Thus, iron casting.
kola 'tiger', kola 'woman' rebus: kolle 'blacksmith' kolhe 'smelter' kol 'working in iron' kolimi 'smithy, forge'
kole.l 'temple' rebus; koe.l 'smithy'
karNika 'rim of jar' rebus: karNI 'supercargo' kanka, karNIka 'scribe' kanga 'brazier'
kamaDha 'crab' rebus: kampaTTa 'mint, coiner'
Oval shaped glyph: muhe 'ingot' PLUS kolmo 'rice plant' rebus: kolimi 'smithy,forge'. Thus, ingot smithy. Alternative: pair of parentheses or curves:
 The 'curve' hieroglyph is a splitting of the ellipse. kuṭila ‘bent’ CDIAL 3230 kuṭi— in cmpd. ‘curve’, kuṭika— ‘bent’ MBh.
The 'curve' hieroglyph is a splitting of the ellipse. kuṭila ‘bent’ CDIAL 3230 kuṭi— in cmpd. ‘curve’, kuṭika— ‘bent’ MBh. Rebus: kuṭila, katthīl = bronze (8 parts copper and 2 parts tin) cf. āra-kūṭa, '
Notch inlaid in rim of jar: karNika 'rim of jar' rebus: karNI 'supercargo' kanka, karNIka 'scribe' kanga 'brazier' PLUS kaNDa 'notch' rebus: kANDA 'tools, pots and pans, implements'.
sãghāṛɔ 'lathe'.(Gujarati) sangaDa 'lathe, portable furnace' rebus: sangara 'proclamation' sangāṭh
Seal 5 (Zebu seal)
kanac 'corner' rebus: kancu 'bronze'.
Hieroglyphs on text and rebus readings:
koḍa 'sluice'; Rebus: koḍ 'artisan's workshop (Kuwi). See alternative reading.
koḍa 'one' Rebus: koḍ 'artisan's workshop (Kuwi). Phonetic determinative.
sal 'splinter' Rebus: sal 'workshop' Phonetic determinative.
kolmo 'three' Rebus: kolimi 'smithy, forge' Phonetic determinative.
kolom 'rice plant' Rebus: kolimi 'smithy, forge'
सांड [ sāṇḍa ] f (षद S) An outlet for superfluous water (as through a dam or mound); a sluice, a floodvent. सांडावा [ sāṇḍāvā ] m (Or सांडवा ) A vent (as through a dam or mound); a watergate or sluice.सांडवा [ sāṇḍavā ] m (सांडणें ) A sluice, watergate, floodgate; a vent (as through a dam or mound): also a built-up channel or passage of masonry for flowing water generally. साटा or ट्या [ sāṭā or ṭyā ] m A frame &c. See साठा or ठ्या . सांठवणी [ sāṇṭhavaṇī ] n (सांठ & पाणी ) Water collected (in a cistern, tank, pond, or other reservoir); also accumulated in a pool, puddle, or any hollow.
Allographs: सांड [ sāṇḍa ] m (षंड S) A bull set at liberty. Hence (such bulls soon becoming fat and lusty) सांडणी
[ sāṇḍaṇī ] f (
सांठा [ sāṇṭhā ] m (संचय S) A collection, heap, hoard, store, stock.साटें [ sāṭēṃ] n (संचय S) A whole investment; the total quantity of merchandise (brought to market by one merchant): also buying up the whole of an investment &c. सांठणें [sāṇṭhaṇēṃ ] v i (संचय , or स Together, अट To go.) To accumulate or collect; to get together in mass or in quantity. 2 To be contained in; to enter into the capacity or hold of.
 Magnetite and pyrite from, Piedmont, Italy.
Magnetite and pyrite from, Piedmont, Italy.Magnetite is one of the three common naturally occurring iron oxides (chemical formula Fe3O4).
pola 'magnetite' Hieroglyph: bos indicus
पोळ [ pōḷa ] m A bull dedicated to the gods, marked with a trident and discus, and set at large. पोळी [ pōḷī ] dewlap. Rebus: पोळें [ pōḷēṃ ], पोळी [ pōḷī ] The cake-form portion of a honeycomb.(Marathi)
पोळी [ pōḷī ] dewlap. Rebus: Russian gloss, bulat is cognate pola 'magnetite' iron in Asuri (Meluhha). Magnetite is the most magnetic of all the naturally occurring igneous and metamorphic rocks with black or brownish-black with a metallic luster. These magnetite ore stones could have been identified as pola iron by Meluhha speakers. Kannada gloss pola meaning 'point of the compass' may link with the characteristic of magnetite iron used to create acompass.pŏlāduwu made of steel; pŏlād प्वलाद् or phōlād फोलाद् मृदुलोहविशेषः ] m. steel (Gr.M.; Rām. 431, 635, phōlād). pŏlödi pōlödi phōlödi लोहविशेषमयः adj. c.g. of steel, steel (Kashmiri) urukku what is melted, fused metal, steel.(Malayalam); ukk 'steel' (Telugu)(DEDR 661) This is cognate with famed 'wootz'steel. "Polad, Faulad" for steel in late Indian languages is traceable to Pokkhalavat, Polahvad. Pokkhalavat is the name of Pushkalavati, capital of Gandhara famed for iron and steel products.pola, ‘magnetite’ is denoted by pōḷī, ‘dewlap, honeycomb’.
 m0491 This is a report on the transition from lapidary to bronze-age metalware in ancient Near East.
m0491 This is a report on the transition from lapidary to bronze-age metalware in ancient Near East. eraka 'nave of wheel' Rebus: moltencast copper
dhatu 'scarf' Rebus: mineral ore dhāū, dhāv m.f. ʻa partic. soft red stoneʼ (Marathi) (whence dhā̆vaḍ m. ʻa caste of iron -- smeltersʼ, dhāvḍī ʻ composed of or relating to iron ʼ)
kōnda 'young bull' Rebus: turner
sãgaḍ 'lathe' Rebus: sangara proclamation
kanga 'portable brazier' Rebus: fireplace, furnace
Glyphic element: erako nave; era = knave of wheel. Glyphic element: āra ‘spokes’. Rebus: āra ‘brass’ as in ārakūṭa (Skt.) Rebus: Tu. eraka molten, cast (as metal); eraguni to melt (DEDR 866) erka = ekke (Tbh. of arka) aka (Tbh. of arka) copper (metal); crystal (Kannada.) cf. eruvai = copper (Ta.lex.) eraka, er-aka = any metal infusion (Ka.Tu.); erako molten cast (Tulu) The same spoked-wheel hieroglyph adorns the Dholavira Sign-board.
āra 'spokes' Rebus: āra 'bronze'. cf. erka = ekke (Tbh. of arka) aka (Tbh. of arka) copper (metal); crystal (Kannada) Glyph: eraka

 Other examples of 'standard device' in front of one-horned young bull. The second from r. is an example of the 'standard' as an object.
Other examples of 'standard device' in front of one-horned young bull. The second from r. is an example of the 'standard' as an object.Note the doted circles on the bottom register of the hieroglyph-multiplex of the standard device. These signify the semantics: 'full of holes'. The signifier is the word: Pk. kāṇa -- ʻ full of holes ʼ, G. kāṇũ ʻ full of holes ʼ, n. ʻ hole ʼ (< ʻ empty eyehole ʼ?(CDIAL 3019)kaṇa (pl. kaṇul) hole; (Go.)(DEDR 1159) Pe. kaṇga (pl. -ŋ, kaṇku) eye. Rebus: kanga ' large portable brazier, fire-place' (Kashmiri). Thus, the standard device is a combination of two hieroglyh components signifying: lathe, portable brazier: sangaDa + kanga Rebus: proclamation (collected products out of)+ fireplace.
 'Eye' hieroglyph shown on Kuwait gold disk signifying kanga 'portable brazier' Rebus: kanga 'fireplace, furnace'
'Eye' hieroglyph shown on Kuwait gold disk signifying kanga 'portable brazier' Rebus: kanga 'fireplace, furnace'See: http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2015/08/indus-script-hieroglyph-multiplex.html
The standard device
2. Detail of gold fillet with punctuated design of standard device
at both ends of the gold fillet. (After Fig. 7.32, Kenoyer, 1998)
at both ends of the gold fillet. (After Fig. 7.32, Kenoyer, 1998)
Guild, caravan
Pali:Sanghaṭita [saŋ+ghaṭita, for ˚ghaṭṭita, pp. of ghaṭṭeti] 1. struck, sounded, resounding with (-- ˚) J v.9 (v. l. ṭṭ); Miln 2. -- 2. pierced together, pegged
together, constructed Miln 161 (nāvā nānā -- dāru˚).Marathi: सांगड [ sāṅgaḍa ] m f (संघट्ट S) A float composed of two canoes or boats bound together: also a link of two pompions &c. to swim or float by. 2 f A body formed of two or more (fruits,
together, constructed Miln 161 (nāvā nānā -- dāru˚).Marathi: सांगड [ sāṅgaḍa ] m f (संघट्ट S) A float composed of two canoes or boats bound together: also a link of two pompions &c. to swim or float by. 2 f A body formed of two or more (fruits,
animals, men) linked or joined together. 3 That member of a turner's apparatus
by which the piece to be turned is confined and steadied. सांगडीस
धरणें To take into linkedness or close connection with, lit. fig.
सांगडणी [ sāṅgaḍaṇī ] f (Verbal of सांगडणें) Linking or joining
together.
सांगडणें [ sāṅgaḍaṇēṃ ] v c (सांगड) To link, join, or unite together (boats, fruits, animals). 2 Freely. To tie or bind up or unto.
सांगडबाहुली [ sāṅgaḍabāhulī ] f A puppet.
सांगडी [ sāṅgaḍī ] f (Commonly सांगड) A float &c.
by which the piece to be turned is confined and steadied. सांगडीस
धरणें To take into linkedness or close connection with, lit. fig.
सांगडणी [ sāṅgaḍaṇī ] f (Verbal of सांगडणें) Linking or joining
together.
सांगडणें [ sāṅgaḍaṇēṃ ] v c (सांगड) To link, join, or unite together (boats, fruits, animals). 2 Freely. To tie or bind up or unto.
सांगडबाहुली [ sāṅgaḍabāhulī ] f A puppet.
सांगडी [ sāṅgaḍī ] f (Commonly सांगड) A float &c.
san:gaḍa ‘lathe, furnace’ san:ghāḍo, saghaḍī (G.) = firepan; saghaḍī,
śaghaḍi = a pot for holding fire (G.)[cula_ sagaḍi_
portable hearth (G.)] aguḍe = brazier (Tu.)
śaghaḍi = a pot for holding fire (G.)[cula_ sagaḍi_
portable hearth (G.)] aguḍe = brazier (Tu.)
san:gaḍa, ‘lathe, portable furnace’; rebus: battle; jangaḍ iyo
‘military guard who accompanies treasure into the treasury’; san:ghāḍiyo, a
worker on a lathe (G.) The dotted circles on the bottom portion of the device
connote ghangar ghongor; rebus: kangar ‘portable furnace’.
‘military guard who accompanies treasure into the treasury’; san:ghāḍiyo, a
worker on a lathe (G.) The dotted circles on the bottom portion of the device
connote ghangar ghongor; rebus: kangar ‘portable furnace’.
Rebus: CDIAL 12858 saṁghara living in the same house . [Cf. ságr̥ha<->
ĀpŚr. -- ghara -- ]Pa. saṅghara -- with one's own family (?); sagghrā accompanied by one's own family ; H. sã̄ghar m. wife's son by former husband . CDIAL 12854 saṁghá m. association, a community Mn. [√han1] Pa. saṅgha -- m. assembly, the priesthood ; Aś. saṁgha -- m. the Buddhist community ; Pk. saṁgha -- m. assembly, collection ; OSi. (Brāhmī inscr.) saga, Si. san̆ga ʻ crowd, collection . -- Rather < saṅga -- : S.saṅgu m. body of pilgrims (whence sã̄go m. caravan ), L. P. saṅg m. CDIAL 12862 saṁghātá saṁghātá m. close union, mass TS., closing (a door) VS., dashing together MBh. [Cf. saṁhata<-> with similar range of meanings. -- ghāta
-- ] Tamil: சங்கத்தார் caṅkattār, n. < id. 1. Members of an assembly,
ĀpŚr. -- ghara -- ]Pa. saṅghara -- with one's own family (?); sagghrā accompanied by one's own family ; H. sã̄ghar m. wife's son by former husband . CDIAL 12854 saṁghá m. association, a community Mn. [√han1] Pa. saṅgha -- m. assembly, the priesthood ; Aś. saṁgha -- m. the Buddhist community ; Pk. saṁgha -- m. assembly, collection ; OSi. (Brāhmī inscr.) saga, Si. san̆ga ʻ crowd, collection . -- Rather < saṅga -- : S.saṅgu m. body of pilgrims (whence sã̄go m. caravan ), L. P. saṅg m. CDIAL 12862 saṁghātá saṁghātá m. close union, mass TS., closing (a door) VS., dashing together MBh. [Cf. saṁhata<-> with similar range of meanings. -- ghāta
-- ] Tamil: சங்கத்தார் caṅkattār, n. < id. 1. Members of an assembly,
academy, a society, council or committee; சபையோர். 2. Buddhist and Jain fraternity of monks; பௌத்த சைன சங்த்தார். (சீவக. 4, உரை; சிலப். 30, 32, அரும்.) 3. The learned body of poets in Madura, in ancient times; மதுரைச் சங்கப்புலவர். சங்கத்தா ரெல்லாம் (திருவிளை. தருமிக்கு. 82) சங்கம்² caṅkam, n. < saṅgha. 1. Mustering, gathering; கூட்டம். சங்கமாகி வெங்கணை வீக்க மொடு (பெருங். மகத. 17, 38). 2. Society, assembly, council, senate, academy; சபை. புலம்பரிச் சங்கம் பொருளொடு முழங்க (மணி. 7, 114). 3. Literati, poets; புலவர். (திவா.) 4. Learned assemblies or academies of ancient times patronised by Pāṇḍya kings, three in number, viz., talai-c-caṅkam, iṭai-c-caṅkam, kaṭai-c-caṅkam; பாண்டி யர் ஆதரவுபெற்று விளங்கிய தலைச்சங்கம், இடைச் சங்கம்,கடைச்சங்கம் என்ற முச்சங்கங்கள். எம்மைப் பவந்தீர்ப்பவர் சங்கமிருந்தது (பெரியபு. மூர்த்திநா. 7). 5. Fraternity of monks among Buddhists and Jains; சங்கமர் caṅkamar , n. < சங்கமம்¹. A class of Vīrašaivas, Lingayats; ஒரு சார் வீரசைவர்.
சங்கநிதி¹ caṅka-niti, n. < id. +. One of the nine treasures of Kubēra; குபேரனது நவநிதி யுள் ஒன்று. சங்கநிதி பதுமநிதி
சங்காத்தம் caṅkāttam, n. < saṅ-gata. 1. Friendship, intimacy, familiar intercourse; இணக்கம்.பூனைக்கும்வீட்டெலிக்குஞ்சங்காத்தமுண்டோ (தனிப்பா. ii, 13, 28). 2. residence; வாசம்.துறை
யூரெனுந்தலத்திற்சங்காத்தங்கொண்டிருப்பாய் (தமிழ்நா. 62). சங்காதம்caṅkātam, n. < saṅ-ghāta. 1. Assembly, multitude, company, association, combination; கூட்டம். (சி. சி. 1, 14, சிவாக்.) Marathi: संघात [ saṅghāta ] m S Assembly or assemblage; multitude or heap; a collection together (of things animate or inanimate). 2 A division of the infernal regions. संघट्टणें [ saṅghaṭṭaṇēṃ ] v i (Poetry. संघट्टन) To come into contact or
meeting; to meet or encounter. Ex. अर्ध योजन आसपास ॥ वास घ्राण देवीसीं संघटे ॥.संघट्टन [ saṅghaṭṭana ] n S संघट्टना f S corruptly संघठण, संघट्टण,
संघष्टण, संघष्टन, संघृष्टन, संघट्ठणें n Close connection and
intercourse; intimate and familiar communication. Ex. तुका
म्हणे जिणें ॥ भलें संत संघट्टणें ॥. 2 Coming into contact with, encountering,
meeting. 3 Close contact;--as the intertwining of wrestlers, the clinging and
cleaving of lovers in their embraces &c. 4 Rubbing together, confrication.
Pali: Sanghara=saghara [sa4+ghara] one's own house J v.222. Sangharaṇa (nt.)
[=saŋharaṇa] accumulation J iii.319 (dhana˚).Sangharati [=saŋharati] 1. to bring
together, collect, accumulate J iii.261; iv.36 (dhanaŋ), 371; v.383. <-> 2. to crush, to pound Ji.493.
Pali: Sanghāṭa [fr. saŋ+ghaṭeti, lit. "binding together"; on etym. see Kern, Toev. ii.68] 1. a raft J ii.20, 332 (nāvā˚); iii.362 (id.), 371. Miln 376. dāru˚ (=nāvā˚) J v.194, 195. -- 2. junction, union VvA 233. -- 3. collection,
aggregate J iv.15 (upāhana˚); Th 1, 519 (papañca˚). Freq. as aṭṭhi˚ (cp.
sankhalā etc.) a string of bones, i. e. a skeleton Th 1, 570; DhA iii.112;
J v.256. -- 4. a weft, tangle, mass (almost="robe," i. e.
sanghāṭī), in taṇhā˚ -- paṭimukka M i.271; vāda˚ -- paṭimukka M i.383 (Neumann "defeat"); diṭṭhi˚ --
paṭimukka Miln 390. <-> 5. a post, in piṭṭha˚ door --
post, lintel Vin ii.120.
intercourse; intimate and familiar communication. Ex. तुका
म्हणे जिणें ॥ भलें संत संघट्टणें ॥. 2 Coming into contact with, encountering,
meeting. 3 Close contact;--as the intertwining of wrestlers, the clinging and
cleaving of lovers in their embraces &c. 4 Rubbing together, confrication.
Pali: Sanghara=saghara [sa4+ghara] one's own house J v.222. Sangharaṇa (nt.)
[=saŋharaṇa] accumulation J iii.319 (dhana˚).Sangharati [=saŋharati] 1. to bring
together, collect, accumulate J iii.261; iv.36 (dhanaŋ), 371; v.383. <-> 2. to crush, to pound Ji.493.
Pali: Sanghāṭa [fr. saŋ+ghaṭeti, lit. "binding together"; on etym. see Kern, Toev. ii.68] 1. a raft J ii.20, 332 (nāvā˚); iii.362 (id.), 371. Miln 376. dāru˚ (=nāvā˚) J v.194, 195. -- 2. junction, union VvA 233. -- 3. collection,
aggregate J iv.15 (upāhana˚); Th 1, 519 (papañca˚). Freq. as aṭṭhi˚ (cp.
sankhalā etc.) a string of bones, i. e. a skeleton Th 1, 570; DhA iii.112;
J v.256. -- 4. a weft, tangle, mass (almost="robe," i. e.
sanghāṭī), in taṇhā˚ -- paṭimukka M i.271; vāda˚ -- paṭimukka M i.383 (Neumann "defeat"); diṭṭhi˚ --
paṭimukka Miln 390. <-> 5. a post, in piṭṭha˚ door --
post, lintel Vin ii.120.
orthography on other seals, h098 and m1408. There are many variants used to
show this sangad.a ‘lathe, portable furnace’.
show this sangad.a ‘lathe, portable furnace’.
kõdā‘to turn in a lathe’(B.) कोंद kōnda ‘engraver, lapidary setting or infixing gems’ (Marathi) koḍ ‘artisan’s workshop’ (Kuwi) koḍ = place where artisans work (G.) ācāri koṭṭya ‘smithy’ (Tu.) कोंडण [kōṇḍaṇa] f A fold or pen. (Marathi) B. kõdā ‘to turn in a lathe’; Or.kū̆nda ‘lathe’, kũdibā, kū̃d ‘to turn’ (→ Drav. Kur. Kū̃d ’ lathe’) (CDIAL 3295) A. kundār, B. kũdār, ri, Or.Kundāru; H. kũderā m. ‘one who works a lathe, one who scrapes’, rī f., kũdernā ‘to scrape, plane, round on a lathe’; kundakara—m. ‘turner’ (Skt.)(CDIAL 3297). कोंदण [ kōndaṇa ] n (कोंदणें) Setting or infixing of gems.(Marathi) খোদকার [ khōdakāra ] n an engraver; a carver. খোদকারি n. engraving; carving; interference in other’s work. খোদাই [ khōdāi ] n engraving; carving. খোদাই করা v. to engrave; to carve. খোদানো v. & n. en graving; carving. খোদিত [ khōdita ] a engraved. (Bengali) खोदकाम [ khōdakāma ] n Sculpture; carved work or work for the carver. खोदगिरी [ khōdagirī ] f Sculpture, carving, engraving: also sculptured or carved work. खोदणावळ [ khōdaṇāvaḷa ] f (खोदणें) The price or cost of sculpture or carving. खोदणी [ khōdaṇī ] f (Verbal of खोदणें) Digging, engraving &c. 2 fig. An exacting of money by importunity. V लाव, मांड. 3 An instrument to scoop out and cut flowers and figures from paper. 4 A goldsmith’s die. खोदणें [ khōdaṇēṃ ] v c & i ( H) To dig. 2 To engrave. खोद खोदून विचारणें or –पुसणें To question minutely and searchingly, to probe. खोदाई [ khōdāī ] f (H.) Price or cost of digging or of sculpture or carving. खोदींव [ khōdīṃva ] p of खोदणें Dug. 2 Engraved, carved, sculptured. (Marathi)
Rebus: Sangara [fr. saŋ+gṛ
Rebus: saṁghāṭa m. ʻ fitting and joining of timber ʼ R. [√
Proclamation of procession on Jasper Akkadian cylinder seal
See: http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2015/08/indus-script-hieroglyph-readings-on.html
Jasper Akkadian cylinder seal ca. 2220-2159 BCE
![]()
Red jasper H. 1 1/8 in. (2.8 cm), Diam. 5/8 in. (1.6 cm) cylinder Seal with four hieroglyphs and four kneeling persons (with six curls on their hair) holding flagposts, c. 2220-2159 B.C.E., Akkadian (Metropolitan Museum of Art) Cylinder Seal (with modern impression). The four hieroglyphs are: from l. to r. 1. crucible PLUS storage pot of ingots, 2. sun, 3. narrow-necked pot with overflowing water, 4. fish A hooded snake is on the edge of the composition. (The dark red color of jasper reinforces the semantics: eruvai 'dark red, copper' Hieroglyph: eruvai 'reed'; see four reedposts held. koThAri 'crucible' Rebus: koThAri 'treasurer, warehouse'
If the hieroglyph on the leftmost is moon, a possible rebus reading: قمر ḳamarA قمر ḳamar, s.m. (9th) The moon. Sing. and Pl. See سپوږمي or سپوګمي (Pashto) Rebus: kamar 'blacksmith'
Part 3: Proclamation on Dholavira Sign Board
See: http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2015/04/dholavira-1-signboard-and-2-stone.htmlDholavira. gateway. A designer's impressions (reconstruction) of the world's first signboard on the gateway of fortification or citadel.![]() This is the huge hoarding on the northern gateway of Dholavira fortification. I call this the Bronze Age Meluhha Standard. The Standard exemplified the gateway to Bronze Age Sarasvati civilization. The Sheffield of the Ancient Near East, Chanhu-daro (River Sarasvati right-bank), is about 150 kms. to the north if a seafaring-riverine merchant from Sumer, Mesopotamia, Dilmun, or Magan moved on the navigable River Sarasvati beyond the port town of Dholavira.
This is the huge hoarding on the northern gateway of Dholavira fortification. I call this the Bronze Age Meluhha Standard. The Standard exemplified the gateway to Bronze Age Sarasvati civilization. The Sheffield of the Ancient Near East, Chanhu-daro (River Sarasvati right-bank), is about 150 kms. to the north if a seafaring-riverine merchant from Sumer, Mesopotamia, Dilmun, or Magan moved on the navigable River Sarasvati beyond the port town of Dholavira.
The signboard deciphered in three segments from r.
ḍato ‘claws or pincers of crab’ (Santali) rebus: dhatu ‘ore’ (Santali)
eraka ‘knave of wheel’ Rebus: eraka ‘copper’ (Kannada) eraka ‘molten cast (metal)(Tulu). sangaḍa 'pair' Rebus: sangaḍa‘lathe’ (Gujarati)
![]() Segment 2: Native metal tools, pots and pans, metalware, engraving (molten cast copper)
Segment 2: Native metal tools, pots and pans, metalware, engraving (molten cast copper)
खांडा [ khāṇḍā ] m A jag, notch, or indentation (as upon the edge of a tool or weapon). (Marathi) Rebus: khāṇḍā ‘tools, pots and pans, metal-ware’.
aḍaren, ḍaren lid, cover (Santali) Rebus: aduru ‘native metal’ (Ka.) aduru = gan.iyinda tegadu karagade iruva aduru = ore taken from the mine and not subjected to melting in a furnace (Kannada) (Siddhānti Subrahmaṇya’ śāstri’s new interpretation of the Amarakośa, Bangalore, Vicaradarpana Press, 1872, p. 330)
koṇḍa bend (Ko.); Tu. Kōḍi corner; kōṇṭu angle, corner, crook. Nk. kōnṭa corner (DEDR 2054b) G. khū̃ṭṛī f. ʻangleʼ Rebus:kõdā ‘to turn in a lathe’(B.) कोंद kōnda ‘engraver, lapidary setting or infixing gems’ (Marathi) koḍ ‘artisan’s workshop’ (Kuwi) koḍ = place where artisans work (G.) ācāri koṭṭya ‘smithy’ (Tu.) कोंडण [kōṇḍaṇa] f A fold or pen. (Marathi) B. kõdā ‘to turn in a lathe’; Or.kū̆nda ‘lathe’, kũdibā, kū̃d ‘to turn’ (→ Drav. Kur. Kū̃d ’ lathe’) (CDIAL 3295) A. kundār, B. kũdār, ri, Or.Kundāru; H. kũderā m. ‘one who works a lathe, one who scrapes’, rī f., kũdernā ‘to scrape, plane, round on a lathe’; kundakara— m. ‘turner’ (Skt.)(CDIAL 3297). कोंदण [ kōndaṇa ] n (कोंदणें) Setting or infixing of gems.(Marathi) খোদকার [ khōdakāra ] n an engraver; a carver. খোদকারি n. engraving; carving; interference in other’s work. খোদাই [ khōdāi ] n engraving; carving. খোদাই করা v. to engrave; to carve. খোদানো v. & n. en graving; carving. খোদিত [ khōdita ] a engraved. (Bengali) खोदकाम [ khōdakāma ] n Sculpture; carved work or work for the carver. खोदगिरी [ khōdagirī ] f Sculpture, carving, engraving: also sculptured or carved work. खोदणावळ [ khōdaṇāvaḷa ] f (खोदणें) The price or cost of sculpture or carving. खोदणी [ khōdaṇī ] f (Verbal of खोदणें) Digging, engraving &c. 2 fig. An exacting of money by importunity. V लाव, मांड. 3 An instrument to scoop out and cut flowers and figures from paper. 4 A goldsmith’s die. खोदणें [ khōdaṇēṃ ] v c & i ( H) To dig. 2 To engrave. खोद खोदून विचारणें or –पुसणें To question minutely and searchingly, to probe. खोदाई [ khōdāī ] f (H.) Price or cost of digging or of sculpture or carving. खोदींव [ khōdīṃva ] p of खोदणें Dug. 2 Engraved, carved, sculptured. (Marathi)
eraka ‘knave of wheel’ Rebus: eraka ‘copper’ (Kannada) eraka ‘molten cast (metal)(Tulu).
loa ’fig leaf; Rebus: loh ‘(copper) metal’ kamaḍha 'ficus religiosa' (Skt.); kamaṭa = portable furnace for melting precious metals (Te.); kampaṭṭam = mint (Ta.) The unique ligatures on the 'leaf' hieroglyph may be explained as a professional designation: loha-kāra 'metalsmith'; kāruvu [Skt.] n. 'An artist, artificer. An agent'.(Telugu).
eraka ‘knave of wheel’ Rebus: eraka ‘copper’ (Kannada) eraka ‘molten cast (metal)(Tulu).Dholavira Signboard inscription of gypsum inlays on wood measures 3 m. long. Each of the 10 signs is 37 cm. high and 25 to 27 cm. wide and made of pieces of white gypsum inlays; the signs were apparently inlaid in a wooden plank. The conjecture is that this wooden plank was mounted on the Northern Gateway as a Signboard.
Dholavira Signboard
The Signboard which adorned the Northern Gateway of the citadel of Dholavira was an announcement of the metalwork repertoire of dhokra kamar, cire perdue metalcasters and other smiths working with metal alloys. The entire Indus Script Corpora are veritable metalwork catalogs. The phrase dhokra kamar is rendered on a tablet discovered at Dholavira presented in this monograph (earlier discussed at
http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2014/01/meluhha-hieroglyphs-1-dhokra-lost-wax.html ). The 10-hieroglyph inscription of Dholavira Signboard has been read rebus and presented at
http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2013/08/dholavira-gateway-to-meluhha-gateway-to.html
Excerpts from Excavation Report on Dholavira released by ASI in 2015:
"8.1 Inscriptions. Literacy of the Harappans is best exemplified in their inscriptions written in a script that is unparalleled in its characters hitherto unknown and undeciphered so far. These inscriptions are best represented on their seals and seals-impressions in addition to those engraved or painted on the objects of metal, terracotta, pottery, faience, ivory, bone and stone, albeit sometimes appearing in a single sign inscription or scratching particularly on pottery or terracotta objects. 8.1.1 Signboard. One of the most prominent discoveries from the excavations at Dholavira is the find of a 10 large sized signboard presently lying in the western chamber of North Gate. This inscription was found lying in the western chamber of north gate, and the nature of find indicates that it could have been fitted on a wooden signboard, most probably fitted above the lintel of the central passageway of the gate. The central passageway of north gate itself measures 3.5 m in width and the length of the inscription along with the wooden frame impression is also more or less same thereby indicating the probable location. The inscription consists of 10 large-sized letters of the typical Harappan script, and is actually gypsum inlays cut into various sizes and shapes, which were utilized to create each size as, indicated above. The exact meaning of the inscription is not known in the absence of decipherment of script." (pp.227-229, Section 8.1.1 Signboard)
"The central passageway of north gate itself measures 3.5 m in width and the length of the inscription along with the wooden frame impression is also more or less same thereby indicating the probable location. The inscription consists of 10 large-sized letters of the typical Harappan script, and is actually gypsum inlays cut into various sizes and shapes, which were utilized to create each size as, indicated above. The exact meaning of the inscription is not known in the absence of decipherment of the script. (p.231)
Fig. 8.2: Location of ten large sized inscription in North Gate
Fig. 8.3: Close-up of inscription
Fig. 8.4: Drawing showing the ten letters of inscription
Fig. 8.5: Photograph showing the details of inscription in situ.
Fig. 8.6: Close-up of some of the letters from the inscription
Fig. 8.7: Gypsum inlays used for the inscription
Such proclamations may be noted on other examples from Indus Script Corpora:
![]() Tell Asmar Cylinder seal modern impression [elephant, rhinoceros and gharial (alligator) on the upper register] bibliography and image source: Frankfort, Henri: Stratified Cylinder Seals from the Diyala Region. Oriental Institute Publications 72. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, no. 642. Museum Number: IM14674 3.4 cm. high. Glazed steatite. ca. 2250 - 2200 BCE. karA 'crocodile' Rebus: khAr 'blacksmith' (Kashmiri); karibha 'trunk of elephant' ibha 'elephant' Rebus: karba 'iron' (Tulu); kANDa 'rhinoceros' Rebus: khaNDa 'metal implements'.
Tell Asmar Cylinder seal modern impression [elephant, rhinoceros and gharial (alligator) on the upper register] bibliography and image source: Frankfort, Henri: Stratified Cylinder Seals from the Diyala Region. Oriental Institute Publications 72. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, no. 642. Museum Number: IM14674 3.4 cm. high. Glazed steatite. ca. 2250 - 2200 BCE. karA 'crocodile' Rebus: khAr 'blacksmith' (Kashmiri); karibha 'trunk of elephant' ibha 'elephant' Rebus: karba 'iron' (Tulu); kANDa 'rhinoceros' Rebus: khaNDa 'metal implements'.![]() Dwaraka 1 seal of turbinella pyrum: Ligaturing to the body of an ox: a head of one-horned young bull, and a head of antelope. Thus, there are three hieroglyphs signifying: ox, young bull and antelope.sãgaḍ f. ʻ a body formed of two or more fruits or animals or men &c. linked together (Marathi) Rebus: sangara 'proclamation'; barad, barat 'ox' Rebus: bharata 'alloy of copper, pewter, tin'; ranku 'antelope' Rebus: ranku 'tin'.
Dwaraka 1 seal of turbinella pyrum: Ligaturing to the body of an ox: a head of one-horned young bull, and a head of antelope. Thus, there are three hieroglyphs signifying: ox, young bull and antelope.sãgaḍ f. ʻ a body formed of two or more fruits or animals or men &c. linked together (Marathi) Rebus: sangara 'proclamation'; barad, barat 'ox' Rebus: bharata 'alloy of copper, pewter, tin'; ranku 'antelope' Rebus: ranku 'tin'.
Mohenjo-daro Seal 1927 with epigraphs on two-side is a confirmation that the horns ligatured to the composite animal on m1927b are horns of zebu.
The text message seems to be identical on both sides of the seal m1927: bronze workshop; metal smithy castings; forge. The zebu side a of the seal seems to denote the work of a native-metal-smith; the composite animal side b of the seal seems to denote the expanded work of a blacksmith working with stones, minerals and metals. The composite hieroglyph on m1927b was perhaps called:व्याळ [ vyāḷa ] m (व्याल S) A serpent. Ex. जैसें पायास दंशिलें महा व्याळें ॥ तों मस्तकासीं वृश्चिकें दंशिलें ॥. 2 Applied popularly to the नाग or भुजंग.व्याल [ vyāla ] m S A serpent. (Marathi) யாளவரி yāḷa-vari n. < vyāḷayāḷi யாளி yāḷi, n. < vyāḷa. [K. yāḷi.] A mythological lion-faced animal with elephantine proboscis and tusks; யானையின் தந்தமும் துதிக்கையுஞ் சிங்கத்தின் முகமுமுடையதாகக் கருதப் படும் மிருகம். உழுவையும் யாளியு முளியமும் (குறிஞ் சிப். 252). 1 A vicious elephant; व्यालं बाल- मृणालतन्तुभिरसौ रोद्धुं समुज्जृम्भते Bh.2.6. -2 A beast of prey; वसन्त्यस्मिन् महारण्ये व्यालाश्च रुधिराशनाः Rām.2.119. 19; वनं व्यालनिषेवितम् Rām. -3 A snake; H.3.29. -4 A tiger; Māl.3. -5 A leopard. व्यालकः A vicious or wicked elephant.
The text message on the seal:
kanac ‘corner’ Rebus: kañcu ‘bronze’
kolom ‘three’ (Mu.)
kolmo ‘rice plant' (Mu.) kolom = cutting, graft; to graft, engraft, prune; kolmahoṛo = a variety of the paddy plant (Desi)(Santali.) kolime, kolume, kulame, kulime, kulume, kulme fire-pit, furnace (Ka.); kolimi furnace (Te.); pit (Te.); kolame a very deep pit (Tu.); kulume kanda_ya a tax on blacksmiths (Ka.); kol, kolla a furnace (Ta.) kole.l smithy, temple in Kota village (Ko.); kwala.l Kota smithy (To.); konimi blacksmith; kola id. (Ka.); kolleblacksmith (Kod.); kollusa_na_ to mend implements; kolsta_na, kulsa_na_ to forge;ko_lsta_na_ to repair (of plough-shares); kolmi smithy (Go.); kolhali to forge (Go.)(DEDR 2133).] kolimi-titti = bellows used for a furnace (Te.lex.) kollu- to neutralize metallic properties by oxidation (Ta.lex.) kol brass or iron bar nailed across a door or gate; kollu-t-tat.i-y-a_n.i large nail for studding doors or gates to add to their strength (Ta.lex.) kollan--kamma_lai < + karmas'a_la_, kollan--pat.t.arai, kollan-ulai-k-ku_t.am blacksmith's workshop, smithy (Ta.lex.) cf. ulai smith's forge or furnace (Na_lat.i, 298); ulai-k-kal.am smith's forge; ulai-k-kur-at.u smith's tongs; ulai-t-turutti smith's bellows; ulai-y-a_n.i-k-ko_l smith's poker, beak-iron (Ta.lex.) [kollulaive_r-kan.alla_r: nait.ata. na_t.t.up.); mitiyulaikkollan- mur-iot.ir.r.an-n-a: perumpa_)(Ta.lex.) Temple; smithy: kol-l-ulai blacksmith's forge (kollulaik ku_t.attin-a_l : Kumara. Pira. Ni_tiner-i. 14)(Ta.lex.) cf. kolhua_r sugarcane milkl and boiling house (Bi.); kolha_r oil factory (P.)(CDIAL 3537). kulhu ‘a hindu caste, mostly oilmen’ (Santali) kolsa_r = sugarcane mill and boiling house (Bi.)(CDIAL 3538).Together with kol 'tiger, woman'; the ligatured glyph composition with twig as head-dress connotes: metal alloy furnace-smelter/workshop.
kōlupuli = Bengal tiger (Te.); kol = tiger (Santali) kōla = woman (Nahali)
Rebus: kol metal (Ta.) kol = pan~calōkam (five metals) (Tamil)
A Munda gloss for fish is 'aya'. Read rebus: aya 'iron' (Gujarati) ayas 'metal' (Vedic). The script inscriptions indicate a set of modifiers or ligatures to the hieroglyph indicating that the metal, aya, was worked on during the early Bronze Age metallurgical processes -- to produce aya ingots, aya metalware,aya hard alloys.Fish hieroglyph in its vivid orthographic form is shown in a Susa pot which contained metalware -- weapons and vessels. ![]() Context for use of ‘fish’ glyph. This photograph of a fish and the ‘fish’ glyph on Susa pot are comparable to the ‘fish’ glyph on Indus inscriptions.Read on the arguments at: http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.com/2011/11/decoding-fish-and-ligatured-fish-glyphs.html The modifiers to the 'fish' hieroglyph which commonly occur together are: slanted stroke, notch, fins, lid-of-pot ligatured as superfix:
Context for use of ‘fish’ glyph. This photograph of a fish and the ‘fish’ glyph on Susa pot are comparable to the ‘fish’ glyph on Indus inscriptions.Read on the arguments at: http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.com/2011/11/decoding-fish-and-ligatured-fish-glyphs.html The modifiers to the 'fish' hieroglyph which commonly occur together are: slanted stroke, notch, fins, lid-of-pot ligatured as superfix:![]() For determining the semantics of the messages conveyed by the script. Positional analysis of ‘fish’ glyphs has also been presented in: The Indus Script: A Positional-statistical Approach By Michael Korvink, 2007, Gilund Press.
For determining the semantics of the messages conveyed by the script. Positional analysis of ‘fish’ glyphs has also been presented in: The Indus Script: A Positional-statistical Approach By Michael Korvink, 2007, Gilund Press.
Table from: The Indus Script: A Positional-statistical Approach By Michael Korvink, 2007, Gilund Press. Mahadevan notes (Para 6.5 opcit.) that ‘a unique feature of the FISH signs is their tendency to form clusters, often as pairs, and rarely as triplets also. This pattern has fascinated and baffled scholars from the days of Hunter posing problems in interpretation.’ One way to resolve the problem is to interpret the glyptic elements creating ligatured fish signs and read the glyptic elements rebus to define the semantics of the message of an inscription.
karaṇḍa ‘duck’ (Sanskrit) karaṛa ‘a very large aquatic bird’ (Sindhi) Rebus: करडा [karaḍā] Hard from alloy--iron, silver &c. (Marathi) Rebus: fire-god: @B27990. #16671. Remo <karandi>E155 {N} ``^fire-^god''.(Munda) Rebus:. kharādī ‘ turner’ (Gujarati)The 'parenthesis' modifier is a circumfix for both 'fish' and 'duck' hieroglyphs, the semantics of () two parenthetical modifiers are: kuṭilá— ‘bent, crooked’ KātyŚr., °aka— Pañcat., n. ‘a partic. plant’ [√kuṭ 1] Pa. kuṭila— ‘bent’, n. ‘bend’; Pk. kuḍila— ‘crooked’, °illa— ‘humpbacked’, °illaya— ‘bent’DEDR 2054 (a) Ta. koṭu curved, bent, crooked; koṭumai crookedness, obliquity; koṭukki hooked bar for fastening doors, clasp of an ornament. A pair of curved lines: dol ‘likeness, picture, form’ [e.g., two tigers, two bulls, sign-pair.] Kashmiri. dula दुल । युग्मम् m. a pair, a couple, esp. of two similar things (Rām. 966). Rebus: dul meṛeḍ cast iron (Mundari. Santali) dul ‘to cast metal in a mould’ (Santali) pasra meṛed, pasāra meṛed = syn. of koṭe meṛed = forged iron, in contrast to dul meṛed, cast iron (Mundari.) Thus, dul kuṭila ‘cast bronze’.The parenthetically ligatured fish+duck hieroglyphs thus read rebus: dul kuṭila ayas karaḍā 'cast bronze ayasor cast alloy metal with ayas as component to create karaḍā ''hard alloy with ayas'.![]() Ligatures to fish: parentheses + snout dul kuṭila ayas 'cast bronze ayas alloy with tuttha, copper sulphate'
Ligatures to fish: parentheses + snout dul kuṭila ayas 'cast bronze ayas alloy with tuttha, copper sulphate'
Modifier hieroglyph: 'snout' Hieroglyph: WPah.kṭg. ṭōṭ ʻ mouth ʼ.WPah.kṭg. thótti f., thótthəṛ m. ʻ snout, mouth ʼ, A. ṭhõt(phonet. thõt) (CDIAL 5853). Semantics, Rebus:
tutthá n. (m. lex.), tutthaka -- n. ʻ blue vitriol (used as an eye ointment) ʼ Suśr., tūtaka -- lex. 2. *thōttha -- 4. 3. *tūtta -- . 4. *tōtta -- 2. [Prob. ← Drav. T. Burrow BSOAS xii 381; cf. dhūrta -- 2 n. ʻ iron filings ʼ lex.]1. N. tutho ʻ blue vitriol or sulphate of copper ʼ, B. tuth.2. K. thŏth, dat. °thas m., P. thothā m.3. S.tūtio m., A. tutiyā, B. tũte, Or. tutiā, H. tūtā, tūtiyā m., M. tutiyā m.4. M. totā m.(CDIAL 5855) Ka. tukku rust of iron; tutta, tuttu, tutte blue vitriol. Tu. tukků rust; mair(ů)suttu, (Eng.-Tu. Dict.) mairůtuttu blue vitriol. Te. t(r)uppu rust; (SAN) trukku id., verdigris. / Cf. Skt. tuttha- blue vitriol (DEDR 3343).
Fish + corner, aya koṇḍa, ‘metal turned or forged’Fish, aya ‘metal’Fish + scales, aya ã̄s (amśu) ‘metallic stalks of stone ore’. Vikalpa: badhoṛ ‘a species of fish with many bones’ (Santali) Rebus: baḍhoe ‘a carpenter, worker in wood’; badhoria ‘expert in working in wood’(Santali)Fish + splinter, aya aduru ‘smelted native metal’Fish + sloping stroke, aya ḍhāḷ ‘metal ingot’Fish + arrow or allograph, Fish + circumscribed four short strokes
This indication of the occurrence, together, of two or more 'fish' hieroglyphs with modifiers is an assurance that the modifiers ar semantic indicators of how aya 'metal' is worked on by the artisans.
ayakāṇḍa ‘’large quantity of stone (ore) metal’ or aya kaṇḍa, ‘metal fire-altar’. ayo, hako 'fish'; ãs = scales of fish (Santali); rebus: aya ‘metal, iron’ (G.); ayah, ayas = metal (Skt.) Santali lexeme, hako ‘fish’ is concordant with a proto-Indic form which can be identified as ayo in many glosses, Munda, Sora glosses in particular, of the Indian linguistic area.
S. KalyanaramanSarasvati Research CenterDecember 12, 2015
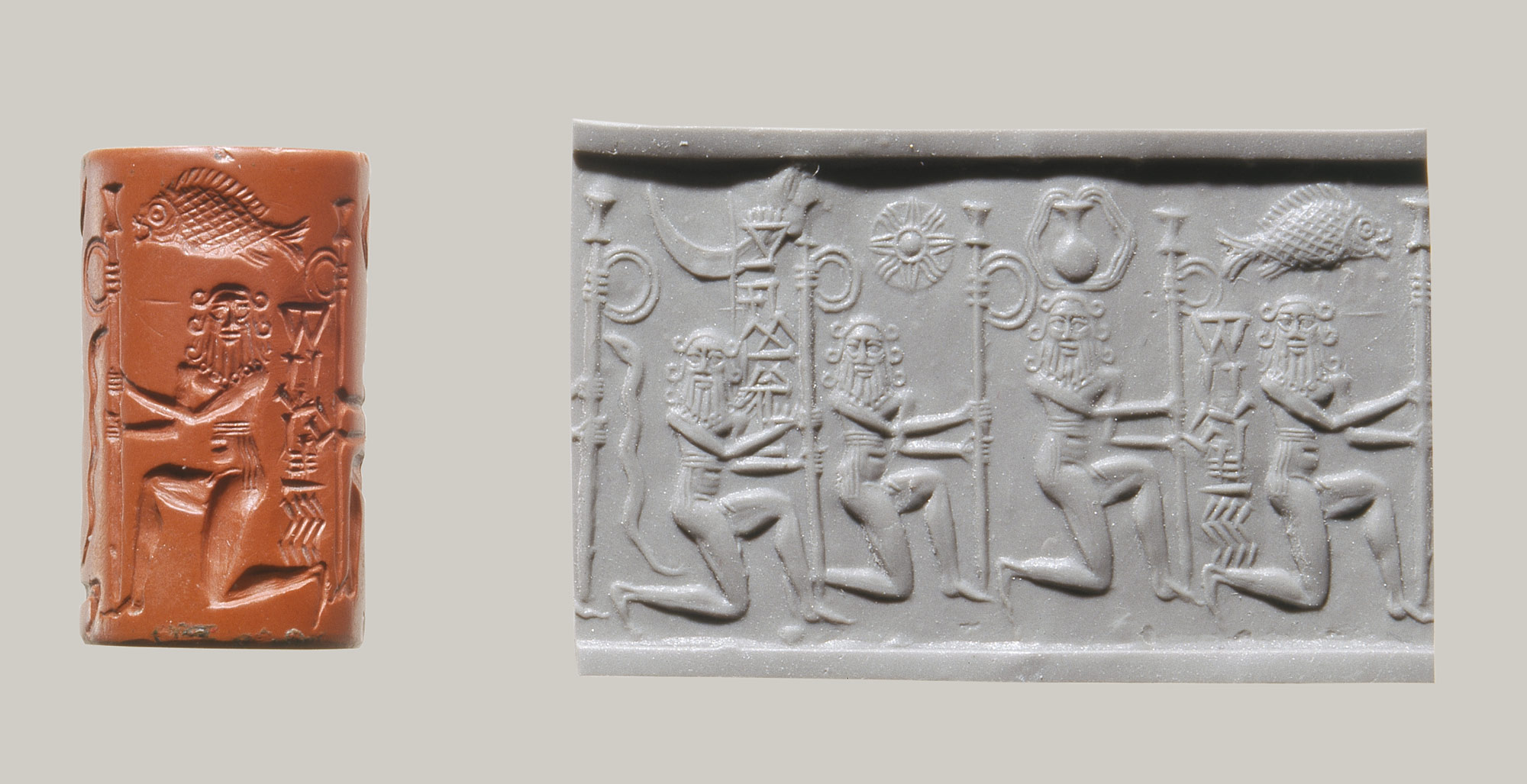


khuṇṭa 'peg’; khũṭi = pin (M.) rebus: kuṭi= furnace (Santali) kūṭa ‘workshop’ kuṇḍamu ‘a pit for receiving and preserving consecrated fire’ (Te.) kundār turner (A.); kũdār, kũdāri (B.)
The text message seems to be identical on both sides of the seal m1927: bronze workshop; metal smithy castings; forge. The zebu side a of the seal seems to denote the work of a native-metal-smith; the composite animal side b of the seal seems to denote the expanded work of a blacksmith working with stones, minerals and metals. The composite hieroglyph on m1927b was perhaps called:व्याळ [ vyāḷa ] m (व्याल S) A serpent. Ex. जैसें पायास दंशिलें महा व्याळें ॥ तों मस्तकासीं वृश्चिकें दंशिलें ॥. 2 Applied popularly to the नाग or भुजंग.व्याल [ vyāla ] m S A serpent. (Marathi) யாளவரி yāḷa-vari n. < vyāḷayāḷi யாளி yāḷi, n. < vyāḷa. [K. yāḷi.] A mythological lion-faced animal with elephantine proboscis and tusks; யானையின் தந்தமும் துதிக்கையுஞ் சிங்கத்தின் முகமுமுடையதாகக் கருதப் படும் மிருகம். உழுவையும் யாளியு முளியமும் (குறிஞ் சிப். 252). 1 A vicious elephant; व्यालं बाल- मृणालतन्तुभिरसौ रोद्धुं समुज्जृम्भते Bh.2.6. -2 A beast of prey; वसन्त्यस्मिन् महारण्ये व्यालाश्च रुधिराशनाः Rām.2.119. 19; वनं व्यालनिषेवितम् Rām. -3 A snake; H.3.29. -4 A tiger; Māl.3. -5 A leopard. व्यालकः A vicious or wicked elephant.
The text message on the seal:
kanac ‘corner’ Rebus: kañcu ‘bronze’
sal ‘splinter’ Rebus: sal ‘workshop’
|| dula ‘pair or two’ Rebus: dul ‘cast metal’
||| kolom ‘three’ Rebus: kolami ‘smithy, forge’
kolmo ‘paddy plant’ Rebus: kolami ‘smithy, forge’
Bronze alloy workshop kañcu sal starting with bronze which is a tin + copper alloy or tin bronze (as distinguished from arsenical bronze, i.e. naturally occurring copper + arsenic).
dula ‘two’ Rebus: dul ‘cast metal’
dolom ‘three’ Rebus: kolami ‘smithy, forge’
kolmo ‘paddy plant’ Rebus: kolami ‘smithy, forge’. Vikalpa: mogge ‘sprout, bud’ Rebus: mū̃h ‘ingot’
kolom ‘three’ (Mu.)
kolmo ‘rice plant' (Mu.)
kolom = cutting, graft; to graft, engraft, prune; kolmahoṛo = a variety of the paddy plant (Desi)(Santali.)
kolime, kolume, kulame, kulime, kulume, kulme fire-pit, furnace (Ka.); kolimi furnace (Te.); pit (Te.); kolame a very deep pit (Tu.); kulume kanda_ya a tax on blacksmiths (Ka.); kol, kolla a furnace (Ta.) kole.l smithy, temple in Kota village (Ko.); kwala.l Kota smithy (To.); konimi blacksmith; kola id. (Ka.); kolleblacksmith (Kod.); kollusa_na_ to mend implements; kolsta_na, kulsa_na_ to forge;ko_lsta_na_ to repair (of plough-shares); kolmi smithy (Go.); kolhali to forge (Go.)(DEDR 2133).] kolimi-titti = bellows used for a furnace (Te.lex.) kollu- to neutralize metallic properties by oxidation (Ta.lex.) kol brass or iron bar nailed across a door or gate; kollu-t-tat.i-y-a_n.i large nail for studding doors or gates to add to their strength (Ta.lex.) kollan--kamma_lai < + karmas'a_la_, kollan--pat.t.arai, kollan-ulai-k-ku_t.am blacksmith's workshop, smithy (Ta.lex.) cf. ulai smith's forge or furnace (Na_lat.i, 298); ulai-k-kal.am smith's forge; ulai-k-kur-at.u smith's tongs; ulai-t-turutti smith's bellows; ulai-y-a_n.i-k-ko_l smith's poker, beak-iron (Ta.lex.) [kollulaive_r-kan.alla_r: nait.ata. na_t.t.up.); mitiyulaikkollan- mur-iot.ir.r.an-n-a: perumpa_)(Ta.lex.) Temple; smithy: kol-l-ulai blacksmith's forge (kollulaik ku_t.attin-a_l : Kumara. Pira. Ni_tiner-i. 14)(Ta.lex.) cf. kolhua_r sugarcane milkl and boiling house (Bi.); kolha_r oil factory (P.)(CDIAL 3537). kulhu ‘a hindu caste, mostly oilmen’ (Santali) kolsa_r = sugarcane mill and boiling house (Bi.)(CDIAL 3538).
Together with kol 'tiger, woman'; the ligatured glyph composition with twig as head-dress connotes: metal alloy furnace-smelter/workshop.
kōlupuli = Bengal tiger (Te.); kol = tiger (Santali) kōla = woman (Nahali)
Rebus: kol metal (Ta.) kol = pan~calōkam (five metals) (Tamil)
A Munda gloss for fish is 'aya'. Read rebus: aya 'iron' (Gujarati) ayas 'metal' (Vedic). The script inscriptions indicate a set of modifiers or ligatures to the hieroglyph indicating that the metal, aya, was worked on during the early Bronze Age metallurgical processes -- to produce aya ingots, aya metalware,aya hard alloys. Fish hieroglyph in its vivid orthographic form is shown in a Susa pot which contained metalware -- weapons and vessels.  Context for use of ‘fish’ glyph. This photograph of a fish and the ‘fish’ glyph on Susa pot are comparable to the ‘fish’ glyph on Indus inscriptions. Read on the arguments at: http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.com/2011/11/decoding-fish-and-ligatured-fish-glyphs.html The modifiers to the 'fish' hieroglyph which commonly occur together are: slanted stroke, notch, fins, lid-of-pot ligatured as superfix: Table from: The Indus Script: A Positional-statistical Approach By Michael Korvink, 2007, Gilund Press. Mahadevan notes (Para 6.5 opcit.) that ‘a unique feature of the FISH signs is their tendency to form clusters, often as pairs, and rarely as triplets also. This pattern has fascinated and baffled scholars from the days of Hunter posing problems in interpretation.’ One way to resolve the problem is to interpret the glyptic elements creating ligatured fish signs and read the glyptic elements rebus to define the semantics of the message of an inscription. karaṇḍa ‘duck’ (Sanskrit) karaṛa ‘a very large aquatic bird’ (Sindhi) Rebus: करडा [karaḍā] Hard from alloy--iron, silver &c. (Marathi) Rebus: fire-god: @B27990. #16671. Remo <karandi>E155 {N} ``^fire-^god''.(Munda) Rebus:. kharādī ‘ turner’ (Gujarati) The 'parenthesis' modifier is a circumfix for both 'fish' and 'duck' hieroglyphs, the semantics of () two parenthetical modifiers are: kuṭilá— ‘bent, crooked’ KātyŚr., °aka— Pañcat., n. ‘a partic. plant’ [√kuṭ 1] Pa. kuṭila— ‘bent’, n. ‘bend’; Pk. kuḍila— ‘crooked’, °illa— ‘humpbacked’, °illaya— ‘bent’DEDR 2054 (a) Ta. koṭu curved, bent, crooked; koṭumai crookedness, obliquity; koṭukki hooked bar for fastening doors, clasp of an ornament. A pair of curved lines: dol ‘likeness, picture, form’ [e.g., two tigers, two bulls, sign-pair.] Kashmiri. dula दुल । युग्मम् m. a pair, a couple, esp. of two similar things (Rām. 966). Rebus: dul meṛeḍ cast iron (Mundari. Santali) dul ‘to cast metal in a mould’ (Santali) pasra meṛed, pasāra meṛed = syn. of koṭe meṛed = forged iron, in contrast to dul meṛed, cast iron (Mundari.) Thus, dul kuṭila ‘cast bronze’. The parenthetically ligatured fish+duck hieroglyphs thus read rebus: dul kuṭila ayas karaḍā 'cast bronze ayasor cast alloy metal with ayas as component to create karaḍā ''hard alloy with ayas'. Modifier hieroglyph: 'snout' Hieroglyph: WPah.kṭg. ṭōṭ ʻ mouth ʼ.WPah.kṭg. thótti f., thótthəṛ m. ʻ snout, mouth ʼ, A. ṭhõt(phonet. thõt) (CDIAL 5853). Semantics, Rebus: tutthá n. (m. lex.), tutthaka -- n. ʻ blue vitriol (used as an eye ointment) ʼ Suśr., tūtaka -- lex. 2. *thōttha -- 4. 3. *tūtta -- . 4. *tōtta -- 2. [Prob. ← Drav. T. Burrow BSOAS xii 381; cf. dhūrta -- 2 n. ʻ iron filings ʼ lex.]1. N. tutho ʻ blue vitriol or sulphate of copper ʼ, B. tuth.2. K. thŏth, dat. °thas m., P. thothā m.3. S.tūtio m., A. tutiyā, B. tũte, Or. tutiā, H. tūtā, tūtiyā m., M. tutiyā m.4. M. totā m.(CDIAL 5855) Ka. tukku rust of iron; tutta, tuttu, tutte blue vitriol. Tu. tukků rust; mair(ů)suttu, (Eng.-Tu. Dict.) mairůtuttu blue vitriol. Te. t(r)uppu rust; (SAN) trukku id., verdigris. / Cf. Skt. tuttha- blue vitriol (DEDR 3343). Fish + corner, aya koṇḍa, ‘metal turned or forged’ Fish, aya ‘metal’ Fish + scales, aya ã̄s (amśu) ‘metallic stalks of stone ore’. Vikalpa: badhoṛ ‘a species of fish with many bones’ (Santali) Rebus: baḍhoe ‘a carpenter, worker in wood’; badhoria ‘expert in working in wood’(Santali) Fish + splinter, aya aduru ‘smelted native metal’ Fish + sloping stroke, aya ḍhāḷ ‘metal ingot’ Fish + arrow or allograph, Fish + circumscribed four short strokes This indication of the occurrence, together, of two or more 'fish' hieroglyphs with modifiers is an assurance that the modifiers ar semantic indicators of how aya 'metal' is worked on by the artisans. ayakāṇḍa ‘’large quantity of stone (ore) metal’ or aya kaṇḍa, ‘metal fire-altar’. ayo, hako 'fish'; ãs = scales of fish (Santali); rebus: aya ‘metal, iron’ (G.); ayah, ayas = metal (Skt.) Santali lexeme, hako ‘fish’ is concordant with a proto-Indic form which can be identified as ayo in many glosses, Munda, Sora glosses in particular, of the Indian linguistic area. beḍa hako (ayo) ‘fish’ (Santali); beḍa ‘either of the sides of a hearth’ (G.) Munda: So. ayo `fish'. Go. ayu `fish'. Go <ayu> (Z), <ayu?u> (Z),, <ayu?> (A) {N} ``^fish''. Kh. kaDOG `fish'. Sa. Hako `fish'. Mu. hai (H) ~ haku(N) ~ haikO(M) `fish'. Ho haku `fish'. Bj. hai `fish'. Bh.haku `fish'. KW haiku ~ hakO |Analyzed hai-kO, ha-kO (RDM). Ku. Kaku`fish'.@(V064,M106) Mu. ha-i, haku `fish' (HJP). @(V341) ayu>(Z), <ayu?u> (Z) <ayu?>(A) {N} ``^fish''. #1370. <yO>\\<AyO>(L) {N} ``^fish''. #3612. <kukkulEyO>,,<kukkuli-yO>(LMD) {N} ``prawn''. !Serango dialect. #32612. <sArjAjyO>,,<sArjAj>(D) {N} ``prawn''. #32622. <magur-yO>(ZL) {N} ``a kind of ^fish''. *Or.<>. #32632. <ur+GOl-Da-yO>(LL) {N} ``a kind of ^fish''. #32642.<bal.bal-yO>(DL) {N} ``smoked fish''. #15163. Vikalpa: Munda: <aDara>(L) {N} ``^scales of a fish, sharp bark of a tree''.#10171. So<aDara>(L) {N} ``^scales of a fish, sharp bark of a tree''. Indian mackerel Ta. ayirai, acarai, acalai loach, sandy colour, Cobitis thermalis; ayilai a kind of fish. Ma.ayala a fish, mackerel, scomber; aila, ayila a fish; ayira a kind of small fish, loach (DEDR 191) aduru native metal (Ka.); ayil iron (Ta.) ayir, ayiram any ore (Ma.); ajirda karba very hard iron (Tu.)(DEDR 192). Ta. ayil javelin, lance, surgical knife, lancet.Ma. ayil javelin, lance; ayiri surgical knife, lancet. (DEDR 193). aduru = gan.iyinda tegadu karagade iruva aduru = ore taken from the mine and not subjected to melting in a furnace (Ka. Siddhānti Subrahmaṇya’ Śastri’s new interpretation of the AmarakoŚa, Bangalore, Vicaradarpana Press, 1872, p.330); adar = fine sand (Ta.); ayir – iron dust, any ore (Ma.) Kur. adar the waste of pounded rice, broken grains, etc. Malt. adru broken grain (DEDR 134). Ma. aśu thin, slender;ayir, ayiram iron dust.Ta. ayir subtlety, fineness, fine sand, candied sugar; ? atar fine sand, dust. அய.ர³ ayir, n. 1. Subtlety, fineness; நணசம. (த_வ_.) 2. [M. ayir.] Fine sand; நணமணல. (மலசலப. 92.) ayiram, n. Candied sugar; ayil, n. cf. ayas. 1. Iron; 2. Surgical knife, lancet; Javelin, lance; ayilavaṉ, Skanda, as bearing a javelin (DEDR 341).Tu. gadarů a lump (DEDR 1196) kadara— m. ‘iron goad for guiding an elephant’ lex. (CDIAL 2711). अयोगूः A blacksmith; Vāj.3.5. अयस् a. [इ-गतौ-असुन्] Going, moving; nimble. n. (-यः) 1 Iron (एति चलति अयस्कान्तसंनिकर्षं इति तथात्वम्; नायसोल्लिख्यते रत्नम् Śukra 4.169. अभितप्तमयो$पि मार्दवं भजते कैव कथा शरीरिषु R.8.43. -2 Steel. -3 Gold. -4 A metal in general. ayaskāṇḍa 1 an iron-arrow. -2 excellent iron. -3 a large quantity of iron. -क_नत_(अयसक_नत_) 1 'beloved of iron', a magnet, load-stone; 2 a precious stone; ˚मजण_ a loadstone; ayaskāra 1 an iron-smith, blacksmith (Skt.Apte) ayas-kāntamu. [Skt.] n. The load-stone, a magnet. ayaskāruḍu. n. A black smith, one who works in iron. ayassu. n. ayō-mayamu. [Skt.] adj. made of iron (Te.) áyas— n. ‘metal, iron’ RV. Pa. ayō nom. sg. n. and m., aya— n. ‘iron’, Pk. aya— n., Si. ya. AYAŚCŪRṆA—, AYASKĀṆḌA—, *AYASKŪṬA—. Addenda: áyas—: Md. da ‘iron’, dafat ‘piece of iron’. ayaskāṇḍa— m.n. ‘a quantity of iron, excellent iron’ Pāṇ. gaṇ. viii.3.48 [ÁYAS—, KAA ́ṆḌA—]Si.yakaḍa ‘iron’.*ayaskūṭa— ‘iron hammer’. [ÁYAS—, KUU ́ṬA—1] Pa. ayōkūṭa—, ayak m.; Si. yakuḷa‘sledge —hammer’, yavuḷa (< ayōkūṭa) (CDIAL 590, 591, 592). cf. Lat. aes , aer-is for as-is ; Goth. ais , Thema aisa; Old Germ. e7r , iron ;Goth. eisarn ; Mod. Germ. Eisen. S. Kalyanaraman Sarasvati Research Center December 12, 2015 |