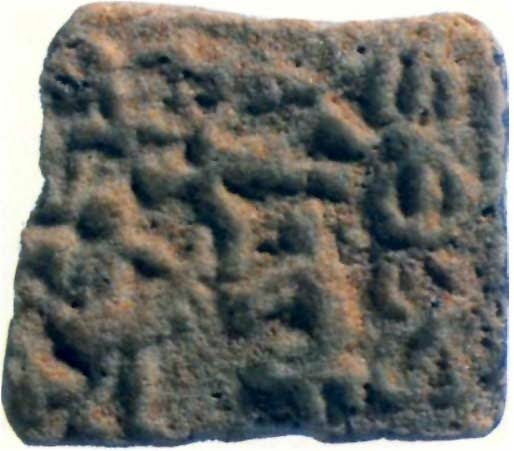
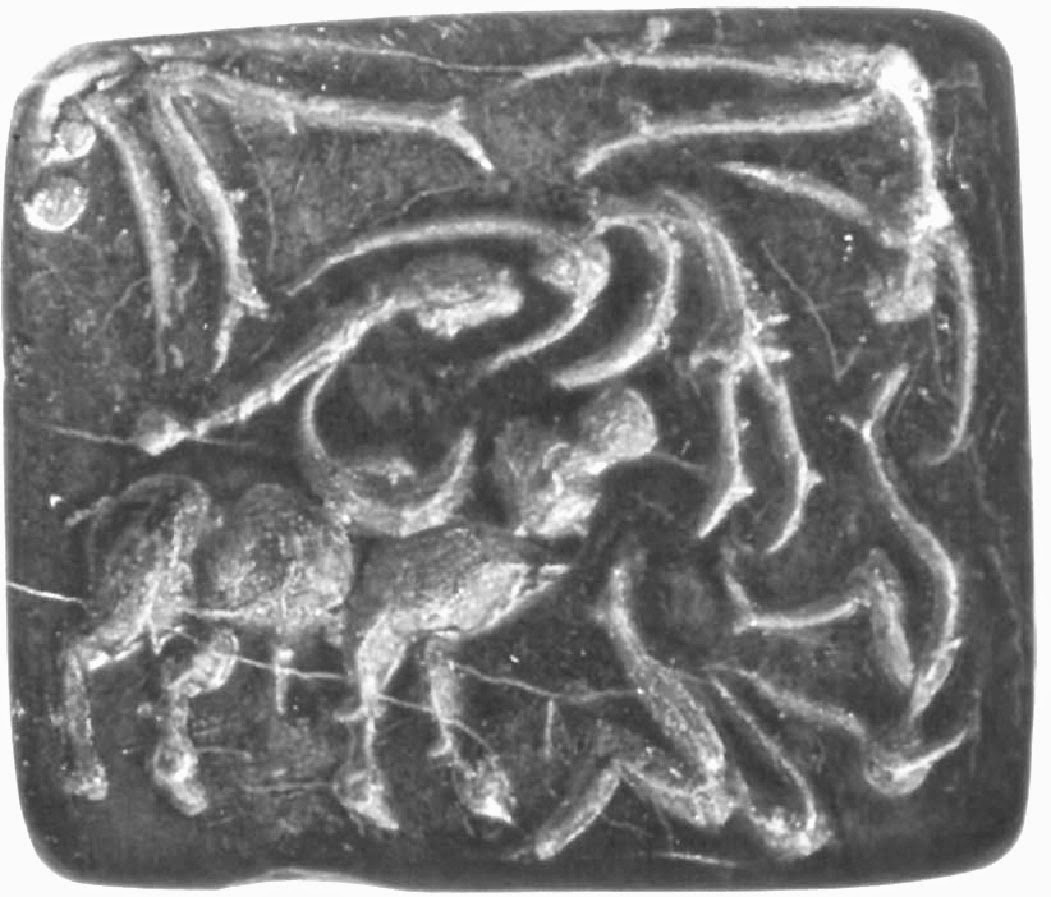
Hieroglyphs: thread of three stands + drummer + tumblers
dhollu ‘drummer’ (Western Pahari) dolutsu 'tumble' Rebus: dul ‘cast metal’
dhAtu 'strands of rope' Rebus: dhAtu 'mineral, metal, ore'

Kalibangan seal. k020 Hieroglyphs: thread of three strands + water-carrier + one-horned young bull.
Examples of acrobats as hieroglyphs:
Mehrgarh. Terracotta circular button seal. (Shah, SGM & Parpola, A., 1991, Corpus of Indus Seals and Inscriptions 2: Collections in Pakistan, Helsinki: Suomalainen Tiedeakatemia, MR-17. A humped bull (water buffalo?) and abstract forms (one of which is like a human body) around the bull. The human body is tossed from the horns of the bovine.
m0312 Persons vaulting over a water buffalo. The water buffalo tosses a person on its horns. Four or five bodies surround the animal. Rounded edges indicate frequent use to create clay seal impressions.
Impression of a steatite stamp seal (2300-1700 BCE) with a water-buffalo and acrobats. Buffalo attack or bull-leaping scene, Banawali (after UMESAO 2000:88, cat. no. 335). A figure is impaled on the horns of the buffalo; a woman acrobat wearing bangles on both arms and a long braid flowing from the head, leaps over the buffalo bull. The action narrative is presented in five frames of the acrobat getting tossed by the horns, jumping and falling down.Two Indus script glyphs are written in front of the buffalo. (ASI BNL 5683).
Rebus readings of hieroglyphs: ‘1. arrow, 2. jag/notch, 3. buffalo, 4.acrobatics’:
1. kaṇḍa ‘arrow’ (Skt.) H. kãḍerā m. ʻ a caste of bow -- and arrow -- makers (CDIAL 3024). Or. kāṇḍa, kã̄ṛ ʻstalk, arrow ʼ(CDIAL 3023). ayaskāṇḍa ‘a quantity of iron, excellent iron’ (Pāṇ.gaṇ)
2. खांडा [ khāṇḍā ] m A jag, notch, or indentation (as upon the edge of a tool or weapon). (Marathi) Rebus: khāṇḍā ‘tools, pots and pans, metal-ware’.
3. rāngo ‘water buffalo bull’ (Ku.N.)(CDIAL 10559)
Rebus: rango ‘pewter’. ranga, rang pewter is an alloy of tin, lead, and antimony (anjana) (Santali).
4. ḍullu to fall off; ḍollu to roll over (DEDR 2698) Te. ḍul(u)cu, ḍulupu to cause to fall; ḍollu to fall; ḍolligillu to fall or tumble over (DEDR 2988) డొలుచు [ḍolucu] or ḍoluṭsu. [Tel.] v. n. To tumble head over heels as dancing girls do (Telugu) Rebus 1: dul ‘to cast in a mould’; dul mẽṛhẽt, dul meṛeḍ, 'cast iron'; koṭe meṛeḍ ‘forged iron’ (Santali) Bshk. ḍōl ʻ brass pot (CDIAL 6583). Rebus 2: WPah. ḍhōˋḷ m. ʻstoneʼ, ḍhòḷṭɔ m. ʻbig stone or boulderʼ, ḍhòḷṭu ʻsmall id.ʼ Him.I 87(CDIAL 5536). Rebus: K. ḍula m. ʻ rolling stoneʼ(CDIAL 6582).
Rebus: M. dhāū, dhāv m.f. ʻ a partic. soft red stone ʼ (whence dhā̆vaḍ m. ʻ a caste of iron -- smelters ʼ, dhāvḍī ʻ composed of or relating to iron ʼ); dhāˊtu n. ʻ substance ʼ RV., m. ʻ element ʼ MBh., ʻ metal, mineral, ore (esp. of a red colour) ʼ; Pk. dhāu -- m. ʻ metal, red chalk ʼ; N. dhāu ʻ ore (esp. of copper) ʼ; Or. ḍhāu ʻ red chalk, red ochre ʼ (whence ḍhāuā ʻ reddish ʼ; (CDIAL 6773) धातु primary element of the earth i.e. metal , mineral, ore (esp. a mineral of a red colour) Mn. MBh. &c element of words i.e. grammatical or verbal root or stem Nir. Pra1t. MBh. &c (with the southern Buddhists धातु means either the 6 elements [see above] Dharmas. xxv ; or the 18 elementary spheres [धातु-लोक] ib. lviii ; or the ashes of the body , relics L. [cf. -गर्भ]) (Monier-Williams. Samskritam).
The twisted snakes are distinguished in the context of a temple in Ancient Near East.

The Sumerian deity, Ningizzida, is accompanied by two gryphons Mushussu; it is the oldest known image of two snakes coiling around an axial rod, dating from before 2000 BCE.http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Serpent_(symbolism)
nAga 'serpent' Rebus: nAga 'lead'; dhAtu 'strands' Rebus: dhAtu 'mineral' Thus, nAga dhAtu 'lead mineral'
Hieroglyph: karada 'leopard': Kol. keḍiak tiger. Nk. khaṛeyak panther. Go. (A.) khaṛyal tiger; (Haig) kariyāl panther (Voc. 999). Kui kṛāḍi, krānḍi tiger, leopard, hyena. Kuwi (F.) kṛani tiger; (S.) klā'ni tiger, leopard; (Su. P. Isr.) kṛaˀni (pl. -ŋa) tiger. / Cf. Pkt. (DNM) karaḍa- id. (DEDR 1132) करडा [karaḍā] Hard from alloy--iron, silver &c. (Marathi)
 Bronze flag, Shahdad Kerman, Iran dated to 3rd millennium BCE. See: http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2013/07/ancient-near-east-shahdad-bronze-age.html
Bronze flag, Shahdad Kerman, Iran dated to 3rd millennium BCE. See: http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2013/07/ancient-near-east-shahdad-bronze-age.html
“The shaft is set on a 135 mm high pyramidal base. The thin metal plate is a square with curved sides set in a 21 mm wide frame. On the plate there is a figure of a goddess sitting on a chair and facing forward. The goddess has a long face, long hair and round eyes. Her left hand is extended as if to take a gift…a square garden divided into ten squares. In the center of each square there is a small circle. Beside this garden there is a row of two date palm trees…Under this scene the figure of a bull flanked by two lions is shown…The sun appears between the heads of the goddess and, one of the women and it is surrounded by a row of chain decorative motives.” (Hakemi, Ali, 1997, Shahdad, archaeological excavations of a bronze age center in Iran, Reports and Memoirs, Vol. XXVII, IsMEO, Rome. 766 pp, p.271, p.649). The inscriptional evidence discovered at this site which is on the crossroads of ancient bronze age civilizations attests to the possibility of Meluhha settlements in Shahdad, Tepe Yahya and other Elam/Susa region sites. The evolution of bronze age necessitated a writing system -- the answer was provided by Indus writing using hieroglyphs and rebus method of rendering Meluhha (mleccha) words of Indian sprachbund.
"The inscriptional evidence discovered at this site which is on the crossroads of ancient bronze age civilizations attests to the possibility of Meluhha settlements in Shahdad, Tepe Yahya and other Elam/Susa region sites. The evolution of bronze age necessitated a writing system -- the answer was provided by Indus writing using hieroglyphs and rebus method of rendering Meluhha (mleccha) words of Indian sprachbund." http://bharatkalyan97.blogspot.in/2015/08/ingots-of-arakuta-orichalcum-brass.html
Shown are the glyphs of 1. zebu and 2. tigers which are also glyphs on Indus writing which I decode as related respectively to 1. blacksmithy on unsmelted metal (Adar Dhangar 'native blacksmith', poLa 'zebu' Rebus: poLa 'magnetite') 2. working with alloys (kol, tiger) The tree is a smelter furnace (kuTi).
The twisted rope hieroglyph: धातु dhātu 'strand of rope' (Rigveda) Rebus: 'metal, mineral, ore (esp. of copper, esp. of red colour) Alternative: The endless-knot motif is iron (meD, knot, iron).
Twisted strands of rope as hieroglyph on Ancient Near East artifacts
Cylinder seal and impression Syria (ca. 1720–1650 B.C.E) Hematite 21 x 10 mm Seal no. 937 http://www.themorgan.org/collections/collectionsList.asp?id=Seals
Hieroglyphs on the cylinder seal read rebus:
The glyph of a crescent with a ball above may denote a crucible + ingot.
Hieroglyphs on the cylinder seal read rebus:
The glyph of a crescent with a ball above may denote a crucible + ingot.
koThAri 'crucible' Rebus: koThAri 'treaurer, warehouse'
kola 'woman' Rebus: kolhe‘smelter’.
H. mẽṛā, mẽḍā m. ʻ ram with curling horns ʼ (CDIAL 10120). Rebus: mẽṛhẽt, meḍ ‘iron’ (Mu.Ho.)
kuṛī f. ʻ girl (Punjabi) Rebus: kuṭhi 'smelter'; dula 'pair' Rebus: dul 'cast metal'. Thus, the two young girls denote dul kuṭhi 'smelter for cast metal'.
मेढा [ mēḍhā ] 'polar star' Rebus: mẽṛhẽt, meḍ ‘iron’ (Mu.Ho.) ayo 'fish' Rebus: ayo 'iron' (Gujarati); ayas 'alloyed metal' (Sanskrit) eruvai 'eagle' Rebus: eruvai 'copper'.
kola 'woman' Rebus: kolhe‘smelter’.
H. mẽṛā, mẽḍā m. ʻ ram with curling horns ʼ (CDIAL 10120). Rebus: mẽṛhẽt, meḍ ‘iron’ (Mu.Ho.)
kuṛī f. ʻ girl (Punjabi) Rebus: kuṭhi 'smelter'; dula 'pair' Rebus: dul 'cast metal'. Thus, the two young girls denote dul kuṭhi 'smelter for cast metal'.
मेढा [ mēḍhā ] 'polar star' Rebus: mẽṛhẽt, meḍ ‘iron’ (Mu.Ho.) ayo 'fish' Rebus: ayo 'iron' (Gujarati); ayas 'alloyed metal' (Sanskrit) eruvai 'eagle' Rebus: eruvai 'copper'.
1. kulai ‘a hare’ (Santali) Allograph: kul ‘tiger’ (Santali) Rebus: kolhe‘smelter’. (Hieroglyph attached) A pair of hares: dul kolhe 'cast metal smelter'. (Hieroglyph: dula 'pair')
2. karaDi 'safflower' Rebus: karaDa 'hard alloy'.(Hieroglyph attached)
3. Twisted rope: dhAtu 'strands of rope' Rebus: dhAtu 'mineral, metal, ore' Alternative: मेढा [ mēḍhā ] A twist or tangle arising in thread or cord, a curl or snarl.(Marathi)(CDIAL 10312).L. meṛh f. ʻrope tying oxen to each other and to post on threshing floorʼ(CDIAL 10317) Rebus: meḍ'iron'. mẽṛhet ‘iron’ (Mu.Ho.) (Hieroglyph attached; below the cord/twist are two seated lions)
4. arye 'lion' Rebus: araa 'brass'.
5. dula 'pair' Rebus: dul 'cast (metal). Thus a cast iron-brass alloy indicated.
6. The person on the right holding an antelope is mlekh 'goat' Rebus: meṛh 'helper of merchant' (Desinaamamaalaa of Hemachandra)
7. eraka 'wing' Rebus: erako 'moltencast copper'.
8. kola 'woman' Rebus: kol 'working in iron'; kolhe 'smelter'.
9. kuTi 'girl' (cf. two girls held upside down); Rebus: kuThi 'smelter furnace'. Thus, a copper smelter furnace is indicated.
10. khamḍa 'copulation' (Santali) Rebus: kampaṭṭa ‘mint, coiner’.

Print of a seal: Two-headed eagle, a twisted cord below. From Bogazköy . 18th c.B.C. (Museum Ankara).
 eruvai 'eagle' Rebus: eruvai 'copper'. kōḍe, kōḍiya. [Tel.] n. A bullcalf. Rebus: koḍ artisan’s workshop (Kuwi) kunda ‘turner’ kundār turner (Assamese) Technical description Votive bas-relief of Dudu, priest of Ningirsu in the time of Entemena, prince of Lagash C. 2400 BCE Tello (ancient Girsu) Bituminous stone H. 25 cm; W. 23 cm; Th. 8 cm De Sarzec excavations, 1881 AO 2354 Plaques perforated in the center and decorated with scenes incised or carved in relief were particularly widespread in the Second and Third Early Dynastic Periods (2800-2340 BC), and have been found at many sites in Mesopotamian and more rarely in Syria or Iran. The perforated plaque of Dudu, high priest of Ningirsu in the reign of Entemena, prince of Lagash (c.2450 BC), belongs to this tradition. It has some distinctive features, however, such as being made of bitumen.This plaque belongs to the category of perforated plaques, widespread throughout Phases I and II of the Early Dynastic Period, c.2800-2340BC, and found at many sites in Mesopotamia (especially in the Diyala region), and more rarely in Syria (Mari) and Iran (Susa). Some 120 examples are known, of which about 50 come from religious buildings. These plaques are usually rectangular in form, perforated in the middle and decorated with scenes incised or carved in relief. They are most commonly of limestone or gypsum: this plaque, being of bitumen, is an exception to the rule. The precise function of such plaques is unknown, and the purpose of the central perforation remains a mystery. : dhAtu 'strands of rope' Rebus: dhAtu 'mineral, metal, ore' Alternative: मेढा [ mēḍhā ] A twist or tangle arising in thread or cord, a curl or snarl.(Marathi)(CDIAL 10312).L. meṛh f. ʻrope tying oxen to each other and to post on threshing floorʼ(CDIAL 10317) Rebus: mẽṛhẽt, meḍ ‘iron’ (Mu.Ho.)
eruvai 'eagle' Rebus: eruvai 'copper'. kōḍe, kōḍiya. [Tel.] n. A bullcalf. Rebus: koḍ artisan’s workshop (Kuwi) kunda ‘turner’ kundār turner (Assamese) Technical description Votive bas-relief of Dudu, priest of Ningirsu in the time of Entemena, prince of Lagash C. 2400 BCE Tello (ancient Girsu) Bituminous stone H. 25 cm; W. 23 cm; Th. 8 cm De Sarzec excavations, 1881 AO 2354 Plaques perforated in the center and decorated with scenes incised or carved in relief were particularly widespread in the Second and Third Early Dynastic Periods (2800-2340 BC), and have been found at many sites in Mesopotamian and more rarely in Syria or Iran. The perforated plaque of Dudu, high priest of Ningirsu in the reign of Entemena, prince of Lagash (c.2450 BC), belongs to this tradition. It has some distinctive features, however, such as being made of bitumen.This plaque belongs to the category of perforated plaques, widespread throughout Phases I and II of the Early Dynastic Period, c.2800-2340BC, and found at many sites in Mesopotamia (especially in the Diyala region), and more rarely in Syria (Mari) and Iran (Susa). Some 120 examples are known, of which about 50 come from religious buildings. These plaques are usually rectangular in form, perforated in the middle and decorated with scenes incised or carved in relief. They are most commonly of limestone or gypsum: this plaque, being of bitumen, is an exception to the rule. The precise function of such plaques is unknown, and the purpose of the central perforation remains a mystery. : dhAtu 'strands of rope' Rebus: dhAtu 'mineral, metal, ore' Alternative: मेढा [ mēḍhā ] A twist or tangle arising in thread or cord, a curl or snarl.(Marathi)(CDIAL 10312).L. meṛh f. ʻrope tying oxen to each other and to post on threshing floorʼ(CDIAL 10317) Rebus: mẽṛhẽt, meḍ ‘iron’ (Mu.Ho.) S. Kalyanaraman
Sarasvati Research Center
August 18, 2015