Mirror: http://tinyurl.com/pua3fzc
Scorpion is a hieroglyph displayed on Ancient Near East artefacts and also on inscriptions of Indus Script Corpora.
The underlying Meluhha gloss in Indus Script Corpora, mlecchita vikalpa, Meluhha cipher is: bicha 'scorpion' Rebus: bica 'hematite, sandstone iron ore'; meṛed-bica'iron stone ore'.(Santali)
Hematite, haematite, is the mineral form of iron oxide (Fe2O3)
![]()
Hieroglyph: bichā 'scorpion' (Bengali. Oriya): vŕ̊ścika m. (vr̥ścana -- m. lex.) ʻ scorpion ʼ RV., ʻ cater- pillar covered with bristles ʼ lex. [Variety of form for ʻ scorpion ʼ in MIA. and NIA. due to taboo? <-> √vraśc ?]Pa. vicchika -- m. ʻ scorpion ʼ, Pk. vicchia -- , viṁchia -- m., Sh.koh. bičh m. (< *vr̥ści -- ?), Ku. bichī, A. bisā (also ʻ hairy caterpillar ʼ: -- ī replaced by m. ending -- ā), B. Or. bichā, Mth. bīch, Bhoj. Aw.lakh. bīchī, H. poet. bīchī f., bīchā m., G. vīchī, vĩchī m.; -- *vicchuma -- : Paš.lauṛ. uċúm, dar. učum, S. vichū̃ m., (with greater deformation) L.mult. vaṭhũhã, khet. vaṭṭhũha; -- Pk. vicchua -- , viṁchua -- m., L. vichū m., awāṇ. vicchū, P. bicchū m., Or. (Sambhalpur) bichu, Mth. bīchu, H. bicchū, bīchū m., G. vīchu m.; -- Pk. viccu -- , °ua -- , viṁcua -- m., K. byucu m. (← Ind.), P.bhaṭ. biccū, WPah.bhal. biċċū m., cur. biccū, bhiḍ. biċċoṭū n. ʻ young scorpion ʼ, M. vīċũ, vĩċū m. (vĩċḍā m. ʻ large scorpion ʼ), vĩċvī, °ċvīṇ, °ċīṇ f., Ko. viccu, viṁcu, iṁcu. -- N. bacchiũʻ large hornet ʼ? (Scarcely < *vapsi -- ~ *vaspi -- ).Garh. bicchū, °chīʻ scorpion ʼ, A. also bichā (phonet. -- s -- )(CDIAL 12081) , n. < vṛšcika. 1. Scorpion;தேள். (திவா.) 2. Scorpio of the zodiac; ராசி மண்டலத்தின் எட்டாம் பகுதி. (திவா.) 3. The eighth solar month; கார்த்திகை மாதம். விருச்சிகத்துறு மாறனாள் (தணிகைப்பு. இந்திர. 18). 4. Crab; நண்டு. (இலக். அக.)
விருச்சிகம்² viruccikam
Image 1. Eight fish, four peacocks holding four fish, slanting strokes surround
Image 2. Six women, curl in hair, six scorpions
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() A symbolism of a woman spreading her legs apart, which recurs on an SSVC inscribed object. Cylinder-seal impression from Ur showing a squatting female. L. Legrain, 1936, Ur excavations, Vol. 3, Archaic Seal Impressions.
A symbolism of a woman spreading her legs apart, which recurs on an SSVC inscribed object. Cylinder-seal impression from Ur showing a squatting female. L. Legrain, 1936, Ur excavations, Vol. 3, Archaic Seal Impressions.
kut.hi, kut.i (Or.; Sad. kot.hi) (1) the smelting furnace of the blacksmith; kut.ire bica duljad.ko talkena, they were feeding the furnace with ore; (2) the name of e_kut.i has been given to the fire which, in shellac factories, warms the water bath for softening the lac so that it can be spread into sheets; to make a smelting furnace; kut.hi-o of a smelting furnace, to be made; the smelting furnace of the blacksmith is made of mud, cone-shaped, 2’ 6” dia. At the base and 1’ 6” at the top. The hole in the centre, into which the mixture of charcoal and iron ore is poured, is about 6” to 7” in dia. At the base it has two holes, a smaller one into which the nozzle of the bellow is inserted, as seen in fig. 1, and a larger one on the opposite side through which the molten iron flows out into a cavity (Mundari.lex.)
kut.hi = pubes. kola ‘foetus’ [Glyph of a foetus emerging from pudendum muliebre on a Harappa tablet.] kut.hi = the pubes (lower down than pan.d.e) (Santali.lex.) kut.hi = the womb, the female sexual organ; sorrege kut.hi menaktaea, tale tale gidrakoa lit. her womb is near, she gets children continually (H. kot.hi_, the womb) (Santali.Bodding)
![]() The squatting woman on the Ur cylinder seal impression may be showing dishevelled hair providing for rebus reading: <rabca?>(D) {ADJ} ``with ^dishevelled ^hair''. Rebus: రాచ (adj.) Pertaining to a stone. bicha, bichā ‘scorpion’ (Assamese) Rebus: bica ‘stone ore’ (Mu.) sambr.o bica = gold ore (Mundarica) Thus, the reading of the Ur cylinder seal impression may depict: meṛed-bica ‘iron stone-ore’ kuṭhi‘smelter, furnace’.
The squatting woman on the Ur cylinder seal impression may be showing dishevelled hair providing for rebus reading: <rabca?>(D) {ADJ} ``with ^dishevelled ^hair''. Rebus: రాచ (adj.) Pertaining to a stone. bicha, bichā ‘scorpion’ (Assamese) Rebus: bica ‘stone ore’ (Mu.) sambr.o bica = gold ore (Mundarica) Thus, the reading of the Ur cylinder seal impression may depict: meṛed-bica ‘iron stone-ore’ kuṭhi‘smelter, furnace’.
![]()
Scorpion is a hieroglyph displayed on Ancient Near East artefacts and also on inscriptions of Indus Script Corpora.
The underlying Meluhha gloss in Indus Script Corpora, mlecchita vikalpa, Meluhha cipher is: bicha 'scorpion' Rebus: bica 'hematite, sandstone iron ore'; meṛed-bica'iron stone ore'.(Santali)
Hematite, haematite, is the mineral form of iron oxide (Fe2O3)

Hieroglyph: bichā 'scorpion' (Bengali. Oriya): vŕ̊ścika m. (vr̥ścana -- m. lex.) ʻ scorpion ʼ RV., ʻ cater- pillar covered with bristles ʼ lex. [Variety of form for ʻ scorpion ʼ in MIA. and NIA. due to taboo? <-> √
Hieroglyphs of two Samarra bowls
Image 1. Eight fish, four peacocks holding four fish, slanting strokes surround
Image 2. Six women, curl in hair, six scorpions
ayo ‘fish’; rebus: ayas ‘metal’
mora peacock; morā ‘peafowl’ (Hindi); rebus: morakkhaka loha, a kind of copper, grouped with pisācaloha (Pali). moraka "a kind of steel" (Sanskrit)
mora peacock; morā ‘peafowl’ (Hindi); rebus: morakkhaka loha, a kind of copper, grouped with pisācaloha (Pali). moraka "a kind of steel" (Sanskrit)
gaṇḍa set of four (Santali); rebus: kaṇḍ ‘fire-altar, furnace’ (Santali)
मेढा [mēḍhā] A twist or tangle arising in thread or cord, a curl or snarl (Marathi). S. mī˜ḍhī f., °ḍho m. ʻ braid in a woman's hair ʼ, L. mē̃ḍhī f.; G. mĩḍlɔ, miḍ° m. ʻbraid of hair on a girl's forehead ʼ (CDIAL 10312). मेंढा [ mēṇḍhā ] A crook or curved end (of a stick, horn &c.) and attrib. such a stick, horn, bullock. मेढा [ mēḍhā ] A twist or tangle arising in thread or cord, a curl or snarl. Rebus: mē̃ḍ ‘iron’ (Mu.) meṛha M. meṛhi F.’twisted, crumpled, as a horn’; meṛha deren ‘a crumpled horn’ (Santali)
मेढा [mēḍhā] A twist or tangle arising in thread or cord, a curl or snarl (Marathi). S. mī˜ḍhī f., °ḍho m. ʻ braid in a woman's hair ʼ, L. mē̃ḍhī f.; G. mĩḍlɔ, miḍ° m. ʻbraid of hair on a girl's forehead ʼ (CDIAL 10312). मेंढा [ mēṇḍhā ] A crook or curved end (of a stick, horn &c.) and attrib. such a stick, horn, bullock. मेढा [ mēḍhā ] A twist or tangle arising in thread or cord, a curl or snarl. Rebus: mē̃ḍ ‘iron’ (Mu.) meṛha M. meṛhi F.’twisted, crumpled, as a horn’; meṛha deren ‘a crumpled horn’ (Santali)
bicha, bichā ‘scorpion’ (Assamese) Rebus: bica ‘stone ore’ (Mu.) sambr.o bica = gold ore (Mundarica) meṛed-bica = iron stone ore, in contrast to bali-bica, iron sand ore (Mu.lex.)
bhaṭa ‘six ’; rebus: bhaṭa ‘furnace’.
satthiya ‘svastika glyph’; rebus: satthiya ‘zinc’, jasta ‘zinc’ (Kashmiri), satva, ‘zinc’ (Pkt.)
kola ‘woman’; rebus: kol ‘iron’. kola ‘blacksmith’ (Ka.); kollë ‘blacksmith’ (Koḍ)
bhaṭa ‘six ’; rebus: bhaṭa ‘furnace’.
satthiya ‘svastika glyph’; rebus: satthiya ‘zinc’, jasta ‘zinc’ (Kashmiri), satva, ‘zinc’ (Pkt.)
kola ‘woman’; rebus: kol ‘iron’. kola ‘blacksmith’ (Ka.); kollë ‘blacksmith’ (Koḍ)
Sources for the images:
Image 1. The Samarra bowl (ca. 4000 BC) at on exhibit at the Pergamon museum, Berlin. The bowl was excavated as Samarra by Ernst Herzfeld in the 1911-1914 campaign, and described in a 1930 publication. The design consists of a rim, a circle of eight fish, and four fish swimming towards the center being caught by four birds. At the center is a swastika symbol. (Ernst Herzfeld, Die vorgeschichtlichen Töpfereien von Samarra, Die Ausgrabungen von Samarra 5, Berlin 1930.)
Image 2. Women with flowing hair and scorpions, Samarra, Iraq. After Ernst Herzfeld, Die Ausgrabungen von Samarra V: Die vorgeschichtischenTopfereien, Univ. of Texas Press, pl. 30. Courtesy Dietrich Reimer. This image is discussed in Denise Schmandt-Besserat, When writing met art, p.19. “The design features six humans in he center of the bowl and six scorpions around the inner rim. The six identical anthropomorphic figures, shown frontally, are generally interpreted as females because of their wide hips, large thighs, and long, flowing hair…Six identical scorpions, one following after the other in a single line, circle menacingly around the women.”
Image 1. The Samarra bowl (ca. 4000 BC) at on exhibit at the Pergamon museum, Berlin. The bowl was excavated as Samarra by Ernst Herzfeld in the 1911-1914 campaign, and described in a 1930 publication. The design consists of a rim, a circle of eight fish, and four fish swimming towards the center being caught by four birds. At the center is a swastika symbol. (Ernst Herzfeld, Die vorgeschichtlichen Töpfereien von Samarra, Die Ausgrabungen von Samarra 5, Berlin 1930.)
Image 2. Women with flowing hair and scorpions, Samarra, Iraq. After Ernst Herzfeld, Die Ausgrabungen von Samarra V: Die vorgeschichtischenTopfereien, Univ. of Texas Press, pl. 30. Courtesy Dietrich Reimer. This image is discussed in Denise Schmandt-Besserat, When writing met art, p.19. “The design features six humans in he center of the bowl and six scorpions around the inner rim. The six identical anthropomorphic figures, shown frontally, are generally interpreted as females because of their wide hips, large thighs, and long, flowing hair…Six identical scorpions, one following after the other in a single line, circle menacingly around the women.”
Scorpion hieroglyph on an Assyrian tablet

- After Figs. 439-440. Tablet with envelope: Marriage contract of an Assyrian merchant with an Anatolian woman. 1950-1835 BCE. Clay. Ankara Museum of Anatolian civilisations. Meluhha hieroglyphs (Bottom register): bull, ram, scorpion, serpent. ḍhangra ‘bull’. Rebus: ḍhangar ‘blacksmith’. meḍh ‘ram’. Rebus:meḍ ‘iron’. bicha ‘scorpion’ Rebus: bica ‘stone ore’. nāga ‘serpent Rebus: nāga ‘lead’. The merchant is perhaps trades: lead, stone ore, iron.After Fig. 410. Tablet: A notary document. 1830-1700 BCE. Clay. Ankara Museum of Anatolian civilisations. Kt. n/k.032, inv. no. 165-32-64. Top register seal impression.Hieroglyphs: lion, goat looking back, two tigers. kol 'tiger' Rebus: kol 'working in iron'. dula 'pair' Rebus: dul 'cast metal'. arye 'lion' Rebus: arā ‘brass’ mlekh 'goat' Rebus: milakkhu 'copper'. krammara 'look back' Rebus: kamar 'smith, artisan'. Thus, milakkhu kamar 'copper smith'.

After Figure 7. a-b: lions and palm trees; c: young lion and scorpion; d: fighting lionesses over the prey; e: lion and lionesses; f: zebus and lions. (Note the scorpion on 7c).

Figure 11: a. mountains landscape and waers; (upper part) a man under an arch with sun and crescent moon symbols; (lower part) man seated on his heels holding zebus; b. man holding a snake; c. two men (drinking) and zebus, on a small cylindrical vessel; d. Head of woman protruding from jar, and snakes; 3. man falling from a tree to the trunk of which a zebu is tied; f. man with clas and bull-man playing with cheetahs, and a scorpion in the center (on a cylindrical vessel). http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/jiroft-iv-iconography-of-chlorite-artifacts.
Hieroglyph: leopard: Kol. keḍiak tiger. Nk. khaṛeyak panther. Go. (A.) khaṛyal tiger; (Haig) kariyāl panther (Voc. 999). Kuikṛāḍi, krānḍi tiger, leopard, hyena. Kuwi (F.) kṛani tiger; (S.) klā'ni tiger, leopard; (Su. P. Isr.) kṛaˀni (pl. -ŋa) tiger. / Cf. Pkt. (DNM) karaḍa- id (DEDR 1132) Rebus: karaDa 'hard alloy' (Marathi)
Jiroft artifacts with Meluhha hieroglhyphs referencing dhokra kamar working with metals.

The founder of Mesopotamia ’s Akkadian dynasty, Sargon the Great, boasted that: The
ships from Meluhha / the ships from Magan / the ships from Dilmun / he made tie-up alongside / the quay of Akkad (translated by Samuel Noah Kramer). Magan and Dilmun are modern Oman and Bahrain Iraq ) and Meluhha (modern Pakistan and India British Museum
Hieroglyph: wallet: *dhōkka1 ʻ sacking, matting ʼ. 2. *dhōkha -- . 3. *dhōṅga -- 2 . 4. *ḍhōkka -- 1 . [Cf. *ṭōkka -- 1 ]1. Ext. -- ḍ -- : N. dhokro ʻ large jute bag ʼ, B. dhokaṛ; Or. dhokaṛa ʻ cloth bag ʼ; Bi. dhŏkrā ʻ jute bag ʼ; Mth. dhokṛā ʻ bag, vessel, receptacle ʼ; H. dhukṛī f. ʻ small bag ʼ; G. dhokṛũ n. ʻ bale of cotton ʼ; -- with -- ṭṭ -- : M. dhokṭī f. ʻ wallet ʼ; -- with -- n -- : G. dhokṇũ n. ʻ bale of cotton ʼ; -- with -- s -- : N. (Tarai) dhokse ʻ place covered with a mat to store rice in ʼ.2. L. dhohẽ (pl. dhūhī˜) m. ʻ large thatched shed ʼ.3. M. dhõgḍā m. ʻ coarse cloth ʼ, dhõgṭī f. ʻ wallet ʼ.4. L. ḍhok f. ʻ hut in the fields ʼ; Ku. ḍhwākā m. pl. ʻ gates of a city or market ʼ; N. ḍhokā (pl. of *ḍhoko) ʻ door ʼ; -- OMarw. ḍhokaro m. ʻ basket ʼ; -- N. ḍhokse ʻ place covered with a mat to store rice in, large basket ʼ.(CDIAL 6880)
Rebus: dhokra 'cire perdue metalcasting artisan'
Meluhha vernacular of Indian sprachbund
kuṭire bica duljad.ko talkena, ‘they were feeding the furnace with ore’. (Santali) This use of bica in the context of feeding a smelter clearly defines bica as ‘stone ore, mineral’, in general.
kuṭhi ‘vagina’; rebus: kuṭhi ‘smelting furnace bichā 'scorpion' (Assamese). Rebus: bica 'stone ore' as in meṛed-bica = iron stone ore, in contrast to bali-bica, iron sand ore (Mu.lex.) dul 'pair, likeness' Rebus: dul 'cast metal' (Santali) Thus the hieroglyphs connote a smelter for smelting and casting metal stone ore.
Glyph of a crocodile and a lying-in woman
This glyph is part of one side of h180 Harappa tablet. A sequence of signs is repeated on both sides of the tablet.
h705B, h172B Harappa tablets show variants of crocodile hieroglyph.
The object between the outspread legs of the woman lying upside down is comparable orthography of a crocodile holding fiish in its jaws shown on tablets h705B and h172B. The snout of the crocodile is shown in copulation with the lying-in woman (as seen from the enlarged portion of h180 Harappa tablet).
Hieroglyph: r-an:ku, ran:ku = fornication, adultery (Telugu) Rebus: ranku ‘tin’ (Santali)
Hieroglyph: kamḍa, khamḍa 'copulation' (Santali) Rebus: kammaṭi a coiner (Ka.); kampaṭṭam coinage, coin, mint (Ta.) kammaṭa = mint, gold furnace (Te.) kamaṭa = portable furnace for melting precious metals (Telugu); kampaṭṭam = mint (Tamil)
Glyph: kuṭhi = pubes. Hieroglyph: kuṭhi pubes (lower down than paṇḍe) (Santali), pudendum muliebre (Munda, Santali) Cognates: koṭṭha (m. nt.) [Sk. koṣṭha abdomen, any cavity for holding food, cp. kuṣṭa groin, and also Gr.ku/tos cavity, ku/sdos pudendum muliebre, ku/stis bladder = E. cyst, chest; Lat. cunnus pudendum. kuṭhi = the womb, the female sexual organ; sorrege kuṭhi menaktaea, tale tale gidrakoa lit. her womb is near, she gets children continually (H. koṭhī, the womb) (Santali.Bodding) kōṣṭha = anyone of the large viscera (MBh.); koṭṭha = stomach (Pali.Pkt.); kuṭṭha (Pkt.); koṭhī heart, breast (L.); koṭṭhā, koṭhābelly (P.); koṭho (G.); koṭhā (M.)(CDIAL 3545). kottha pertaining to the belly (Pkt.); kothā corpulent (Or.)(CDIAL 3510). koṭho [Skt. koṣṭha inner part] the stomach, the belly (Gujarat) kūti = pudendum muliebre (Ta.); posteriors, membrum muliebre (Ma.); ku.0y anus, region of buttocks in general (To.); kūdi = anus, posteriors, membrum muliebre (Tu.)(DEDR 188). kūṭu = hip (Tu.); kuṭa = thigh (Pe.); kuṭe id. (Mand.); kūṭi hip (Kui)(DEDR 1885). gūde prolapsus of the anus (Ka.Tu.); gūda, gudda id. (Te.)(DEDR 1891).
Rebus: kuṭhi ‘smelter furnace’ (Santali) kuṛī f. ‘fireplace’ (H.); krvṛi f. ‘granary (WPah.); kuṛī, kuṛo house, building’(Ku.)(CDIAL 3232) kuṭi ‘hut made of boughs’ (Skt.) guḍi temple (Telugu)
Rebus: kuṭhi ‘a furnace for smelting iron ore to smelt iron’; kolheko kuṭhieda koles smelt iron (Santali) kuṭhi, kuṭi (Or.; Sad. koṭhi) (1) the smelting furnace of the blacksmith; kuṭire bica duljad.ko talkena, they were feeding the furnace with ore; (2) the name of ēkuṭi has been given to the fire which, in lac factories, warms the water bath for softening the lac so that it can be spread into sheets; to make a smelting furnace; kuṭhi-o of a smelting furnace, to be made; the smelting furnace of the blacksmith is made of mud, cone-shaped, 2’ 6” dia. At the base and 1’ 6” at the top. The hole in the centre, into which the mixture of charcoal and iron ore is poured, is about 6” to 7” in dia. At the base it has two holes, a smaller one into which the nozzle of the bellow is inserted, as seen in fig. 1, and a larger one on the opposite side through which the molten iron flows out into a cavity (Mundari) kuṭhi = a factory; lil kuṭhi = an indigo factory (koṭhi - Hindi) (Santali.Bodding) kuṭhi = an earthen furnace for smelting iron; make do., smelt iron; kolheko do kuṭhi benaokate baliko dhukana, the Kolhes build an earthen furnace and smelt iron-ore, blowing the bellows; tehen:ko kuṭhi yet kana, they are working (or building) the furnace to-day (H. koṭhī ) (Santali. Bodding) kuṭṭhita = hot, sweltering; molten (of tamba, cp. uttatta)(Pali.lex.) uttatta (ut + tapta) = heated, of metals: molten, refined; shining, splendid, pure (Pali.lex.) kuṭṭakam, kuṭṭukam = cauldron (Ma.); kuṭṭuva = big copper pot for heating water (Kod.)(DEDR 1668). gudgā to blaze; gud.va flame (Man.d); gudva, gūdūvwa, guduwa id. (Kuwi)(DEDR 1715). dāntar-kuṭha = fireplace (Sv.); kōti wooden vessel for mixing yeast (Sh.); kōlhā house with mud roof and walls, granary (P.); kuṭhī factory (A.); koṭhābrick-built house (B.); kuṭhī bank, granary (B.); koṭho jar in which indigo is stored, warehouse (G.); koṭhīlare earthen jar, factory (G.); kuṭhī granary, factory (M.)(CDIAL 3546). koṭho = a warehouse; a revenue office, in which dues are paid and collected; koṭhī a store-room; a factory (Gujarat) koḍ = the place where artisans work (Gujarati)
[cf. Nausharo seal with two scorpions flanking a similar glyph with legs apart. This glyphic composition depicts a smelting furnace for stone ore as distinguished from a smelting furnace for sand ore. meṛed-bica = iron stone ore, in contrast to bali-bica, iron sand ore (Mu.lex.)
byucu बिचु; । वृश्चिकः m. (sg. dat. bicis बिचिस्), a scorpion (Kashmiri), WPah.bhal. biċċū m., cur. biccū, bhiḍ. biċċoṭū n. ʻ young scorpionʼ (CDIAL 12081). Rebus: bica, bica-diri (Sad. bicā; Or. bicī) stone ore; meṛeḍ bica, stones containing iron; tambabica, copper-ore stones; samṛobica, stones containing gold (Mundari.lex.)
dula 'pair' rebus: dul 'cast (metal)' (Santali). Hence the scorpion pair are shown on either side of the female of the Ur seal impression reported by Legrain. Pair of tigers: kola 'tiger' rebus: kol 'working in iron' (Tamil) The pair of tigers connote dul 'cast (metal)', as on the glyphs of a pair of scorpions.
kut.hi = pubes. kola ‘foetus’ [Glyph of a foetus emerging from pudendum muliebre on a Harappa tablet.] kut.hi = the pubes (lower down than pan.d.e) (Santali.lex.) kut.hi = the womb, the female sexual organ; sorrege kut.hi menaktaea, tale tale gidrakoa lit. her womb is near, she gets children continually (H. kot.hi_, the womb) (Santali.Bodding)
In Meluhha hieroglyphs (Indus writing of Asuras or Assur), some extraordinary glyphs show bizarre copulation scenes involving crocodile or intercourse a tergo, pudendum muliebre, scorpions...
Hieroglyphs (allographs):
kamaḍha 'penance' (Prakrit)
kamḍa, khamḍa 'copulation' (Santali)
kamaṭha crab (Skt.)
kamaṛkom = fig leaf (Santali.lex.) kamarmaṛā (Has.), kamaṛkom (Nag.); the petiole or stalk of a leaf (Mundari.lex.) kamat.ha = fig leaf, religiosa (Sanskrit)
kamāṭhiyo = archer; kāmaṭhum = a bow; kāmaḍ, kāmaḍum = a chip of bamboo (G.) kāmaṭhiyo a bowman; an archer (Sanskrit)
Rebus: kammaṭi a coiner (Ka.); kampaṭṭam coinage, coin, mint (Ta.) kammaṭa = mint, gold furnace (Te.) kamaṭa = portable furnace for melting precious metals (Telugu); kampaṭṭam = mint (Tamil)
Hieroglyph: kuṭhi pubes (lower down than paṇḍe) (Santali), pudendum muliebre (Munda, Santali) Cognates: koṭṭha (m. nt.) [Sk. koṣṭha abdomen, any cavity for holding food, cp. kuṣṭa groin, and also Gr.ku/tos cavity, ku/sdos
pudendum muliebre, ku/stis bladder = E. cyst, chest; Lat. cunnus pudendum. kuṭhi = the womb, the female sexual organ; sorrege kuṭhi menaktaea, tale tale gidrakoa lit. her womb is near, she gets children continually (H. koṭhī, the womb) (Santali.Bodding) kōṣṭha = anyone of the large viscera (MBh.); koṭṭha = stomach (Pali.Pkt.); kuṭṭha (Pkt.); koṭhī heart, breast (L.); koṭṭhā, koṭhābelly (P.); koṭho (G.); koṭhā (M.)(CDIAL 3545). kottha pertaining to the belly (Pkt.); kothā corpulent (Or.)(CDIAL 3510). koṭho [Skt. koṣṭha inner part] the stomach, the belly (Gujarat) kūti = pudendum muliebre (Ta.); posteriors, membrum muliebre (Ma.); ku.0y anus, region of buttocks in general (To.); kūdi = anus, posteriors, membrum muliebre (Tu.)(DEDR 188). kūṭu = hip (Tu.); kuṭa = thigh (Pe.); kuṭe id. (Mand.); kūṭi hip (Kui)(DEDR 1885). gūde prolapsus of the anus (Ka.Tu.); gūda, gudda id. (Te.)(DEDR 1891).
Rebus: kuṭhi ‘smelter furnace’ (Santali) kuṛī f. ‘fireplace’ (H.); krvṛi f. ‘granary (WPah.); kuṛī, kuṛo house, building’(Ku.)(CDIAL 3232) kuṭi ‘hut made of boughs’ (Skt.) guḍi temple (Telugu)
Rebus: kuṭhi ‘a furnace for smelting iron ore to smelt iron’; kolheko kuṭhieda koles smelt iron (Santali) kuṭhi, kuṭi (Or.; Sad. koṭhi) (1) the smelting furnace of the blacksmith; kuṭire bica duljad.ko talkena, they were feeding the furnace with ore; (2) the name of ēkuṭi has been given to the fire which, in lac factories, warms the water bath for softening the lac so that it can be spread into sheets; to make a smelting furnace; kuṭhi-o of a smelting furnace, to be made; the smelting furnace of the blacksmith is made of mud, cone-shaped, 2’ 6” dia. At the base and 1’ 6” at the top. The hole in the centre, into which the mixture of charcoal and iron ore is poured, is about 6” to 7” in dia. At the base it has two holes, a smaller one into which the nozzle of the bellow is inserted, as seen in fig. 1, and a larger one on the opposite side through which the molten iron flows out into a cavity (Mundari) kuṭhi = a factory; lil kuṭhi = an indigo factory (koṭhi - Hindi) (Santali.Bodding) kuṭhi = an earthen furnace for smelting iron; make do., smelt iron; kolheko do kuṭhi benaokate baliko dhukana, the Kolhes build an earthen furnace and smelt iron-ore, blowing the bellows; tehen:ko kuṭhi yet kana, they are working (or building) the furnace to-day (H. koṭhī ) (Santali. Bodding) kuṭṭhita = hot, sweltering; molten (of tamba, cp. uttatta)(Pali.lex.) uttatta (ut + tapta) = heated, of metals: molten, refined; shining, splendid, pure (Pali.lex.) kuṭṭakam, kuṭṭukam = cauldron (Ma.); kuṭṭuva = big copper pot for heating water (Kod.)(DEDR 1668). gudgā to blaze; gud.va flame (Man.d); gudva, gūdūvwa, guduwa id. (Kuwi)(DEDR 1715). dāntar-kuṭha = fireplace (Sv.); kōti wooden vessel for mixing yeast (Sh.); kōlhā house with mud roof and walls, granary (P.); kuṭhī factory (A.); koṭhābrick-built house (B.); kuṭhī bank, granary (B.); koṭho jar in which indigo is stored, warehouse (G.); koṭhīlare earthen jar, factory (G.); kuṭhī granary, factory (M.)(CDIAL 3546). koṭho = a warehouse; a revenue office, in which dues are paid and collected; koṭhī a store-room; a factory (Gujarat) koḍ = the place where artisans work (Gujarati)
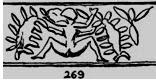 The squatting woman on the Ur cylinder seal impression may be showing dishevelled hair providing for rebus reading: <rabca?>(D) {ADJ} ``with ^dishevelled ^hair''. Rebus: రాచ (adj.) Pertaining to a stone. bicha, bichā ‘scorpion’ (Assamese) Rebus: bica ‘stone ore’ (Mu.) sambr.o bica = gold ore (Mundarica) Thus, the reading of the Ur cylinder seal impression may depict: meṛed-bica ‘iron stone-ore’ kuṭhi‘smelter, furnace’.
The squatting woman on the Ur cylinder seal impression may be showing dishevelled hair providing for rebus reading: <rabca?>(D) {ADJ} ``with ^dishevelled ^hair''. Rebus: రాచ (adj.) Pertaining to a stone. bicha, bichā ‘scorpion’ (Assamese) Rebus: bica ‘stone ore’ (Mu.) sambr.o bica = gold ore (Mundarica) Thus, the reading of the Ur cylinder seal impression may depict: meṛed-bica ‘iron stone-ore’ kuṭhi‘smelter, furnace’.Rahman-dheri seal. Obverse: Two scorpions. Two holes. One T glyph. One frog in the middle. Reverse: two rams.
1.mūxā ‘frog’. Rebus: mũh ‘(copper) ingot’ (Santali) Allograph: mũhe ‘face’ (Santali)
2.bicha ‘scorpion’ (Assamese) Rebus: bica ‘stone ore’ (Mu.)
3.tagaru ‘ram’ (Tulu) Rebus: tagarm ‘tin’ (Kota). damgar ‘merchant’ (Akk.)
4.T-glyph may denote a fire altar like the two fire-altars shown on Warrka vase below two animals: antelope and tiger. kand ‘fire-altar’ (Santali)
5.Two holes may denote ingots. dula ‘pair’ Rebus: dul ‘cast’ (Santali)
kuṛī f. ʻ girl’ Rebus: kuṭhi ‘smelter’
Brass-worker catalog of implements and repertoire:There are five hieroglyphs on the cylinder seal (Figure 270): ‘dishevelled hair’, ‘pudendum muliebre’, ‘lizard’, ‘scorpion’, ‘woman’. The accent is on the sting of the scorpion: koṭṭu (koṭṭi-) to sting (as a scorpion, wasp) (Tamil) Rebus: Pk. koṭṭaga -- m. ʻ carpenter ʼ, koṭṭila -- , °illa -- m. ʻ mallet ʼ. (DEDR 3236). koṭṭu-k-kaṉṉār brass-workers.
On kudurru, boundary stones, the metaphorical, metonymy display of hieroglyphs including scorpion or ligatured scorpion-bird-man with bow and arrow may be explained in a number of ways. I suggest that the scorpion hieroglyph is central to the metalwork traditions. In kole.l 'smithy' these hieroglyphs become divine in kole.l 'temple'. The use of the same gloss to signify both smithy and temple should lead to a hypothesis that the early Bronze Age metalwork was a sacred activity by artisans struck with awe and wonder at the transmutation of mere earth or sand or stones into metal artifacts either as castings cire perdue or as weapons, tools by a kuThAru 'armourer' Hieroglyph: kuThAru 'monkey'.
The stone ore of dhatugarbha, dagoba, becomes sacred and a sacred symbol venerated as witness to dharma-dhamma, cosmic phenomena.
S. Kalyanaraman
Sarasvati Research Center
August 8, 2015


























